We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1120
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
==SRY gene== | ==SRY gene== | ||
| - | The SRY gene encodes the SRY protein. The SRY protein is a transcriptional factor that induces the male phenotype in the embryo. The SRY gene is located on the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Y_chromosome Y chromosome] in the short arm (p) 11.3 <ref>[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/6736 NCBI gene]</ref>. This gene has only one exon that contains the HMG domain (DNA-binding High-Mobility Group box domain). It means that SRY mRNA does not have an alternative splicing, so there is only one isoforme of SRY protein<ref> McElreavey K, Barbaux S, Ion A, Fellous M. The genetic basis of murine and human sex determination: a review. Heredity. 1995 Dec;75 ( Pt 6):599–611. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8575930]</ref>. Moreover, the human genome contains only one copy of the SRY gene, whereas the mouse genome contains 6 copy of this gene<ref> Sekido R, Lovell-Badge R. Genetic control of testis development. Sex Dev Genet Mol Biol Evol Endocrinol Embryol Pathol Sex Determ Differ. 2013;7(1-3):21–32 </ref>. | + | The SRY gene encodes the SRY protein. The SRY protein is a transcriptional factor that induces the male phenotype in the embryo. The SRY gene is located on the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Y_chromosome Y chromosome] in the short arm (p) 11.3 <ref>[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/6736 NCBI gene]</ref>. This gene has only one exon that contains the HMG domain (DNA-binding High-Mobility Group box domain). It means that SRY mRNA does not have an alternative splicing, so there is only one isoforme of SRY protein<ref name!"McE"> McElreavey K, Barbaux S, Ion A, Fellous M. The genetic basis of murine and human sex determination: a review. Heredity. 1995 Dec;75 ( Pt 6):599–611. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8575930]</ref>. Moreover, the human genome contains only one copy of the SRY gene, whereas the mouse genome contains 6 copy of this gene<ref> Sekido R, Lovell-Badge R. Genetic control of testis development. Sex Dev Genet Mol Biol Evol Endocrinol Embryol Pathol Sex Determ Differ. 2013;7(1-3):21–32 </ref>. |
===Sequence of the SRY gene=== | ===Sequence of the SRY gene=== | ||
| Line 122: | Line 122: | ||
The SRY protein contains nuclear localization signals in N and C terminals. An acetylation of these domains allows the exportation of the SRY protein to the nucleus<ref>Harley VR, Clarkson MJ, Argentaro A. The Molecular Action and Regulation of the Testis-Determining Factors, SRY (Sex-Determining Region on the Y Chromosome) and SOX9 [SRY-Related High-Mobility Group (HMG) Box 9]. Endocr Rev. 2003 Aug 1;24(4):466–87. [http://press.endocrine.org/doi/10.1210/er.2002-0025?url_ver=Z39.88-2003&rfr_id=ori%3Arid%3Acrossref.org&rfr_dat=cr_pub%3Dpubmed&]</ref>. | The SRY protein contains nuclear localization signals in N and C terminals. An acetylation of these domains allows the exportation of the SRY protein to the nucleus<ref>Harley VR, Clarkson MJ, Argentaro A. The Molecular Action and Regulation of the Testis-Determining Factors, SRY (Sex-Determining Region on the Y Chromosome) and SOX9 [SRY-Related High-Mobility Group (HMG) Box 9]. Endocr Rev. 2003 Aug 1;24(4):466–87. [http://press.endocrine.org/doi/10.1210/er.2002-0025?url_ver=Z39.88-2003&rfr_id=ori%3Arid%3Acrossref.org&rfr_dat=cr_pub%3Dpubmed&]</ref>. | ||
| - | The SRY protein activates the ''SOX9'' (SRY-box9) gene <ref | + | The SRY protein activates the ''SOX9'' (SRY-box9) gene <ref name="McE" />. This gene is found in long arm 24.3 of the chromosome 17<ref> NCBI [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/6662 NCBI gene: SOX9 SRY-BOX9 Homo sapiens] </ref> and is implicated in the stimulation of the differentiation of pre-Sertori into Sertoli cells rather than granulosa cells. |
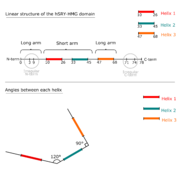
The activation of ''SOX''9 is done by the SRY protein and another transcriptional factor: SF1 (steroidogenic factor 1). These transcriptional factors are bound on an enhancer called: TESCO (Testis-Specific Enhancer of ''SOX9'' core element). The binding of a transcriptional factor on an enhancer provokes a curvature of the DNA (≈75°), allowing a stabilization of the elongation complex on the ''SOX9'' promoter. The SOX9 protein activates the gene ''AMH'' (Anti-Mullerian Hormone)<ref>[http://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/entry/IPR006799?q=AMH EBI-Interpro: Anti-Mullerian-Hormon, N-term] </ref>. Therefore, it allows the degeneration of the channels of Müller in male. <ref>Harley VR, Clarkson MJ, Argentaro A. The Molecular Action and Regulation of the Testis-Determining Factors, SRY (Sex-Determining Region on the Y Chromosome) and SOX9 [SRY-Related High-Mobility Group (HMG) Box 9]. Endocr Rev. 2003 Aug 1;24(4):466–87 [http://press.endocrine.org/doi/10.1210/er.2002-0025?url_ver=Z39.88-2003&rfr_id=ori%3Arid%3Acrossref.org&rfr_dat=cr_pub%3Dpubmed&]</ref>. | The activation of ''SOX''9 is done by the SRY protein and another transcriptional factor: SF1 (steroidogenic factor 1). These transcriptional factors are bound on an enhancer called: TESCO (Testis-Specific Enhancer of ''SOX9'' core element). The binding of a transcriptional factor on an enhancer provokes a curvature of the DNA (≈75°), allowing a stabilization of the elongation complex on the ''SOX9'' promoter. The SOX9 protein activates the gene ''AMH'' (Anti-Mullerian Hormone)<ref>[http://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/entry/IPR006799?q=AMH EBI-Interpro: Anti-Mullerian-Hormon, N-term] </ref>. Therefore, it allows the degeneration of the channels of Müller in male. <ref>Harley VR, Clarkson MJ, Argentaro A. The Molecular Action and Regulation of the Testis-Determining Factors, SRY (Sex-Determining Region on the Y Chromosome) and SOX9 [SRY-Related High-Mobility Group (HMG) Box 9]. Endocr Rev. 2003 Aug 1;24(4):466–87 [http://press.endocrine.org/doi/10.1210/er.2002-0025?url_ver=Z39.88-2003&rfr_id=ori%3Arid%3Acrossref.org&rfr_dat=cr_pub%3Dpubmed&]</ref>. | ||
Revision as of 11:36, 30 January 2016
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 15/12/2015, through 15/06/2016 for use in the course "Structural Biology" taught by Bruno Kieffer at the University of Strasbourg, ESBS. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1120 through Sandbox Reserved 1159. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
SRY protein (AKA TDF protein)
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Tang Y, Nilsson L. Interaction of human SRY protein with DNA: a molecular dynamics study. Proteins. 1998 Jun 1;31(4):417-33. PMID:9626701
- ↑ Sumner, A. T. Sex Chromosomes and Sex Determination. Chromosomes: Organization and Function, 97-108. [1]
- ↑ Bridges CB. TRIPLOID INTERSEXES IN DROSOPHILA MELANOGASTER. Science. 1921 Sep 16;54(1394):252-4. PMID:17769897 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.54.1394.252
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Goodfellow PN, Darling SM. Genetics of sex determination in man and mouse. Development. 1988 Feb;102(2):251-8. PMID:3046910
- ↑ Jost A. Becoming a male. Adv Biosci. 1973;10:3-13. PMID:4805859
- ↑ Gubbay J, Collignon J, Koopman P, Capel B, Economou A, Munsterberg A, Vivian N, Goodfellow P, Lovell-Badge R. A gene mapping to the sex-determining region of the mouse Y chromosome is a member of a novel family of embryonically expressed genes. Nature. 1990 Jul 19;346(6281):245-50. PMID:2374589 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/346245a0
- ↑ Sinclair AH, Berta P, Palmer MS, Hawkins JR, Griffiths BL, Smith MJ, Foster JW, Frischauf AM, Lovell-Badge R, Goodfellow PN. A gene from the human sex-determining region encodes a protein with homology to a conserved DNA-binding motif. Nature. 1990 Jul 19;346(6281):240-4. PMID:1695712 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/346240a0
- ↑ Werner MH, Huth JR, Gronenborn AM, Clore GM. Molecular basis of human 46X,Y sex reversal revealed from the three-dimensional solution structure of the human SRY-DNA complex. Cell. 1995 Jun 2;81(5):705-14. PMID:7774012
- ↑ NCBI gene
- ↑ McElreavey K, Barbaux S, Ion A, Fellous M. The genetic basis of murine and human sex determination: a review. Heredity. 1995 Dec;75 ( Pt 6):599–611. [2]
- ↑ Sekido R, Lovell-Badge R. Genetic control of testis development. Sex Dev Genet Mol Biol Evol Endocrinol Embryol Pathol Sex Determ Differ. 2013;7(1-3):21–32
- ↑ NCBI nucleotide
- ↑ Harley VR, Clarkson MJ, Argentaro A. The Molecular Action and Regulation of the Testis-Determining Factors, SRY (Sex-Determining Region on the Y Chromosome) and SOX9 [SRY-Related High-Mobility Group (HMG) Box 9]. Endocr Rev. 2003 Aug 1;24(4):466–87. [3]
- ↑ Larney C, Bailey TL, Koopman P. Switching on sex: transcriptional regulation of the testis-determining gene Sry. Dev Camb Engl. 2014 Jun;141(11):2195–205
- ↑ Murphy EC, Zhurkin VB, Louis JM, Cornilescu G, Clore GM. Structural basis for SRY-dependent 46-X,Y sex reversal: modulation of DNA bending by a naturally occurring point mutation. J Mol Biol. 2001 Sep 21;312(3):481-99. PMID:11563911 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.2001.4977
- ↑ Harley VR, Clarkson MJ, Argentaro A. The Molecular Action and Regulation of the Testis-Determining Factors, SRY (Sex-Determining Region on the Y Chromosome) and SOX9 [SRY-Related High-Mobility Group (HMG) Box 9]. Endocr Rev. 2003 Aug 1;24(4):466–87. [4]
- ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedMcE - ↑ NCBI NCBI gene: SOX9 SRY-BOX9 Homo sapiens
- ↑ EBI-Interpro: Anti-Mullerian-Hormon, N-term
- ↑ Harley VR, Clarkson MJ, Argentaro A. The Molecular Action and Regulation of the Testis-Determining Factors, SRY (Sex-Determining Region on the Y Chromosome) and SOX9 [SRY-Related High-Mobility Group (HMG) Box 9]. Endocr Rev. 2003 Aug 1;24(4):466–87 [5]
- ↑ Veitia RA. Of adrenaline and SRY in males (comment on DOI 10.1002/bies.201100159). Bioessays. 2014 May;36(5):438. doi: 10.1002/bies.201400026. Epub 2014 Mar 7. PMID:24604382 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/bies.201400026
- ↑ Veitia RA. Of adrenaline and SRY in males (comment on DOI 10.1002/bies.201100159). Bioessays. 2014 May;36(5):438. doi: 10.1002/bies.201400026. Epub 2014 Mar 7. PMID:24604382 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/bies.201400026
- ↑ Cohen, Tamara. The 'macho' gene that makes men behave aggressively has been found. The Daily Mail (2012). [6]
- ↑ Prokop JW, Watanabe IK, Turner ME, Underwood AC, Martins AS, Milsted A. From rat to human: regulation of Renin-Angiotensin system genes by sry. Int J Hypertens. 2012;2012:724240. doi: 10.1155/2012/724240. Epub 2012 Jan 22. PMID:22315667 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2012/724240
- ↑ de la Chapelle A. Analytic review: nature and origin of males with XX sex chromosomes. Am J Hum Genet. 1972 Jan;24(1):71-105. PMID:4622299
- ↑ Xue TC, Zhang L, Ren ZG, Chen RX, Cui JF, Ge NL, Ye SL. Sex-determination gene SRY potentially associates with poor prognosis but not sex bias in hepatocellular carcinoma. Dig Dis Sci. 2015 Feb;60(2):427-35. doi: 10.1007/s10620-014-3377-y. Epub 2014 Oct, 2. PMID:25274159 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10620-014-3377-y