Background
RNA silencing is a gene inactivation system in many eukaryotes that relies on tiny RNAs as the targeting molecules. One function of RNA silencing, which is also called post-transcriptional gene silencing (PTGS) or RNA interference (RNAi), is to act in surveillance against molecular parasites, such as viruses. Double-stranded RNA triggers the RNA silencing pathway and most plant viruses use a double-stranded RNA to replicate their genome. Various plant viruses have developed evasion techniques to circumvent this surveillance system. In one such evasion strategy, the plant viral protein p19 suppresses a plant's anti-viral RNA silencing response. p19 binds with high affinity to the double-stranded RNA silencing mediator, called siRNA, and this binding sequesters the siRNA, preventing its participation in later steps of RNA silencing.
siRNAs are generally characterized by their short length (21–26 nt), 2 nt, 3′ overhanging ends, and 5′ phosphate groups. The most efficient silencing is obtained with siRNA duplexes composed of 21-nt sense and 21-nt antisense strands, paired in a manner to have a 2-nt 3' overhang (see the Tuschl lab's guide for designing siRNAs)[1].
Structural studies [2][3] have revealed how p19 from carnation and tomato viruses selectively recognizes the double-stranded siRNA. p19 from the carnation virus is presented on this page; however the results are relevant to both p19 examples as the solved structures are very similar, consistent with the high percent of identity (89%) for the homologous proteins[4]. See Alignment of 1rpu vs 1r9f.
Results
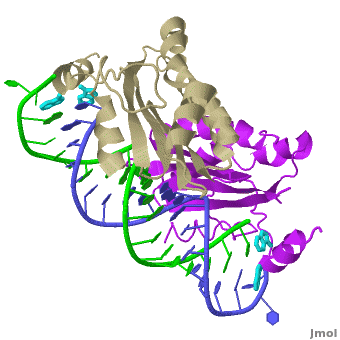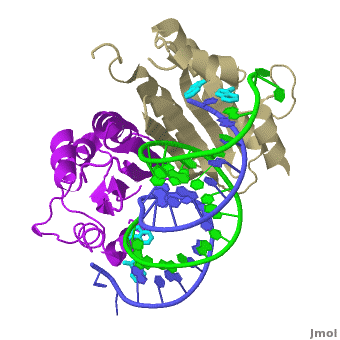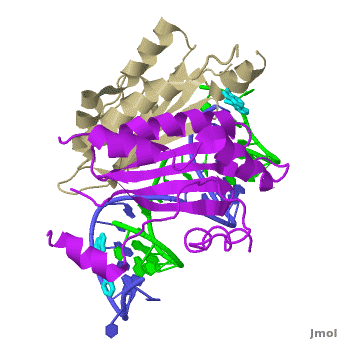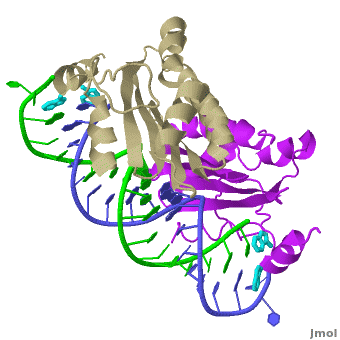
The X-ray crystal structure of includes both protein and RNA in the complex. .
The .
The synthetic RNA substrate mimics the 21-nt double-stranded siRNAs that occur in the double-strand RNA-induced RNAi silencing pathway.
The duplex region is 19 nts and there are 2-nt 3' overhangs.
Here is a schematic illustration of the two strands of the silencing RNA (siRNA) in this structure:
5'-pCGUACGCGUCACGCGUACGUU-OH-3'
|||||||||||||||||||
3'-OH-UUGCAUGCGCACUGCGCAUGCp-5'
p19 binds the siRNA as
.
Individual monomers of the p19 dimer are colored tan and purple.
The apparent breaks seen in the monomer chains internally are due to an inability to model this region because of poor electron density here, presumably as a result of flexibility in the linker.
Each is made of five alpha-helices and a four-stranded beta sheet.
forms a continuous eight-stranded beta-sheet.
The continuous eight-stranded beta-sheet of of the double stranded siRNA. This is unusual because most proteins use loops and helices to bind double-stranded RNA, for example, see 1di2, 2zi0, 2hvy or 2az0. For more detais see P19 complexed with 19-bp small interfering RNA.
Several conserved serine and threonine residues in p19 mediate key interactions with 2'-hydroxyls specifying RNA as the substrate, rather than DNA. This view only shows part of the network of interactions with the ribose sugar 2'-hydroxyls of the RNA. Other interactions with the 2'-hydroxyls involve water-mediated contacts and the sidechains of p19. Additionally, the phosphate backbone of the duplex is extensively contacted in a specific manner by p19. As expected to insure recognition of any anti-viral siRNAs, there are no base-specific contacts.
p19 specifies the presence of a 5'-phosphate at the 5'-end of each RNA strand via hydrogen binding between the phosphate and a conserved tryptophan (W42).
Most unprecedented is the method of size selection where p19 acts as a molecular caliper reading the size of the substrate. The aromatic rings of two tryptophan residues (W39 and W42) project from the 'reading' helix near the N-terminus of each of the two p19 monomers, stacking on the terminal base-pairs and symmetrically bracketing the ends of the duplex region of the siRNA. Thus the p19 'caliper' measures and specifically selects siRNA based on the size of the duplex region. The ability of p19 to efficiently accommodate binding of duplexes ranging from 19 to 21 bp could originate in structural plasticity of the distance separating the two 'reading head' helices. Each 'reading' helix is connected to the structured core of p19 by a short flexible loop and several side-chain interactions this presumably allows some flexibility in the positioning of the RNA end-capping tryptophan residues. Many other structures use aromatic rings to stack on nucleotide bases and cap strands in helices, see F204 and Y208 of 1gm5, W639 of 1msw and 1qln.
Conclusions
The X-ray crystal structure shows the size of the duplex as the major determinant of the siRNA recognized by p19 and biochemical experiments support this assessment. In contrast, the 2-nt 3' overhang seems to have little specific contact with the protein, consistent with Vargason et al. finding comparable binding affinities of p19 for a blunt-ended 19-bp RNA duplex, lacking the typical 2-nt single-stranded 3' overhang.
Thus, p19 seems adequately generalized to bind to any host siRNAs, the highest affinity for those with 19 bps of duplex with 5' phosphates. p19 accommodates the the 2 nts overhang at the 3' end that are produced as part of the generation of the siRNAs, and biochemical analysis show binding is best for the 21 nt siRNAs. The structural basis for the size selective interaction of p19 with siRNAs, where an extended beta-sheet spans the length of the helix positioning flanking helices mediating end-capping stacking interactions with the RNA, has not yet been seen in other interactions of protein with double-stranded RNAs.
About this Structure
1rpu is a Protein complex structure of sequences from Carnation italian ringspot virus. Full crystallographic information is available from OCA. The molecular weight of p19 protein chain designated 'a' seen in the solved structure is 15.6 kDa (138 residues visible). The molecular weight of p19 protein chain designated 'b' seen in the solved structure is 15.2 kDa (135 residues visible). Total size of the p19-RNA complex seen in the structure is 52.1 kDa. Biological Carnation italian ringspot virus p19 is 172 amino acids and full-length p19 was expressed and purified to generate the crystals in this structure.
Reference for the Structure
Size selective recognition of siRNA by an RNA silencing suppressor., Vargason JM, Szittya G, Burgyan J, Tanaka Hall TM, Cell 2003 Dec 26;115(7):799-811. PMID:14697199
3D structures of protein p19
Updated on 17-February-2016
1rpu – P19 + SiRNA – Carnation italian ringspot virus
1rpf, 4jk0, 4kq0 - TbsvP19 (mutant) + SiRNA –Tomato bushy stunt virus
3lzl,3lzn,3lzo,3lzp,3lzq,3lzr – P19 – Campylobacter jejuni
4j39, 4j5v, 4jgn, 4jnx, 4knq, 4ktg - TbsvP19 + SiRNA
Related Structures and Topics
Notes and Literature References
- ↑ Functional anatomy of siRNAs for mediating efficient RNAi in Drosophila melanogaster embryo lysate., Elbashir SM, Martinez J, Patkaniowska A, Lendeckel W, Tuschl T, EMBO J. 2001 Dec 3;20(23):6877-88. PMID:11726523
- ↑ Size selective recognition of siRNA by an RNA silencing suppressor., Vargason JM, Szittya G, Burgyan J, Tanaka Hall TM, Cell 2003 Dec 26;115(7):799-811. PMID:14697199
- ↑ Recognition of small interfering RNA by a viral suppressor of RNA silencing., Ye K, Malinina L, Patel D J, Nature 2003 426(6968):874-878. Epub 2003 Dec 3. PMID:14661029
- ↑ Alignment of Carnation italian ringspot virus p19 (in 1rpu) vs. Tomato bushy stunt virus p19 (in 1r9f).
Additional Literature and Resources
- Tour of p19 bound to an siRNA by Wayne Decatur, in an exploration-friendly interface that is adapted from Eric Martz's FirstGlance in Jmol
- Structural basis for RNA-silencing suppression by Tomato aspermy virus protein 2b., Chen HY, Yang J, Lin C, Yuan YA, EMBO Rep. 2008 Aug;9(8):754-60. Epub 2008 Jul 4.PMID:18600235
- The structure of the flock house virus B2 protein, a viral suppressor of RNA interference, shows a novel mode of double-stranded RNA recognition., Lingel A, Simon B, Izaurralde E, Sattler M. EMBO Rep. 2005 Dec;6(12):1149-55. PMID:16270100
- Dual modes of RNA-silencing suppression by Flock House virus protein B2. Chao JA, Lee JH, Chapados BR, Debler EW, Schneemann A, Williamson JR, Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2005 Nov;12(11):952-7. PMID:16228003
- Recognition of small interfering RNA by a viral suppressor of RNA silencing., Ye K, Malinina L, Patel D J, Nature 2003 426(6968):874-878. Epub 2003 Dec 3. PMID:14661029
- Sizing up small RNAs., Jabri E, Nature Structural & Molecular Biology 2004 11: 112. PMID:14749769
- Crystal structure of p19--a universal suppressor of RNA silencing., Baulcombe DC, Molnar A, Trends Biochem Sci. 2004 29(6):279-281. PMID:15276178
- Plant viral suppressors of RNA silencing., Roth BM, Pruss GJ, Vance VB, Virus Res. 2004 Jun 1;102(1):97-108. PMID:15068885
- Novel modes of protein-RNA recognition in the RNAi pathway. Lingel A, Sattler M, Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2005. 15(1):107-115. PMID:15718141
- Nature Reviews RNAi collection
- The Tombusvirus-encoded P19: from irrelevance to elegance. Scholthof HB, Nature Reviews Microbiology. 22006 May;4(5):405-11. PMID:16518419
- Kieft JS, Pfingsten JS. Weapons in the molecular arms race. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2005 Nov;12(11):938-9. PMID:16419274