We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox 4465
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
Its importance can be exemplified by the fact that the protein has been known to be highly conserved in eukaryotes. Highly conserved structures that do not undergo significant evolutionary changes imply that the structure is mandatory for cell or organism survival and that any mutations in the genetic sequence that codes for the protein would be deleterious. The function of calmodulin is typically studied using yeast as a model organism. This is done for a variety of reasons, including the fact that yeast has a fully annotated genome with human homologues for genes associated with their ion channels, yeast is fast growing and they are heat stable<ref>Wolfe, D. M. D. M. (2006). Channeling studies in yeast: Yeast as a model for channelopathies?</ref>. | Its importance can be exemplified by the fact that the protein has been known to be highly conserved in eukaryotes. Highly conserved structures that do not undergo significant evolutionary changes imply that the structure is mandatory for cell or organism survival and that any mutations in the genetic sequence that codes for the protein would be deleterious. The function of calmodulin is typically studied using yeast as a model organism. This is done for a variety of reasons, including the fact that yeast has a fully annotated genome with human homologues for genes associated with their ion channels, yeast is fast growing and they are heat stable<ref>Wolfe, D. M. D. M. (2006). Channeling studies in yeast: Yeast as a model for channelopathies?</ref>. | ||
| - | + | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
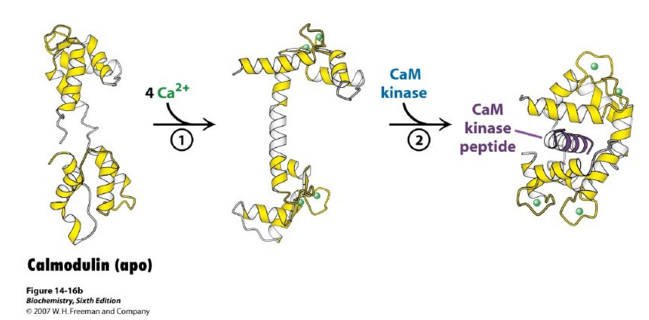
| - | Each end of the globular domains of CaM binds to two Calcium ions, which allows CaM to bind to a total of four Calcium ions. The conformational changes which CaM undergoes allow it to be able to bind more specifically. Calmodulin elicits a pathway signal transduction by activating protein kinases which can then go on to phosphorylate other proteins, or other proteins can directly bind to Calmodulin. This would require that the other proteins have a specific binding motif or substrate binding mechanism for Calmodulin. Because there are many different types of binding motifs used by other proteins to interact with Calmodulin, there are no conserved amino acid sequences for CaM binding. | + | Each end of the globular domains of CaM binds to two Calcium ions, which allows CaM to bind to a total of four Calcium ions. The conformational changes which CaM undergoes allow it to be able to bind more specifically. Calmodulin elicits a pathway signal transduction by activating protein kinases which can then go on to phosphorylate other proteins, or other proteins can directly bind to Calmodulin<ref>doi:10.1128/EC.01.1.119-125.2002</ref>. This would require that the other proteins have a specific binding motif or substrate binding mechanism for Calmodulin. Because there are many different types of binding motifs used by other proteins to interact with Calmodulin, there are no conserved amino acid sequences for CaM binding. |
| + | Some functions of calmodulin are associated with apoptosis, inflammation, metabolism, and smooth muscle contraction<ref>doi:10.1074/jbc.M111.336032</ref>. Based on a study done on Drosophila neuronal cells, calmodulin plays a role in the apoptotic pathways<ref>Ui-Tei, K., Nagano, M., Sato, S., & Miyata, Y. (2000). Calmodulin-dependent and -independent apoptosis in cell of a drosophila neuronal cell line</ref>. | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
== Bibliography == | == Bibliography == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Revision as of 21:55, 5 December 2015
Calmodulin
| |||||||||||
Bibliography
- ↑ Eldik, L., & Watterson, D. (1998). Calmodulin and signal transduction
- ↑ Wolfe, D. M. D. M. (2006). Channeling studies in yeast: Yeast as a model for channelopathies?
- ↑ Berridge MJ, Lipp P, Bootman MD. The versatility and universality of calcium signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2000 Oct;1(1):11-21. PMID:11413485 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/35036035
- ↑ Huang X, Liu Y, Wang R, Zhong X, Liu Y, Koop A, Chen SR, Wagenknecht T, Liu Z. Two potential calmodulin-binding sequences in the ryanodine receptor contribute to a mobile, intra-subunit calmodulin-binding domain. J Cell Sci. 2013 Oct 1;126(Pt 19):4527-35. doi: 10.1242/jcs.133454. Epub 2013 Jul, 18. PMID:23868982 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1242/jcs.133454
- ↑ Wriggers W, Mehler E, Pitici F, Weinstein H, Schulten K. Structure and dynamics of calmodulin in solution. Biophys J. 1998 Apr;74(4):1622-39. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(98)77876-2. PMID:9545028 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0006-3495(98)77876-2
- ↑ Lai M, Brun D, Edelstein SJ, Le Novere N. Modulation of calmodulin lobes by different targets: an allosteric model with hemiconcerted conformational transitions. PLoS Comput Biol. 2015 Jan 22;11(1):e1004063. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1004063. , eCollection 2015 Jan. PMID:25611683 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1004063
- ↑ Chan KF, Chen WH. High performance capillary electrophoresis of calmodulin. Electrophoresis. 1990 Jan;11(1):15-8. PMID:2108018 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/elps.1150110104
- ↑ Bagchi IC, Huang QH, Means AR. Identification of amino acids essential for calmodulin binding and activation of smooth muscle myosin light chain kinase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 15;267(5):3024-9. PMID:1737757
- ↑ Joseph JD, Means AR. Calcium binding is required for calmodulin function in Aspergillus nidulans. Eukaryot Cell. 2002 Feb;1(1):119-25. doi: 10.1128/ec.01.1.119-125.2002. PMID:12455978 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/ec.01.1.119-125.2002
- ↑ Racioppi L, Noeldner PK, Lin F, Arvai S, Means AR. Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase 2 regulates macrophage-mediated inflammatory responses. J Biol Chem. 2012 Mar 30;287(14):11579-91. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.336032. Epub, 2012 Feb 14. PMID:22334678 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.336032
- ↑ Ui-Tei, K., Nagano, M., Sato, S., & Miyata, Y. (2000). Calmodulin-dependent and -independent apoptosis in cell of a drosophila neuronal cell line