We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
User:Jonathan Lloyd/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
[[Image:table 1.png]] | [[Image:table 1.png]] | ||
| + | The superposition of the ATAD2b on top of ATAD2a shows us exactly how closely related they really are. There are minor differences that appear in the loop regions of random coil as the alpha helixes stay the same. When aligned with the lowest identity structure PCAF you can see the locations where they are similar but even some loop regions are not even close to each other. This tool allows you to see the location of bromodomains in other proteins and also how closely the bromodomains match each other. | ||
== AAA ATPase Domain == | == AAA ATPase Domain == | ||
The AAA domains share a common conserved module of approximately 230 amino acid residues. This is a large, functionally diverse protein, which exert their activity through the energy-dependent remodeling or translocation of macromolecules. Members of the AAA family are found in all organisms and they are essential for many cellular functions. They are involved in processes such as DNA replication, protein degradation, membrane fusion, microtubule severing, peroxisome biogenesis, signal transduction and the regulation of gene expression. ATP hydrolysis by AAA ATPases involves a nucleophilic attack on the ATP gamma-phosphate by an activated water molecule, leading to movement of the N-terminal and C-terminal AAA subdomains relative to each other. This movement allows the exertion of mechanical force, amplified by other ATPase domains within the same oligomeric structure. The AAA domain is part of the P-loop containing nucleoside triphosphate hydrolases superfamily which mainly consists of beta sheets. | The AAA domains share a common conserved module of approximately 230 amino acid residues. This is a large, functionally diverse protein, which exert their activity through the energy-dependent remodeling or translocation of macromolecules. Members of the AAA family are found in all organisms and they are essential for many cellular functions. They are involved in processes such as DNA replication, protein degradation, membrane fusion, microtubule severing, peroxisome biogenesis, signal transduction and the regulation of gene expression. ATP hydrolysis by AAA ATPases involves a nucleophilic attack on the ATP gamma-phosphate by an activated water molecule, leading to movement of the N-terminal and C-terminal AAA subdomains relative to each other. This movement allows the exertion of mechanical force, amplified by other ATPase domains within the same oligomeric structure. The AAA domain is part of the P-loop containing nucleoside triphosphate hydrolases superfamily which mainly consists of beta sheets. | ||
| Line 21: | Line 22: | ||
== Evolution == | == Evolution == | ||
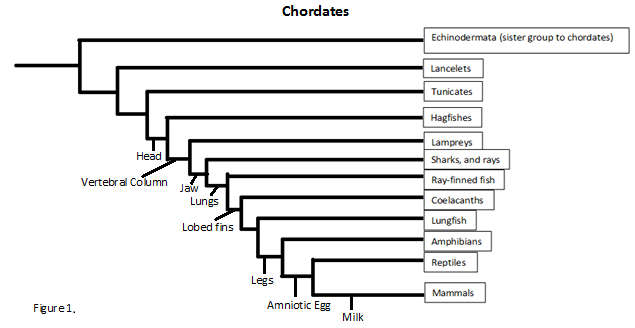
| - | + | Since we know ATAD2b can be found in such species as the Pterois or lionfish we can track the protein all the way back to the phylum chordata. This is not to say all the species under chordata can make ATAD2b but future studies would have to be conducted to find out the exact phylogenetics. But even so chordata contains many species including lancelets, lampreys, amphibians, reptiles and sea squirts. | |
| - | + | [[Image:tree.png]] | |
Revision as of 23:15, 9 December 2015
ATAD2b
| |||||||||||