BACE-1 is a type-1 integral membrane glycoprotein that is affected by the positions on the outer domains of amino acids (7) . BACE-1 prefers the cleavage of longer substrates over smaller peptide based substrates due to approximate acidic pH of 4.5 resulting from the cleavage. The acidic and polar environment of the enzyme allow a wide variety of substrates to bind to the membrane. Cleavage of soluble substrates is possible in external environment due to the enzyme’s high values of Km failing to observe in the internal environment (8). The two catalytic aspartate residues that reside in the active site of BACE-1 are Asp 32 and Asp 228 (7). The active site of BACE-1 has a flexible antiparallel -hairpin, also known as a flap, which is found in the residues of 67 to 77, that controls the accessibility of the substrate to the active site, and the flap also has to set the substrate in the correct orientation for catalysis (8). In an open conformation, the active site allows the substrate to enter without any difficulty and regulates its activity. In an inactive form, the binding affinity to the inhibitor is decreased, which then lowers the substrate binding and enzymatic activity. For the closed conformation, the flap with the inhibitor bound is firmly secured in place (8).
The S3 pocket is adjacent to the Thr 232 and the amino acids from the 10s loop, which contains Glycine and Glutamine. The Glycine located in the 10s loop that the substrate forms a hydrogen bond with helps stabilize the 10s loop which further balances the interaction of the beta secretase-substrate. In an open conformation of the 10s loop, the substrate and the S3 pocket have a greater affinity to bind with each other (9). The stabilization of the structure depends on the active site, flap and 10s loop.
Specifically, BACE-1 is a transmembrane aspartic protease which cleaves the amyloid-beta precursor protein and produces the amyloid-beta peptide. Two water molecules are in the process for the aspartic protease. The location of the first water molecule for BACE-1 is between the Asp 32 and Asp 228 (8).Once the substrate binds, the two aspartate residues form a hydrogen bond with the water molecule. Then, the water molecule becomes the nucleophile that attacks the carbonyl. The second water molecule forms a hydrogen bond with Tyr residue that is found in the flap. The behavior of the two water molecules affects the activity of BACE-1 (8).
Structural Highlights
Active Site Mechanism
The mechanism of this protease activity is an acid-base reaction, common in organic chemistry. The two aspartate molecules coordinate a water molecule through hydrogen bonding. The aspartate molecule takes a hydrogen from a water molecule, which activates the water as a good nucleophile. The good water nucleophile attacks the carbonyl carbon in the peptide bond with the attack forms a tetrahedral intermediate. A pair of electrons is moved to re-create a carbonyl group which breaks the peptide bond and re-generates an aspartic oxyanion. No covalent bonds are formed between the beta-secretase side chains and the substrate on the enzyme and therefore the fragments can exit the active site easily.

Function
BACE-1 plays a main role for the proteolytic processing of APP. The main function is to release the extracellular material of the beta-cleaved soluble APP by the cleaving of the N-terminus of the A-beta peptide sequence while the C-terminal fragment is released by a process of gamma-secretase. (ncbi) However, beta-secretase malfunctions to cleave APP in a different position creating beta-amyloid. These fragments of beta-amyloid then aggregate and form harmful plaques that can spread throughout the body causing Alzheimer’s Disease. Beta-secretase also takes place in the formation of myelin sheaths in the peripheral nerve cells.
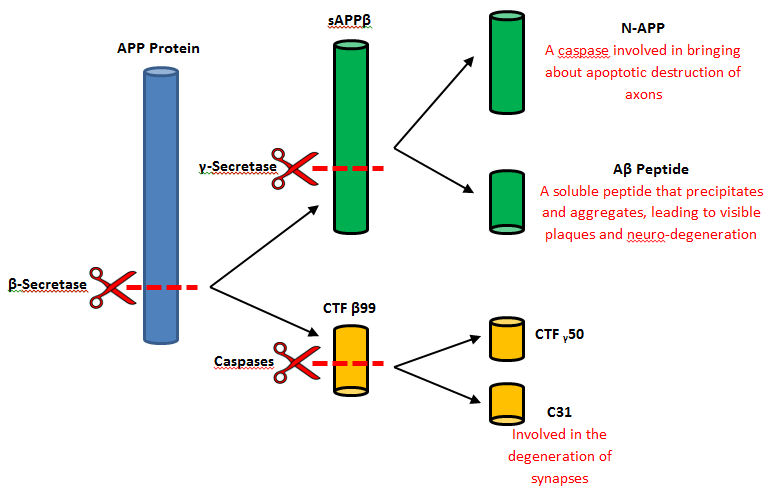
In a general reaction, APP is initially cleaved by alpha-secretase in a certain position every time and then by gamma-secretase. Neurons may benefits from the released fragments produced by the alpha, gamma-secretase cleavage of APP. However, when beta-secretase enters the equation the cleavage of APP changes positions. Once gamma-secretase has officially completed its cleavage, amyloid-beta is released into the extracellular membrane space. Amyloid-beta is most commonly found to aggregate in this area and form plaques that are extremely harmful to the human body. It is thought that this plaque build up is the initial cause of Alzheimer’s Disease.
Associated Health Conditions
Alzheimer's Disease
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is an unfortunate neurodegenerative disease that degrades the nervous system, specifically the destruction of neurons in the brain. The brain mass of a person with this disease is significantly reduced over time as brain neurons and brain function diminishes over time. The amyloid plaque, a product of APP, is what aggregates in the brain and degrades neuron function in the brain. The loss of neuron function and inability to make synapses in the brain eventually leads to dementia in AD patients which reduces the patient’s memory. The reduction of memory results in brain capacity reduced, impacting the functioning of the patient’s normal daily life routines and eventually results in death. In the later stages of AD, when brain capacity and function is very low, typically the patient needs to be cared for because they are not able to live their normal life and care for themselves on a daily basis as a normal person would.
AD occurs because of plaques which are formed from a buildup of amyloid beta. Amyloid beta (AB) is a four kilodalton protein made up of about 39-43 amino acids in length, which aggregates in the brain and causes the destruction of the brain. Amyloid beta is cleaved from the membrane protein APP done so by two proteases, beta-secretase and gamma-secretase. Amyloid betas are amphiphilic peptides with a hydrophilic (water loving) N-terminal side (residues 1-28) and a hydrophobic (water hating) C-terminal side (residues 29-40). These characteristics of the AB is what affects the toxicity of the peptide aggregates in the brain.
Down Syndrome
Inhibitors
In recent years there has been much work done with beta-secretase inhibitors and synthesizing therapeutic drugs that will inhibit the production of beta-amyloids. An area that has specifically been studied is Beta-secretase processing of APP. Processing of APP is the first step in the synthesis of amyloid-beta, and therefore inhibiting it could be a successful way to inhibit the development of Alzheimer's diseases. Two main types of beta-secretase inhibitors that are being studied include; peptidomimetic beta-secretase inhibitors and nonpeptidomimetic beta-secretase inhibitors.
Peptidomimetic beta-secretase inhibitors focus on substrate-based inhibition and were created by analyzing the specificity and kinetics of the beta-secretase enzyme. One specific development of a peptidomimetic beta-secretase inhibitor, by the Elan/Pharmacia team, involves a cell-permeable, dose-dependent, mechanism-specific reduction of the harmful amyloid-beta substance in human embryonic cells. Identification of a specific sequence, P16 to P5’, in beta-secretase substrate was the key discovery that led to the development of a peptidomimetic beta-secretase inhibitor by replacing the P1 residue with a statine, which in uncleavable, and replacing the P1’ Asp with valine. The new analogue created was then used to create purified beta-secretase that was sequenced and cloned. The N-terminus and the C-terminus of the created and purified beta-secretase were truncated to create a small peptide inhibitor, which was then transformed into a cell-permeable peptidomimetic beta-secretase inhibitor by dividing it into three regions. The regions included; an N-terminus, a C-terminus, and central core section that included statine. The Elan targeted these three regions and focused on modifying them to have less peptidic qualities but still keep beta-secretase enzyme activity.
Nonpeptidomimetic beta-secretase inhibitors have been more challenging to create and currently most companies have only published patent applications. Some work is currently being done by Neurologic using heterocyclic compounds, which act by indirectly increasing alpha-sAPP and shifting APP processing. This shift modifies APP processing which acts to inhibit the production of beta-amyloids and the formation beta-amyloid aggregates and harmful plaques.
This is a sample scene created with SAT to by Group, and another to make of the protein. You can make your own scenes on SAT starting from scratch or loading and editing one of these sample scenes.