We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
NF-Y Transcription Factor Sandbox
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<StructureSection load='4awl' size='350' side='right' caption='Structure of Variola Topoisomerase 1B with DNA (PDB entry [[3igc]])' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='4awl' size='350' side='right' caption='Structure of Variola Topoisomerase 1B with DNA (PDB entry [[3igc]])' scene=''> | ||
| - | |||
== Overview == | == Overview == | ||
| Line 6: | Line 5: | ||
== Protein Structure == | == Protein Structure == | ||
| + | |||
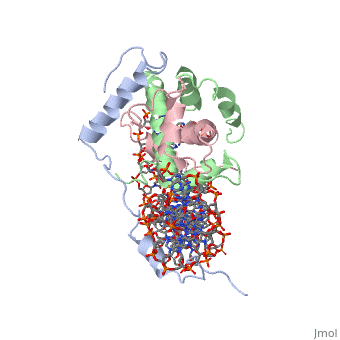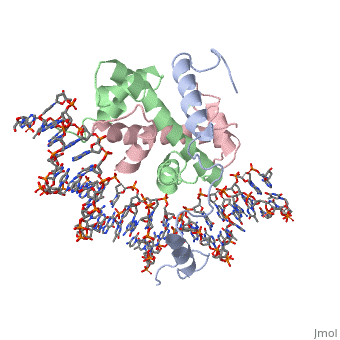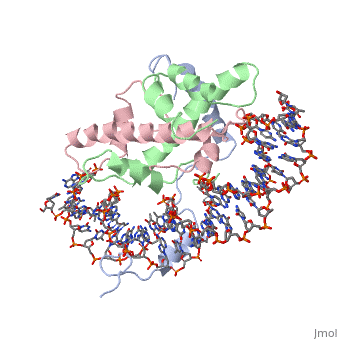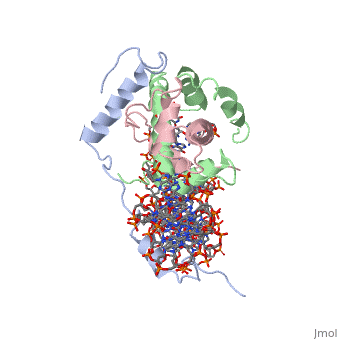
The NF-Y transcription factor consists of <scene name='56/566534/Nf-ya_real/1'>NF-YA</scene>, | The NF-Y transcription factor consists of <scene name='56/566534/Nf-ya_real/1'>NF-YA</scene>, | ||
<scene name='56/566534/Nf-yb_real/1'>NF-YB</scene>, and <scene name='56/566534/Nf-yc_real/1'>NF-YC</scene> subunits. NF-YA subunit contains two α-helices, NF-YB subunit contains four α-helices and two β-sheets, and NF-YC subunit contains three α-helices and two β-sheets. The NF-YB and NF-YC subunits each contain a histone fold motif and form a NF-YB/NF-YC histone folding domain (HFD) dimer<ref>PMID: 24030830</ref>. The composition of mostly α-helices gives the protein flexibility. One of the two α helices of the NF-YA subunit, the N terminal <scene name='56/566534/Nf-ya_a1_helix/1'>A1 helix</scene>, interacts with NF-YB/NF-YC heterodimer resulting in a heterotrimer. The NF-Y heterotrimer is stabilized by ionic interactions, interactions between the backbone atoms of residues, and hydrophobic residues. Stabilizing ionic interactions occur between Asn239(NF-YA) with Asp109(NF-YC) and Asp112(NF-YC)<ref name="mainarticle" />. Residue backbone interactions occur between Leu123(NF-YB) with Phe113(NF-YC), Arg245(NF-YA) with Glu98(NF-YB) and Glu101(NF-YB), Arg249(NF-YA) with Glu90(NF-YB), and Arg250(NF-YA) with Asp116(NF-YC)<ref name="mainarticle" />. <scene name='56/566534/Hydrophobic_residues/1'>Hydrophobic residues</scene> that contribute to the stabilization of the NF-Y heterotrimer are only located at NF-YA and NF-YB subunits at residues Ile246(NF-YA), Phe94(NF-YB), and Ile115(NF-YB)<ref name="mainarticle" />({{Template:ColorKey_Hydrophobic}} | <scene name='56/566534/Nf-yb_real/1'>NF-YB</scene>, and <scene name='56/566534/Nf-yc_real/1'>NF-YC</scene> subunits. NF-YA subunit contains two α-helices, NF-YB subunit contains four α-helices and two β-sheets, and NF-YC subunit contains three α-helices and two β-sheets. The NF-YB and NF-YC subunits each contain a histone fold motif and form a NF-YB/NF-YC histone folding domain (HFD) dimer<ref>PMID: 24030830</ref>. The composition of mostly α-helices gives the protein flexibility. One of the two α helices of the NF-YA subunit, the N terminal <scene name='56/566534/Nf-ya_a1_helix/1'>A1 helix</scene>, interacts with NF-YB/NF-YC heterodimer resulting in a heterotrimer. The NF-Y heterotrimer is stabilized by ionic interactions, interactions between the backbone atoms of residues, and hydrophobic residues. Stabilizing ionic interactions occur between Asn239(NF-YA) with Asp109(NF-YC) and Asp112(NF-YC)<ref name="mainarticle" />. Residue backbone interactions occur between Leu123(NF-YB) with Phe113(NF-YC), Arg245(NF-YA) with Glu98(NF-YB) and Glu101(NF-YB), Arg249(NF-YA) with Glu90(NF-YB), and Arg250(NF-YA) with Asp116(NF-YC)<ref name="mainarticle" />. <scene name='56/566534/Hydrophobic_residues/1'>Hydrophobic residues</scene> that contribute to the stabilization of the NF-Y heterotrimer are only located at NF-YA and NF-YB subunits at residues Ile246(NF-YA), Phe94(NF-YB), and Ile115(NF-YB)<ref name="mainarticle" />({{Template:ColorKey_Hydrophobic}} | ||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
===DNA Interaction=== | ===DNA Interaction=== | ||
| + | |||
NF-Y interacts with DNA in several ways; one particular way is by using the C terminal <scene name='56/566534/Nf-ya_a2_helix_in_minor_groo/1'>A2 helix</scene> of the NF-YA subunit inserts deep into the minor groove of DNA. NF-YA A2 helix binds to the <scene name='56/566534/Ccaat_box/4'>CCAAT</scene> box and causes the minor groove to widen at the CCAAT box<ref name="mainarticle" />. Van der Waals and <scene name='56/566534/Nf-y_dna_complex/1'>electrostatic interactions</scene> provide the stabilization of the NF-Y/DNA complex due to the highly basic surface of the NF-YB/NF-YC HFD dimer and negatively charged DNA<ref name="mainarticle" />({{Template:ColorKey_Hydrophobic}} | NF-Y interacts with DNA in several ways; one particular way is by using the C terminal <scene name='56/566534/Nf-ya_a2_helix_in_minor_groo/1'>A2 helix</scene> of the NF-YA subunit inserts deep into the minor groove of DNA. NF-YA A2 helix binds to the <scene name='56/566534/Ccaat_box/4'>CCAAT</scene> box and causes the minor groove to widen at the CCAAT box<ref name="mainarticle" />. Van der Waals and <scene name='56/566534/Nf-y_dna_complex/1'>electrostatic interactions</scene> provide the stabilization of the NF-Y/DNA complex due to the highly basic surface of the NF-YB/NF-YC HFD dimer and negatively charged DNA<ref name="mainarticle" />({{Template:ColorKey_Hydrophobic}} | ||
{{Template:ColorKey_Polar}}). | {{Template:ColorKey_Polar}}). | ||
Revision as of 05:28, 7 November 2013
| |||||||||||