We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sulfatase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
(New page: <StructureSection load='1vz4' size='340' side='right' caption='Caption for this structure' scene=''> == Function == '''Sulfatase''' hydrolyzes sulfate esters. The enzymes take part in ...) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
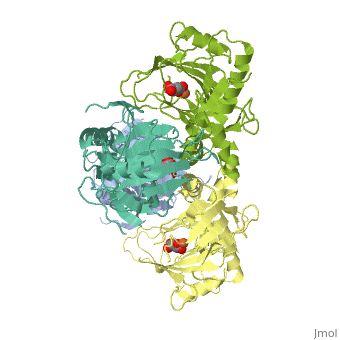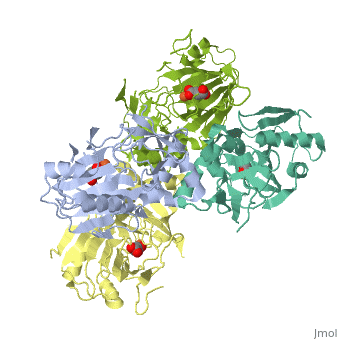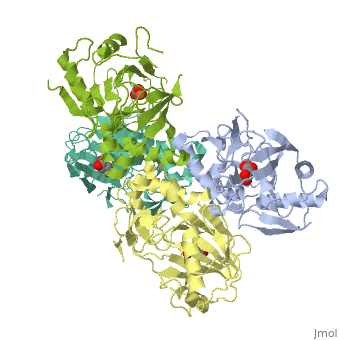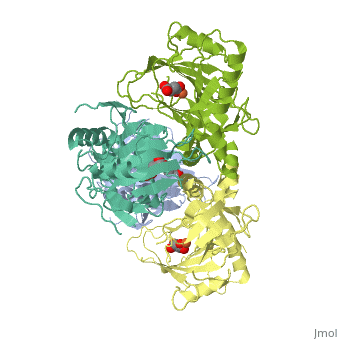
| - | + | <StructureSection load='1vz4' size='340' side='right' caption='Alkylsulfatase complex with succinate and Fe+2 ion (PDB code [[1vz4]])' scene=''> | |
| - | <StructureSection load='1vz4' size='340' side='right' caption=' | + | |
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| - | '''Sulfatase''' hydrolyzes sulfate esters. The enzymes take part in the cycling of sulfur<ref>PMID:15493058</ref>. | + | '''Sulfatase''' hydrolyzes sulfate esters. The enzymes take part in the cycling of sulfur<ref>PMID:15493058</ref>. The '''arylsulfatase''' name is derived from the fact that nitrophenyl-sulfate is their standard substrate. |
* '''Arylsulfatase A''' hydrolyzes cerebroside-sulfate.<br /> | * '''Arylsulfatase A''' hydrolyzes cerebroside-sulfate.<br /> | ||
* '''Arylsulfatase B''' hydrolyzes dermatan sulfate.<br /> | * '''Arylsulfatase B''' hydrolyzes dermatan sulfate.<br /> | ||
| + | * '''Alkylsulfatase''' hydrolyzes SDS and other alkyl sulfate derivatives.<br /> | ||
* '''Estrone sulfatase''' hydrolyzes sulfated steroids.<br /> | * '''Estrone sulfatase''' hydrolyzes sulfated steroids.<br /> | ||
* '''N-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfatase''' hydrolyzes chondroitin sulfate and keratin sulfate. For details see [[Molecular Playground/Human Galactosamine-6-sulfatase]].<br /> | * '''N-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfatase''' hydrolyzes chondroitin sulfate and keratin sulfate. For details see [[Molecular Playground/Human Galactosamine-6-sulfatase]].<br /> | ||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
Mutations in arylsulfatase result in lysosomal storage disorders. Sulfatases are implicated in pathophysiological conditions in hormone-dependent cancer, developmental abnormalities and bacterial pathogenesis. | Mutations in arylsulfatase result in lysosomal storage disorders. Sulfatases are implicated in pathophysiological conditions in hormone-dependent cancer, developmental abnormalities and bacterial pathogenesis. | ||
| - | |||
| - | == Relevance == | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
Revision as of 10:10, 15 February 2016
| |||||||||||
3D Structures of sulfatase
Updated on 15-February-2016
References
- ↑ Hanson SR, Best MD, Wong CH. Sulfatases: structure, mechanism, biological activity, inhibition, and synthetic utility. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2004 Nov 5;43(43):5736-63. PMID:15493058 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/anie.200300632