We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Flagellar protein
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
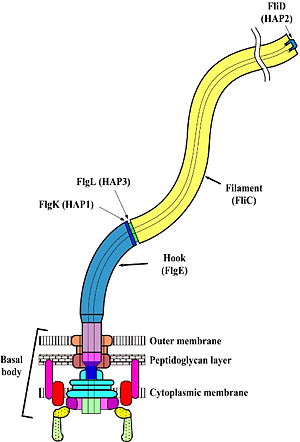
[[Image:Flagellum1 800px.jpg|left|thumb|The bacterial flagellum consists of a filament, a universal joint (hook), and a motor (basal body).|300px]]<br /> | [[Image:Flagellum1 800px.jpg|left|thumb|The bacterial flagellum consists of a filament, a universal joint (hook), and a motor (basal body).|300px]]<br /> | ||
Flagella (singular: flagellum) enable bacteria to swim towards sources of nutrition, and away from sources of toxins. Such directed motility is termed ''[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chemotaxis chemotaxis]''. Rapid swimming helps [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bdellovibrio Bdellovibrio] penetrate and parasitize their host bacteria, but flagella are not always essential for virulence<ref name="virulence1">PMID: 2152887</ref>. Flagella are important in responses to quorum sensing<ref name="quorum1">PMID: 15449604</ref> and biofilm formation<ref name="biofilms1">PMID: 19231189</ref><ref name="biofilms2">PMID: 17416647</ref>. Flagella may also be involved in functions other than motility<ref name="otherfunctions">PMID: 17920274</ref>. | Flagella (singular: flagellum) enable bacteria to swim towards sources of nutrition, and away from sources of toxins. Such directed motility is termed ''[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chemotaxis chemotaxis]''. Rapid swimming helps [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bdellovibrio Bdellovibrio] penetrate and parasitize their host bacteria, but flagella are not always essential for virulence<ref name="virulence1">PMID: 2152887</ref>. Flagella are important in responses to quorum sensing<ref name="quorum1">PMID: 15449604</ref> and biofilm formation<ref name="biofilms1">PMID: 19231189</ref><ref name="biofilms2">PMID: 17416647</ref>. Flagella may also be involved in functions other than motility<ref name="otherfunctions">PMID: 17920274</ref>. | ||
| - | |||
For further information, please see [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Flagellum Flagellum at Wikipedia]. | For further information, please see [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Flagellum Flagellum at Wikipedia]. | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
can't get this journal thru umass:<ref name="flagrev1">PMID: 19081534</ref> | can't get this journal thru umass:<ref name="flagrev1">PMID: 19081534</ref> | ||
--> | --> | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
The bacterial flagellum is made up of about 25 different proteins. There are only a few copies of some proteins, and tens of thousands of copies of the filament protein, FliC. The flagellum is made up of three major regions, as follows. | The bacterial flagellum is made up of about 25 different proteins. There are only a few copies of some proteins, and tens of thousands of copies of the filament protein, FliC. The flagellum is made up of three major regions, as follows. | ||
| Line 27: | Line 24: | ||
* [[Flagellar hook of bacteria]]<br /> | * [[Flagellar hook of bacteria]]<br /> | ||
* [[Samatey/5]] | * [[Samatey/5]] | ||
| - | |||
| - | {{Clear}} | ||
==Assembly== | ==Assembly== | ||
Revision as of 21:02, 6 January 2018
| |||||||||||
Contents |
Flagellar Protein Structures
- 1io1: Flagellin major fragment of Salmonella typhimurium (FliC41).
- 1ucu: R-type straight flagellar filament made of full-length flagellin.
- 1wlg: Hook monomer major fragment of Salmonella typhimurium (FlgE31).
- 2zbi: Cell surface "flagellin" functioning as an alginate receptor, not forming filaments.
- 3a5x: L-type straight flagellar filament made of full-length flagellin.
Lists of Flagellar Structures
These are automatically-generated lists of PDB codes.
- Special:Prefixindex/Category:Flagell includes categories beginning with Flagellar, Flagellin, Flagella, Flagellum.
- Special:Prefixindex/Category:Bacterial flagell
- Category:Chlamydomonas flagella
- Category:The bacterial flagellar motor
- Category:Putative flagellar motor switch protein flin
and there are undoubtedly other flagellum-related Categories ...
See Also
Within Proteopedia:
External Links
- Flagellum at Wikipedia
- Protonic Nanomachine Group, Osaka University
- MOVIES from the Protonic Nanomachine Project, Osaka University
References and Notes
- ↑ Lockman HA, Curtiss R 3rd. Salmonella typhimurium mutants lacking flagella or motility remain virulent in BALB/c mice. Infect Immun. 1990 Jan;58(1):137-43. PMID:2152887
- ↑ Daniels R, Vanderleyden J, Michiels J. Quorum sensing and swarming migration in bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2004 Jun;28(3):261-89. PMID:15449604
- ↑ Yildiz FH, Visick KL. Vibrio biofilms: so much the same yet so different. Trends Microbiol. 2009 Mar;17(3):109-18. Epub 2009 Feb 21. PMID:19231189 doi:10.1016/j.tim.2008.12.004
- ↑ Lemon KP, Higgins DE, Kolter R. Flagellar motility is critical for Listeria monocytogenes biofilm formation. J Bacteriol. 2007 Jun;189(12):4418-24. Epub 2007 Apr 6. PMID:17416647 doi:10.1128/JB.01967-06
- ↑ Guerry P. Campylobacter flagella: not just for motility. Trends Microbiol. 2007 Oct;15(10):456-61. Epub 2007 Oct 24. PMID:17920274 doi:10.1016/j.tim.2007.09.006
- ↑ Minamino T, Imada K, Namba K. Mechanisms of type III protein export for bacterial flagellar assembly. Mol Biosyst. 2008 Nov;4(11):1105-15. Epub 2008 Sep 24. PMID:18931786 doi:10.1039/b808065h
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Eric Martz, Joel L. Sussman, Fadel A. Samatey, Jaime Prilusky