Adrenergic receptor
From Proteopedia
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
* [[Beta-2 Adrenergic Receptor]]<br /> | * [[Beta-2 Adrenergic Receptor]]<br /> | ||
* [[G protein-coupled receptor]]<br /> | * [[G protein-coupled receptor]]<br /> | ||
| + | * [[Beta2 adregenic receptor-Gs protein complex]]<br /> | ||
* [[Neurodevelopmental Disorders]]. | * [[Neurodevelopmental Disorders]]. | ||
<scene name='Adrenergic_receptor/Cv/1'>Click here to see transition from active to inactive conformation of alpha adrenergic receptor</scene> (morph was taken from [http://molmovdb.org/cgi-bin/movie.cgi Gallery of Morphs] of the [http://molmovdb.org Yale Morph Server]). | <scene name='Adrenergic_receptor/Cv/1'>Click here to see transition from active to inactive conformation of alpha adrenergic receptor</scene> (morph was taken from [http://molmovdb.org/cgi-bin/movie.cgi Gallery of Morphs] of the [http://molmovdb.org Yale Morph Server]). | ||
Revision as of 10:53, 28 January 2016
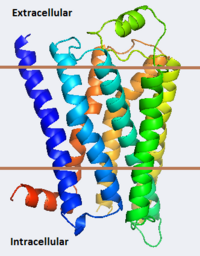
The adrenergic receptors are metabolic G protein-coupled receptors. They are the targets of catecholamines. The binding of an agonist to them causes a sympathetic response.
- The α-2 adrenergic receptor (A2AR) inhibits insulin or glucagons release.
- The β-1 adrenergic receptor (B1AR) increases cardiac output and secretion of rennin and ghrelin.[1]
- The β-2 adrenergic receptor (B2AR) triggers many relaxation reactions.
See also
- Beta-2 Adrenergic Receptor
- G protein-coupled receptor
- Beta2 adregenic receptor-Gs protein complex
- Neurodevelopmental Disorders.
(morph was taken from Gallery of Morphs of the Yale Morph Server).
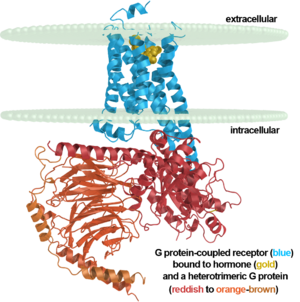
β2 adrenergic receptor binding a hormone analog |
| |||||||||||
| |||||||||||
This is the first structure of an activated GPCR in a complex with its G protein.
See also The Madison West High School 2008 SMART Team's Page on the β-2 adrenergic receptor
Contents |
Nobel Prize Related to the Structures
Robert J. Lefkowitz and Brian K. Kobilka share the 2012 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for work on GPCRs that includes solving the first structures of a ligand-activated GPCR (2r4r, 2r4s, & 2rh1 in 2007)[1][2][3] and the first activated GPCR in complex with its G protein (3sn6 in 2011)[4][5][6][7]. A detailed description of the laureates' body of work on this class of receptors with images is here.
3D Structures of Adrenergic receptor
Updated on 28-January-2016
References
- ↑ Huang J, Chen S, Zhang JJ, Huang XY. Crystal structure of oligomeric beta1-adrenergic G protein-coupled receptors in ligand-free basal state. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2013 Apr;20(4):419-25. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2504. Epub 2013 Feb, 24. PMID:23435379 doi:10.1038/nsmb.2504
See Also
- G protein-coupled receptor
- Beta-2 Adrenergic Receptor topic page
- Nobel Prizes for 3D Molecular Structure
- Highest impact structures of all time
- G proteins
- Rhodopsin
- GTP-binding protein
- Pharmaceutical Drugs
- Membrane proteins
- Hormone
External Resources
- Robert J. Lefkowitz and Brian K. Kobilka share the 2012 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for work on GPCRs that includes solving the first structures of a ligand-activated GPCR (2007) and the first activated GPCR in complex with its G protein (2011). A detailed description of the laureates' body of work on this class of receptors with images is here.
- The April 2008 RCSB PDB Molecule of the Month feature on Adrenergic Receptors by David S. Goodsell is 10.2210/rcsb_pdb/mom_2008_4.
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Wayne Decatur, Karsten Theis, Alexander Berchansky