We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox 4465
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
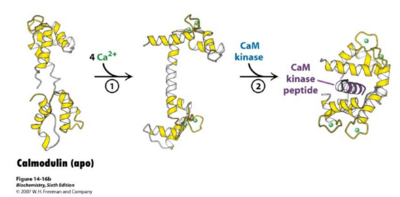
| - | [[Image:Calmodulin_fig_1.png | thumb |right|400px| '''Figure 1''' The figure highlights the structural importance of the flexibility of calmodulin in order to bind better to the 4 calcium ions at the ends and to undergo reactions with the CaM kinase peptides in order to begin a signaling transduction pathway. Click on the thumbnail to enlarge figure.]] | + | [[Image:Calmodulin_fig_1.png | thumb |right|400px| '''Figure 1: Calmodulin binds to 4 Calcium Ions and Undergoes Conformational Changes''' The figure highlights the structural importance of the flexibility of calmodulin in order to bind better to the 4 calcium ions at the ends and to undergo reactions with the CaM kinase peptides in order to begin a signaling transduction pathway. Click on the thumbnail to enlarge figure.]] |
== Calmodulin in the body == | == Calmodulin in the body == | ||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
Some functions of calmodulin are associated with apoptosis, inflammation, metabolism, and smooth muscle contraction<ref>doi:10.1074/jbc.M111.336032</ref>. Based on a study done on Drosophila neuronal cells, calmodulin plays a role in the apoptotic pathways<ref>Ui-Tei, K., Nagano, M., Sato, S., & Miyata, Y. (2000). Calmodulin-dependent and -independent apoptosis in cell of a drosophila neuronal cell line</ref>. | Some functions of calmodulin are associated with apoptosis, inflammation, metabolism, and smooth muscle contraction<ref>doi:10.1074/jbc.M111.336032</ref>. Based on a study done on Drosophila neuronal cells, calmodulin plays a role in the apoptotic pathways<ref>Ui-Tei, K., Nagano, M., Sato, S., & Miyata, Y. (2000). Calmodulin-dependent and -independent apoptosis in cell of a drosophila neuronal cell line</ref>. | ||
| + | |||
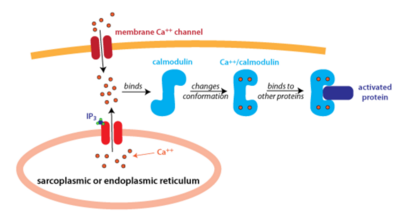
| + | [[Image:Calmodulin_fig_2.png| thumb|left|400px| '''Figure 2: An Overview of Calmodulin Pathway''' Calmodulin binds to 4 Calcium Ions and Undergoes Conformational Changes]] | ||
| + | |||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
| + | |||
== Bibliography == | == Bibliography == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Revision as of 23:14, 5 December 2015
Calmodulin
| |||||||||||
Bibliography
- ↑ Eldik, L., & Watterson, D. (1998). Calmodulin and signal transduction
- ↑ Wolfe, D. M. D. M. (2006). Channeling studies in yeast: Yeast as a model for channelopathies?
- ↑ Berridge MJ, Lipp P, Bootman MD. The versatility and universality of calcium signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2000 Oct;1(1):11-21. PMID:11413485 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/35036035
- ↑ Huang X, Liu Y, Wang R, Zhong X, Liu Y, Koop A, Chen SR, Wagenknecht T, Liu Z. Two potential calmodulin-binding sequences in the ryanodine receptor contribute to a mobile, intra-subunit calmodulin-binding domain. J Cell Sci. 2013 Oct 1;126(Pt 19):4527-35. doi: 10.1242/jcs.133454. Epub 2013 Jul, 18. PMID:23868982 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1242/jcs.133454
- ↑ Wriggers W, Mehler E, Pitici F, Weinstein H, Schulten K. Structure and dynamics of calmodulin in solution. Biophys J. 1998 Apr;74(4):1622-39. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(98)77876-2. PMID:9545028 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0006-3495(98)77876-2
- ↑ Lai M, Brun D, Edelstein SJ, Le Novere N. Modulation of calmodulin lobes by different targets: an allosteric model with hemiconcerted conformational transitions. PLoS Comput Biol. 2015 Jan 22;11(1):e1004063. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1004063. , eCollection 2015 Jan. PMID:25611683 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1004063
- ↑ Chan KF, Chen WH. High performance capillary electrophoresis of calmodulin. Electrophoresis. 1990 Jan;11(1):15-8. PMID:2108018 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/elps.1150110104
- ↑ Bagchi IC, Huang QH, Means AR. Identification of amino acids essential for calmodulin binding and activation of smooth muscle myosin light chain kinase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 15;267(5):3024-9. PMID:1737757
- ↑ Joseph JD, Means AR. Calcium binding is required for calmodulin function in Aspergillus nidulans. Eukaryot Cell. 2002 Feb;1(1):119-25. doi: 10.1128/ec.01.1.119-125.2002. PMID:12455978 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/ec.01.1.119-125.2002
- ↑ Racioppi L, Noeldner PK, Lin F, Arvai S, Means AR. Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase 2 regulates macrophage-mediated inflammatory responses. J Biol Chem. 2012 Mar 30;287(14):11579-91. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.336032. Epub, 2012 Feb 14. PMID:22334678 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.336032
- ↑ Ui-Tei, K., Nagano, M., Sato, S., & Miyata, Y. (2000). Calmodulin-dependent and -independent apoptosis in cell of a drosophila neuronal cell line