Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR or ERBB1) is found on the cell surface and associates to homodimers upon binding of its ligands such as the Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF) to its extracellular domain. The dimerization stimulates autophosphorylation of several tyrosine residues in the intracellular kinase domain which signal downstream transduction cascades. A human EGFR-2 (HER-2 or ERBB2) is involved in breast cancer and is a major target for breast cancer therapeutics. ERBB3 uses neuregulin as a ligand. ERBB4 is a closely related receptor tyrosine kinase. at the right correspond to one representative EGFR, i.e. crystal structure of unliganded Drosophila Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor ectodomain (3i2t).
EGFR and Lung Cancer
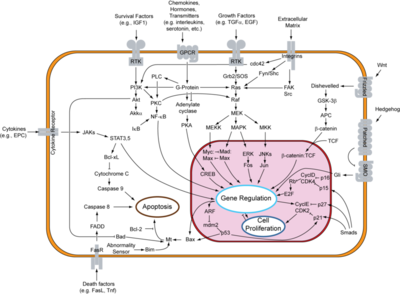
Signal Transduction Pathways Including that of EGFR
The binding of epidermal growth factor (EGF) to epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) results in the activation of its protein tyrosine kinase activity due to an induced dimerization of the receptor(1). This binding of EGF to the EGF receptor is an essential part of the signal transduction pathway that occurs in cells. This binding results eventually in cell division. Problems in this pathway can result in cancerous cells and tumors that eventually can lead to death. Therefore, understanding all parts of signal transduction is essential for understanding the cause of cancer and possible treatments of it. When EGF binds to EGFR, it results in an activation of the receptor which causes a chain of signaling events that leads to cell proliferation. This occurs by transmission of the signal across the plasma membrane because EGFR is a plasma membrane protein and in this sense a transmembrane receptor (1). Although it is present in normal cells, EGFR is overexpressed in many types of tumor cell lines, and its activation also plays an important role in resistance to chemotherapy and radiation treatment which makes treatment of cancer even more difficult(2). Since overexpression of EGFR is an attribute of some cancers, it is a plausible idea to find EGFR inhibitors to decrease the activity of EGFR and therefore inhibit cell proliferation and help control the growth of cancer and tumors. EGFR inhibitors have been developed and seem to contribute at times to the regression of tumors (2).
EGFR and Lung Cancers of "Never Smokers"
Tyrosine kinases in general control critical cellular activities through regulation of signal pathways (3). This regulation is essential for controlling the cell and making sure it acts normally and goes through the normal cell cycle. However, when these kinases are mutated, they can lead to cancer as a result (3). Mutations in EGFR as a result can also lead to cancers, and this is why understanding how EGFR works is an essential aspect for the treatment of certain cancers. In cancer, cells divide rapidly without control and an uncontrolled or unregulated EGF receptor will and can result in uncontrolled cell division. Therefore, inhibition of EGFR can be an essential part of controlling cancers caused by mutations in EGFR.
Gefitinib is an inhibitor of EGFR, and it is used to treat some cancers especially non-small cell lung cancers (NSCLC) (3). If one is able to inhibit the ability of EGF to bind to its receptor, one can control the rate of cell division in tumor cells caused by mutations or problems in EGFR. Gefitinib binds to EGFR at its highly important ATP binding activation site which is located at lysine 745 (3). When Gefitinib binds to this ATP binding site, it obviously does not allow for ATP to attach and phosphorylate in order to activate EGFR (). If ATP cannot bind, less EGF receptors will be activated and therefore this should help inhibit cell division in tumor cells and even cause regression. According to a study with two phase trials, regression of tumors were found in 28% of patients treated in Japan and 10% of those treated in Europe and U.S.A. (3).
The real question to answer was why is gefitinib effective against some tumors and not against others. Through studying ten patients who showed response to gefitinib, 70% had mutations in exons 18-24 of EGFR using mutational profiling of exons 18-24 (3). Of these 7 patients, six showed the exact same mutation at the critical ATP binding site of K745 () while the other patient showed a L858R mutation () (3). These two mutations seem to be the two prevalent mutations seen in patients that have shown responses to gefitinib. Through studying 8 refractory tumors not affected by gefitinib, none of the eight showed any mutations in exons 18-24 of EGFR (3). This shows the connection between a mutation in EGFR and its ability to be treated by gefitinib which binds to the critical ATP binding site. Many of these mutations occurred at the same ATP binding site. Another drug, Erlotinib, showed almost exactly the same results as gefitinib (3).
Ten percent of lung cancers occur in patients who are deemed to be "never smokers" which are people who have smoked less than 100 cigarettes in lifetime (3). Therefore, a large number of people are affected by lung cancer without smoking, and this is quite important. What do these people have in common if they are not smoking cigarettes? A study showed that 75% of cancers with a mutation in EGFR were from these "never smokers" (3). This means that gefitinib and erlotinib are most likely going to be effective on people who have not smoked because there is a high correlation of them having these mutations in EGFR. Studying these mutations and what causes them could be the next step in understanding how to prevent these types of lung cancers.

