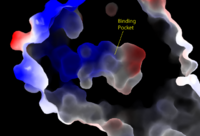
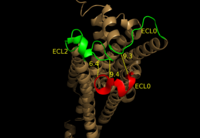
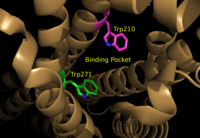
We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1172
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| - | The LPA<sub>1</sub> receptor is present in nearly all cells and tissues | + | The LPA<sub>1</sub> receptor is present in nearly all cells and tissues, and deletion of the LPA<sub>1</sub> receptor has physiological effects on every organ system, indicating its wide range of functions. Specifically, this receptor initiates downstream signaling cascades with three G<sub>α</sub> proteins: G<sub>i/o</sub>, G<sub>q/11</sub>, and G<sub>12/13</sub>. Specifically, G<sub>α</sub> proteins begin signaling cascades that activate [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phospholipase_C phospholipase C] and [[MAPK]]s that signal for cell proliferation, survival, and migration. <ref name = 'Yung'>Yung, Y. C., N. C. Stoddard, and J. Chun. "LPA Receptor Signaling: Pharmacology, Physiology, and Pathophysiology." The Journal of Lipid Research 55.7 (2014): 1192-214. Web. 17 Feb. 2016.' </ref>.Despite this receptor being expressed ubiquitously, LPA<sub>1</sub> is highly expressed in neural tissue, aiding in several different neurodevelopmental processes including growth and folding of the [https://www.dartmouth.edu/~rswenson/NeuroSci/chapter_11.html cerebral cortex] and the growth, survival, and migration of neural [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Progenitor_cell progenitor cells] through its different [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/G_protein G-protein] regulated pathways.<ref name = 'Chun'>Chun, J., Hla, T., Spiegel, S., and Moolenaar, W.H. “Lysophospholipid Receptors: Signaling and Biochemistry.” John Wiley & Sons, Inc. (2013) pp.i-xviii. 5 Feb. 2016.' </ref>. Finally, LPA1 receptors expressed in neural tissue aid in Schwann cell migration and myelination through a signaling pathway with the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/RAC1 Rac1] G-protein.<ref name="number5">PMID: 24115248</ref>. |
Revision as of 01:29, 14 April 2016
| This Sandbox is Reserved from Jan 11 through August 12, 2016 for use in the course CH462 Central Metabolism taught by R. Jeremy Johnson at the Butler University, Indianapolis, USA. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1160 through Sandbox Reserved 1184. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Lysophosphatidic Acid Receptor 1
References
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 Chrencik JE, Roth CB, Terakado M, Kurata H, Omi R, Kihara Y, Warshaviak D, Nakade S, Asmar-Rovira G, Mileni M, Mizuno H, Griffith MT, Rodgers C, Han GW, Velasquez J, Chun J, Stevens RC, Hanson MA. Crystal Structure of Antagonist Bound Human Lysophosphatidic Acid Receptor 1. Cell. 2015 Jun 18;161(7):1633-43. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.06.002. PMID:26091040 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2015.06.002
- ↑ Hernández-Méndez, Aurelio, Rocío Alcántara-Hernández, and J. Adolfo García-Sáinz. "Lysophosphatidic Acid LPA1-3 Receptors: Signaling, Regulation and in Silico Analysis of Their Putative Phosphorylation Sites." Receptors & Clinical Investigation Receptor Clin Invest 1.3 (2014). Web. 15 Feb. 2016.'
- ↑ Yung, Y. C., N. C. Stoddard, and J. Chun. "LPA Receptor Signaling: Pharmacology, Physiology, and Pathophysiology." The Journal of Lipid Research 55.7 (2014): 1192-214. Web. 17 Feb. 2016.'
- ↑ Chun, J., Hla, T., Spiegel, S., and Moolenaar, W.H. “Lysophospholipid Receptors: Signaling and Biochemistry.” John Wiley & Sons, Inc. (2013) pp.i-xviii. 5 Feb. 2016.'
- ↑ Anliker B, Choi JW, Lin ME, Gardell SE, Rivera RR, Kennedy G, Chun J. Lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) and its receptor, LPA1 , influence embryonic schwann cell migration, myelination, and cell-to-axon segregation. Glia. 2013 Dec;61(12):2009-22. doi: 10.1002/glia.22572. Epub 2013 Sep 24. PMID:24115248 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/glia.22572
- ↑ Chun, E., Thompson, A.A., Lui, W., Roth, C.B., Griffith, M.T., Katritch, V., Kunken, J., Xu, F., Cherezov, V., Hanson, M.A., and Stevens, R.C. “Fusion partner tool chest for the stabilization and crystallization of G protein-coupled receptors.” Structure 20, (2012) 967-976.'
- ↑ Van Durme, J., Horn, F., Costagliola, S., Vriend, G., and Vassart, G. “GRIS: glycoprotein-hormone receptor information system.” Mol. (2006) Endocrinol. 20, 2247-2255'
- ↑ Lin ME, Herr DR, Chun J. Lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) receptors: signaling properties and disease relevance. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2010 Apr;91(3-4):130-8. doi:, 10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2009.02.002. Epub 2009 Mar 4. PMID:20331961 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2009.02.002
- ↑ Justus CR, Dong L, Yang LV. Acidic tumor microenvironment and pH-sensing G protein-coupled receptors. Front Physiol. 2013 Dec 5;4:354. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2013.00354. PMID:24367336 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2013.00354