We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 930
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
(→Section 3) |
|||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
<!-- PLEASE ADD YOUR CONTENT BELOW HERE --> | <!-- PLEASE ADD YOUR CONTENT BELOW HERE --> | ||
=Scallop myosin head in its pre power stroke state= | =Scallop myosin head in its pre power stroke state= | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
| + | [[Image:Actin myosin anim.gif|300px|left|thumb| The movement of myosin motor domain on actin filament, [[1cnt]]]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Muscle contraction is achieved by the sliding of myosin filament (thick filament) and actin filament (thin filament). | ||
| + | As the major constituent of myosin filament, a myosin molecule is a multifunctional protein, which has a ATP catalytic site and a actin binding site on each of the globular subfragment-1 unit. With the presence of Ca and Mg, ATP ís able to be hydrolyzed and triggers following myosin-actin detachment, reattachment and power stroke. This process transformed chemical energy to mechanical force. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <StructureSection load='1CNT_trunc.pdb' size='500' frame='true' side='right' caption='Myosin subfragment 1' scene='57/579700/Whole_structure/3' > | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| - | Muscle contraction is achieved by the sliding of myosin filament (thick filament) and actin filament (thin filament). As the major constituent of myosin filament, a myosin molecule is a multifunctional protein, which has a ATP catalytic site and a actin binding site on each of the globular subfragment-1 unit. With the presence of Ca and Mg, ATP ís able to be hydrolyzed and triggers following myosin-actin detachment, reattachment and power stroke. This process transformed chemical energy to mechanical force. | ||
| - | [[Image:Actin myosin anim.gif]] | ||
| - | S1 unit plus Mg and ADP..... | ||
==Myosin subfragment-1 with MgADP== | ==Myosin subfragment-1 with MgADP== | ||
Revision as of 14:08, 15 May 2014
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 01/04/2014, through 30/06/2014 for use in the course "510042. Protein structure, function and folding" taught by Prof Adrian Goldman, Tommi Kajander, Taru Meri, Konstantin Kogan and Juho Kellosalo at the University of Helsinki. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 923 through Sandbox Reserved 947. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Contents |
Scallop myosin head in its pre power stroke state
Introduction
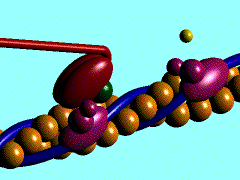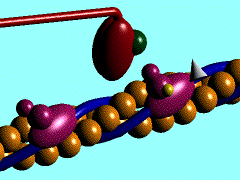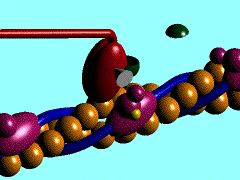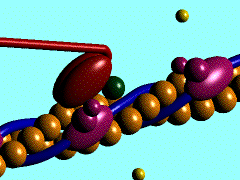
The movement of myosin motor domain on actin filament, 1cnt
Muscle contraction is achieved by the sliding of myosin filament (thick filament) and actin filament (thin filament). As the major constituent of myosin filament, a myosin molecule is a multifunctional protein, which has a ATP catalytic site and a actin binding site on each of the globular subfragment-1 unit. With the presence of Ca and Mg, ATP ís able to be hydrolyzed and triggers following myosin-actin detachment, reattachment and power stroke. This process transformed chemical energy to mechanical force.
| |||||||||||
Mg
Mg and its coordination with other atoms
ADP
Section 3
This is the structure for to show. sdfbbsjfjsbfskjbf sjdfnjldns. IJI RR.
Conclusions
| |||||||||||
