Aspartate carbamoyltransferase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
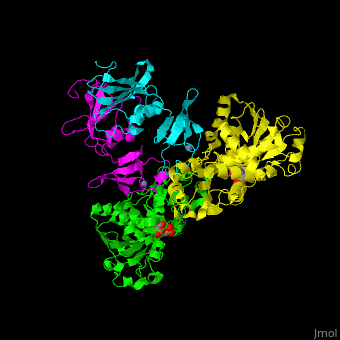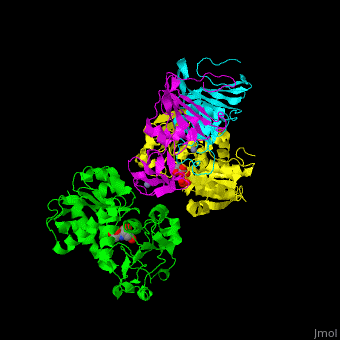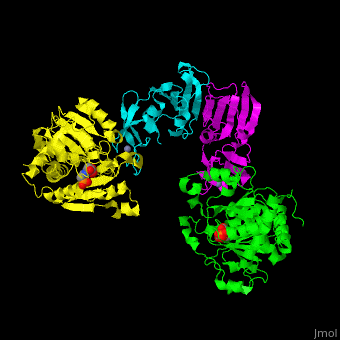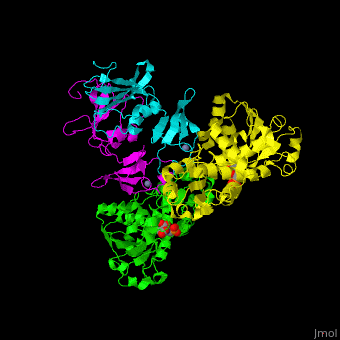
| - | <StructureSection load='1d09' size=' | + | <StructureSection load='1d09' size='450' side='right' caption='Structure of E. coli aspartate carbamoyltransferase catalytic (grey and pink) and regulatory (green and yellow) subunits complex with inhibitor PALA and Zn+2 ions (grey) (PDB code [[1d09]]).' scene='59/592660/Cv/2'> |
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
| - | ATC is composed of 2 trimers of catalytic subunits (C) and 3 dimers of regulatory subunits (R). The catalytic subunit contains an aspartate-binding domain and a carbamoyl-phosphate-binding domain. The regulatory subunit contains a nucleotide effectors-binding domain and a zinc domain. | + | ATC is composed of <scene name='59/592660/Cv/1'>2 trimers of catalytic subunits (C) and 3 dimers of regulatory subunits (R)</scene>. The catalytic subunit contains an aspartate-binding domain and a carbamoyl-phosphate-binding domain. The regulatory subunit contains a nucleotide effectors-binding domain and a zinc domain. |
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
Revision as of 15:13, 10 November 2015
| |||||||||||
3D structures of aspartate carbamoyltransferase
Updated on 10-November-2015