We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 765
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
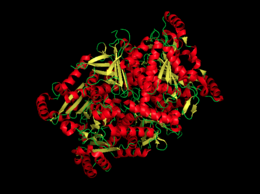
[[Image:Chorismate Synthase.png|thumb|left|260px|Figure 1. A cartoon image of chorismate synthase.]] | [[Image:Chorismate Synthase.png|thumb|left|260px|Figure 1. A cartoon image of chorismate synthase.]] | ||
| - | '''Scientific Name''': Aquifex aeolicus <ref name=1qxo/> | + | '''Scientific Name''': Aquifex aeolicus <ref>name=1qxo>/ref> |
| - | '''Genus''': Aquifex <ref name=1qxo/> | + | '''Genus''': Aquifex <ref>name=1qxo>/ref> |
| - | '''Gene''': Aroc <ref name=1qxo/> | + | '''Gene''': Aroc <ref>name=1qxo>/ref> |
| - | '''Formula weight''': 43494.9 Da <ref name=1qxo/> | + | '''Formula weight''': 43494.9 Da <ref>name=1qxo>/ref> |
| - | '''Classification''': Lyase <ref name=1qxo/> | + | '''Classification''': Lyase <ref>name=1qxo>/ref> |
| - | '''Length''': 388 residues <ref name=1qxo/> | + | '''Length''': 388 residues <ref>name=1qxo>/ref> |
| - | '''Isoelectric point''': 5.5 <ref name=1qxo/> | + | '''Isoelectric point''': 5.5 <ref>name=1qxo>/ref> |
| - | '''Chains''': A,B,C,D <ref name=1qxo/> | + | '''Chains''': A,B,C,D <ref>name=1qxo>/ref> |
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
==Structural Content== | ==Structural Content== | ||
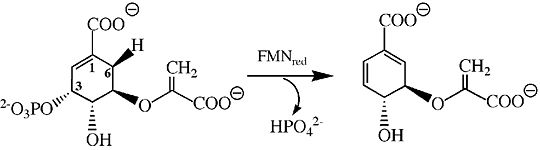
| - | Chorismate synthase is a homo 4-mer structure, which is composed of four identical monomer subunits. The tetramer crystal structure of chorismate synthase was solved at 2.0 Å using the multiwavelength anomalous dispersion (MAD) method. Each monomer within the structure has a β-α-β fold motif. | + | Chorismate synthase is a homo 4-mer structure, which is composed of four identical monomer subunits. The tetramer crystal structure of chorismate synthase was solved at 2.0 Å using the multiwavelength anomalous dispersion (MAD) method. Each monomer within the structure has a β-α-β fold motif<ref>PMID:11279147</ref>. One of the four monomers differs in structure slight close to the active site. This difference makes the active site a lot more accessible, making this monomer an “open” conformation. The monomer structure is composed of 35% <scene name='56/564041/Helices/2'>helices</scene> (17 helices) and 18% <scene name='56/564041/Beta_sheets/1'>beta sheets</scene> (21 strands). |
[[Image:Chorismate Synthase sequencee.png|thumb|right|240px|Figure 2. This image is representative of the sequence of chorismate synthase.]] | [[Image:Chorismate Synthase sequencee.png|thumb|right|240px|Figure 2. This image is representative of the sequence of chorismate synthase.]] | ||
Revision as of 02:39, 7 December 2013
| This Sandbox is Reserved from Sep 25, 2013, through Mar 31, 2014 for use in the course "BCH455/555 Proteins and Molecular Mechanisms" taught by Michael B. Goshe at the North Carolina State University. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 299, Sandbox Reserved 300 and Sandbox Reserved 760 through Sandbox Reserved 779. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Chorismate Synthase
| |||||||||||