Lauren Ferris/Sandbox 2
From Proteopedia
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
Recently, a structure for Deinococcus radiodurans in complex with ssDNA has been solved.<ref>PMID: 23975200 </ref> The structure revealed that ssDNA bind in two clefts between three subunits. One 4 base pair strand of DT bound in the cleft between E and A, while the other 4 base pair strand of DT bound between A and B. Interestingly, when symmetry was applied to the crystal the dT strands appeared continuous. <ref>PMID: 23975200 </ref> | Recently, a structure for Deinococcus radiodurans in complex with ssDNA has been solved.<ref>PMID: 23975200 </ref> The structure revealed that ssDNA bind in two clefts between three subunits. One 4 base pair strand of DT bound in the cleft between E and A, while the other 4 base pair strand of DT bound between A and B. Interestingly, when symmetry was applied to the crystal the dT strands appeared continuous. <ref>PMID: 23975200 </ref> | ||
| - | [[Image:Pentamers.jpg]] | + | [[Image:Pentamers.jpg|300px|left|thumb|]] |
| + | |||
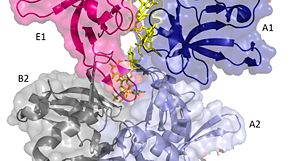
The crystal structure also determined that the pentameric ring binds to another pentameric ring. Given the continuous chain formed by the DT strands it appears that the chain passes through the channel formed by subunits A and E in one pentamer. (which will now be referred to as A1 and E1). To pass through the channel in the second pentamer between A and B (now A2 and B2). In this direction the DNA strand runs in the 5’ to 3’ direction.<ref>PMID: 23975200 </ref> | The crystal structure also determined that the pentameric ring binds to another pentameric ring. Given the continuous chain formed by the DT strands it appears that the chain passes through the channel formed by subunits A and E in one pentamer. (which will now be referred to as A1 and E1). To pass through the channel in the second pentamer between A and B (now A2 and B2). In this direction the DNA strand runs in the 5’ to 3’ direction.<ref>PMID: 23975200 </ref> | ||
| - | [[Image:DNA channel.jpg]] | + | [[Image:DNA channel.jpg|300px|left|thumb|]] |
The interactions between DdrB and the DNA strand include: | The interactions between DdrB and the DNA strand include: | ||
| Line 73: | Line 74: | ||
It should be noted that the quarternary structure enables the formation of a ssDNA channel. This structure forms independent of ssDNA binding and is stabilized by a variety of factors. The major interaction involve the interactions between the B6’-B7’ hairpin of chain E1 with the cleft from chains A2 and B2. Stabilization factors include electrostatic interactions and hydrogen bonding. Three essential salt bridges have also been identified in stabilizing this structure, they involve residues E51 and R83. <ref>PMID: 23975200 </ref> | It should be noted that the quarternary structure enables the formation of a ssDNA channel. This structure forms independent of ssDNA binding and is stabilized by a variety of factors. The major interaction involve the interactions between the B6’-B7’ hairpin of chain E1 with the cleft from chains A2 and B2. Stabilization factors include electrostatic interactions and hydrogen bonding. Three essential salt bridges have also been identified in stabilizing this structure, they involve residues E51 and R83. <ref>PMID: 23975200 </ref> | ||
| - | [[Image:Hairpin2.jpg]] | + | [[Image:Hairpin2.jpg|300px|left|thumb|]] |
Revision as of 13:48, 28 April 2014
DdrB
A Brief Description: DdrB is a single-stranded DNA binding protein that is found in bacteria from the genus Deinococcus. DdrB is thought to mediate the repair of genomic DNA following extensive genomic fragmentation induced by radiation and other agents. In this role, DdrB’s function has been compared to that of a unique stress-inducible equivalent of a single-stranded DNA binding protein. However, its function is not limited to DNA binding, as the protein has also been implicated in suppressing Rec J exonuclease activity [1] and promoting the annealing of complementary nucleotides [2].
General DescriptionDdrB is a 20kDa protein that is found in the bacterial genus Deinococcus. While it is not limited to Deinococcus radiodurans, its functional relevance has been clearly noted in this species. Deinococcus radiodurans is known for being a resilient bacteria that can withstand 15,000 Gy of γ radiation. This effectively shatters the genome into hundreds of 20-30kB fragments. [3] However, this bacteria is able to accurately repair its genome in a matter of hours and survive. This is an especially remarkable feat considering that the lethal dose of γ radiation in humans is 2-10 Gy. As a result, this finding has lead researchers to ask why Deinococcus radiodurans is able to survive such high levels of radiation? This ability is not due to any notable alterations in the bacteria’s DNA. In other words, the radiation still induces many double stranded breaks (which are a prime contributor to lethality in other organisms [4]). Instead, the resistance to radiation-induced death has been attributed to two components 1.) reactive oxygen species scavengers [5][6] and 2.) a unique repair pathway [7][8][9]. The repair pathway in Deinococcus radiodurans is thought to be a two step process. In the first part of repair, 5’ exonucleases generate long 3’ ssDNA extensions in the DNA fragments.[10] The second part of the repair process involves the extensions being put together through RecA mediated homologous recombination or through single-strand annealing.[11] These processes are also accompanied by an induction in the expression of a variety of proteins.[12] DdrB is one of the proteins that becomes highly upregulated following extensive DNA damage. This has been confirmed through evaluation of mRNA transcripts[13] and mass spectrometry proteomic analysis [14]. These studies revealed that DdrB is one of the top five upregulated genes following radiation exposure. To be specific, DdrB expression increases by over 40 fold following exposure to 3,000 Gy of γ radiation.[15] This is in sharp contrast to single stranded DNA binding proteins, which only have a minor increase in expression. As a result, DdrB is thought to act as stress inducible equivalent of a single stranded DNA binding protein protecting and stabilizing any ssDNA that is present in the repair process.[16] [17] To further support the idea that DdrB has an essential role in the repair process of Deinococcus radiodurans, bacteria with no expression of DdrB experienced a 100 fold decrease in viability compared to the wild-type following exposure to 10,000 Gy of γ radiation. [18] Subsequent studies have revealed that this protein is unique to the Deinococcus genus and varies in primary sequence length and composition depending upon the species. However, the protein structure and function remains similar. Electromobility shift assays have been used to further define DdrB function in terms of binding to nucleic acid.[19] These experiments have shown that DdrB preferentially binds to ssDNA with low uM affinity. [20] These studies also showed that DdrB has slight affinity for RNA and does not bind to double-stranded DNA. Even more recently, studies have shown that the function of DdrB is not limited to ssDNA binding. It has also been shown to promote the annealing of complementary oligonucleotides [21] and surprisingly has been shown to suppress RecJ exonuclease activity [22], further implicating DdrB in the repair of fragmented genomic DNA.
Structure DescriptionDdrB MonomersCrystal Structures have revealed that DdrB is a mulitmeric protein composed of . The units contain 1 , 4 , 8 , 4 , 5 , and regions of undefined structure. [23] [24] The N-terminal Domain The N-terminal domain contains a . The is amphipathic, in which the hydrophobic regions pack toward features in the DdrB core.[25] The DdrB Core This is followed by , which contain a solvent exposed face and another face that against the N-terminal motif. The beta sheets are anti-parallel and do not form an OB fold as determined by multiple servers iCOPS, DALI, 3D-BLAST, and MATRAS.[26] At the time of this finding (2010), the lack of an OB fold was surprising, since all ssDNA binding proteins were thought to bind to DNA through an OB fold. The OB fold is two three-stranded anti-parallel β sheets that form a five stranded β barrel. The OB folds adopt greek key motifs. The differences between the DdrB beta strands and those in the OB fold include the topology of the β strands. DdrB strands form an up and down topology and not a Greek key. Furthermore, monomeric DdrB β strands do not form a beta barrel. Additionally, DdrB has different connectivity, no conserved glycine, and no β bulge.[27] Positively Charged amino acids reside in the solvent exposed beta strands, which may potentially enable the binding of ssDNA. that link beta sheet 6 to sheet 7 and beta sheet 7 to sheet 8 contain flexible regions with poor order as determined by limited to no density in the crystal structure. This finding suggests that these loops are intrinsically disordered.[28] The C-terminal Domain The C-terminal domain also contains regions with predicted intrinsic disorder.[29] The PSIpred server predicts that the last 35 residues of Deinococcus geothermalis are disordered. This prediction is supported by the solved crystal structure as the last 51 residues could not be determined. While, the structure of the C-terminal end is not known, it may still be of interest. A BLAST search revealed an 83 amino acid protein in Deinococcus geothermalis with 72% similarity and 62% identity to the disordered region of the C-terminus.[30] However, the function of this protein remains unknown. One hypothesis is that this region may mediate protein-protein interactions. Single stranded binding proteins also have disordered C-termini and contain negatively charged residues that mediate protein-protein interactions. As DdrB contains several conserved negatively charged residues it is thought that the C-terminus of this protein could also mediate protein-protein interactions.[31] However, this hypothesis may be debated as the C-terminus was not needed for radioresistance in Deinococcus radiodurans.[32] DdrB PentamerThe monomeric units of DdrB collectively form a with a 10 A pore in the center of this structure.[33] Other DNA binding proteins can thread DNA through a central pore, however this seems highly unlikely in the case of DdrB. The pore size appears too small (would need to be 14-40A) and has a net negative charge making it highly unfavorable for DNA interactions.[34] The beta-beta-alpha motif at the N-terminus of the monomer facilitates the formation of this as the beta sheets of the N-terminal beta-beta-alpha motif form a 10 stranded . This structure is stabilized by interactions with the alpha helices. [35] The pentamer also contains a positive residue track on one side of the pentamer. These residues facilitate ssDNA binding and DdrB functionality. [36]
Structural features that relate to functionRecently, a structure for Deinococcus radiodurans in complex with ssDNA has been solved.[37] The structure revealed that ssDNA bind in two clefts between three subunits. One 4 base pair strand of DT bound in the cleft between E and A, while the other 4 base pair strand of DT bound between A and B. Interestingly, when symmetry was applied to the crystal the dT strands appeared continuous. [38]
The interactions between DdrB and the DNA strand include: Nucleotides 1, 2, 3 (T1, T2, and T3 respectively): Interact with Chains A1 and E1 -T1 hydrogen bonds to Q137 of chain E1. -T1 and T2 base stack and form a cation pi interaction with R64 of the β3 strand in chain A1. -T3 hydrogen bonds to R64 of chain A1, forms a pi-pi interaction with W66 from chain A. T3 also forms hydrogen bonds with the 5’ phosphate and amino group of G134 in chain E1. [40] Nucleotides 4, 5, 6 (T4, T5, and T6 respectively): Bridge the Pentamers -T4 stabilized by electrostatic interactions with R83 from chain A and E51 from chain A. -T5 forms hydrogen bonds with K96 of Chain E and forms van der Waal contacts with K135 chain A. (There are also van der wall interactions between the hydrophobic patch of the B6’-B7’ hairpin (L95E and L97E) and electrostatic interactions between K108 from the chain A loop between B7 and 8 and the 5’ phosphate) -T6 forms a hydrogen bond with R64 of chain B, van der Waal interactions with L95E and L97E, and pi-pi interactions with W66 of chain B. -The 5’ phosphate of T6 hydrogen bonds with the amino group of G134 of chain A. [41] Nucleotides 7 and 8 (T7 and T8 respectively): Interact with Chains A2 and B2 -The 5’ phosphate of T7 hydrogen bonds with K94 of chain A and R132 of chain A. -T7 forms pi-pi interactions with W66 of chain B and forms a hydrogen bond with K96. -T8 is stabilized by a hydrophobic patch on the B6’-B7’ hairpin (V90 chain A) -Phosphate groups of T8 stabilized through hydrogen bonding with A81, H80, and G106. [42]
Interestingly the residues involved in DNA interactions are highly conserved among DdrB homologues. These binding interactions are not highly specific and contain a very small number of specific hydrogen bonds, suggesting that DdrB can bind to a variety of ssDNA strands.[43]
It should be noted that the quarternary structure enables the formation of a ssDNA channel. This structure forms independent of ssDNA binding and is stabilized by a variety of factors. The major interaction involve the interactions between the B6’-B7’ hairpin of chain E1 with the cleft from chains A2 and B2. Stabilization factors include electrostatic interactions and hydrogen bonding. Three essential salt bridges have also been identified in stabilizing this structure, they involve residues E51 and R83. [44]
Related ProteinsDdrB is unique to the genus Deinococcus and shares very few similarities with other ssDNA binding proteins. As mentioned above, many ssDNA binding proteins function through an OB fold. However, this fold is missing in DdrB and Ddrb present a novel ssDNA binding mechanism. Within the Deinococcus genus, DdrB is relatively conserved between species. The crystal structures of Deinococcus radiodurans and Deinococcus geothermalis are quite similar. However, there are some differences in the regions connecting B6-B7 and B7-B8. This difference may be due to difference in stability, the DNA present in the Deinococcus radiodurans structure may provide stabilize this part of the structure leading to the discrepancy.[47] there may also be similarities between DdrB and another Deinococcus DNA binding protein DdrA - however, more research is needed on the latter protein before any conclusions can be made. [48]
Links to Available structuresReferences and Notes
| ||||||||||||