We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1166
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
== Background == | == Background == | ||
| - | [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ | + | [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/G_protein%E2%80%93coupled_receptor G-protein coupled receptors] |
| + | |||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| Line 26: | Line 27: | ||
== Clinical Relevance == | == Clinical Relevance == | ||
| - | + | [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glucagon_receptor clinical relevance] | |
| - | + | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Revision as of 13:10, 29 March 2016
| This Sandbox is Reserved from Jan 11 through August 12, 2016 for use in the course CH462 Central Metabolism taught by R. Jeremy Johnson at the Butler University, Indianapolis, USA. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1160 through Sandbox Reserved 1184. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
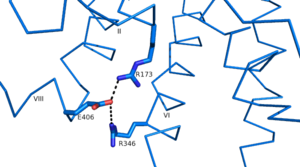
class B Human Glucagon Receptor
| |||||||||||