Photosystem II
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
==Background== | ==Background== | ||
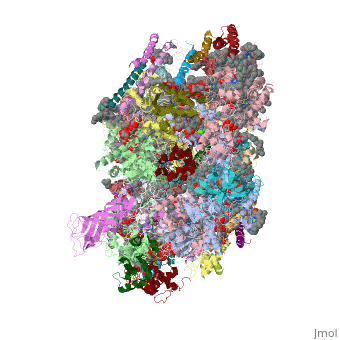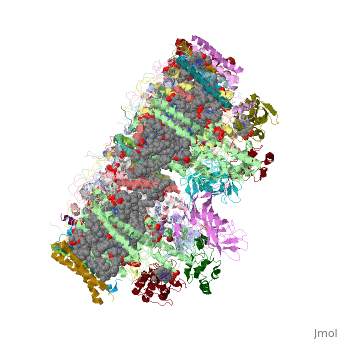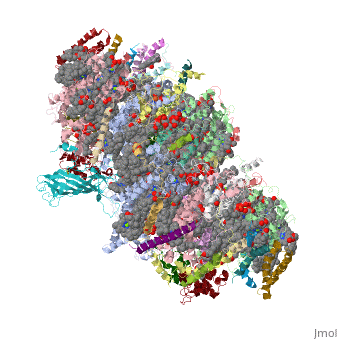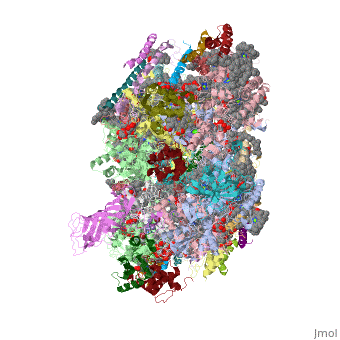
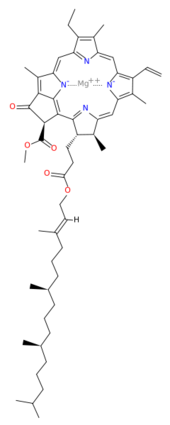
| - | This structure of '''Photosystem II''' was crystallized from the cyanobacteria, ''Thermosynechococcus elongatus'', at 3.0Å <ref>PMID: 16355230</ref> and at 3.50 Å <ref>PMID: 14764885</ref>. PDB codes are [[2axt]] and [[1s5l]], respectively. Cyanobacteria and plants both contain Photosystem II while photosynthetic bacteria contain the bacterial reaction center. This photosynthetic protein complex is associated with a variety of functional ligands. It is a <scene name='Photosystem_II/Psii_dimer/1'>dimer</scene> composed mainly of alpha-helices. Nineteen <scene name='Photosystem_II/Protein_only/1'>subunits</scene> are in each monomer, with multiple extrinsic subunits associated with the oxygen evolving complex missing from this crystallization. Photosystem II is a membrane bound protein complex that in plants is associated with the thylakoid membrane of chloroplasts. <scene name='Photosystem_II/Hydrophobic_polar/1'>Polar and hydrophobic</scene> regions correlate with membrane associated nature of the protein. '''<span style="color:gray;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">Hydrophobic</span>''' helices make up the transmembranal portion, while '''<FONT COLOR="#C031C7">polar</FONT>''' residues are concentrated externally on either side of the membrane. | + | This structure of '''Photosystem II''' was crystallized from the cyanobacteria, ''Thermosynechococcus elongatus'', at 3.0Å <ref>PMID: 16355230</ref> and at 3.50 Å <ref name="Archit">PMID: 14764885</ref>. PDB codes are [[2axt]] and [[1s5l]], respectively. Cyanobacteria and plants both contain Photosystem II while photosynthetic bacteria contain the bacterial reaction center. This photosynthetic protein complex is associated with a variety of functional ligands. It is a <scene name='Photosystem_II/Psii_dimer/1'>dimer</scene> composed mainly of alpha-helices. Nineteen <scene name='Photosystem_II/Protein_only/1'>subunits</scene> are in each monomer, with multiple extrinsic subunits associated with the oxygen evolving complex missing from this crystallization. Photosystem II is a membrane bound protein complex that in plants is associated with the thylakoid membrane of chloroplasts. <scene name='Photosystem_II/Hydrophobic_polar/1'>Polar and hydrophobic</scene> regions correlate with membrane associated nature of the protein. '''<span style="color:gray;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">Hydrophobic</span>''' helices make up the transmembranal portion, while '''<FONT COLOR="#C031C7">polar</FONT>''' residues are concentrated externally on either side of the membrane. |
==Photosynthesis== | ==Photosynthesis== | ||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
{{Clear}} | {{Clear}} | ||
==Oxygen Evolution== | ==Oxygen Evolution== | ||
| - | Another important facet of Photosystem II is its ability to oxidize water to oxygen with its <scene name='Photosystem_II/Oxygen_evolving_centers/11'>oxygen evolving centers</scene>. These centers are <scene name='Photosystem_II/Single_oxygen_evolving/1'>cubane-like</scene> structures with 3 '''<FONT COLOR="#8D38C9">manganese</FONT>''', 4 '''<FONT COLOR="#C11B17">oxygen</FONT>''' and a '''<span style="color:lime;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">calcium</span>''' linked to a fourth manganese<ref | + | Another important facet of Photosystem II is its ability to oxidize water to oxygen with its <scene name='Photosystem_II/Oxygen_evolving_centers/11'>oxygen evolving centers</scene>. These centers are <scene name='Photosystem_II/Single_oxygen_evolving/1'>cubane-like</scene> structures with 3 '''<FONT COLOR="#8D38C9">manganese</FONT>''', 4 '''<FONT COLOR="#C11B17">oxygen</FONT>''' and a '''<span style="color:lime;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">calcium</span>''' linked to a fourth manganese<ref name="Archit" />. Oxidation of water leaves 2 H <sup>+</sup> on the lumenal side of the membrane, helping to establish the proton gradient essential for ATP synthesis in the CF<sub>1</sub>CF<sub>0</sub>-ATP sythase protein. |
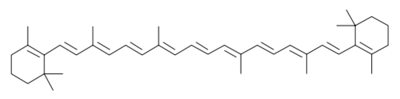
[[Image:b-car.svg.png|b-car.svg.png|thumb|left|400px|structure of beta carotene]] | [[Image:b-car.svg.png|b-car.svg.png|thumb|left|400px|structure of beta carotene]] | ||
Revision as of 09:00, 21 August 2018
| |||||||||||
3D structures of photosystem II
Updated on 21-August-2018
Additional Resources
For additional information, see: Photosynthesis
References
- ↑ Loll B, Kern J, Saenger W, Zouni A, Biesiadka J. Towards complete cofactor arrangement in the 3.0 A resolution structure of photosystem II. Nature. 2005 Dec 15;438(7070):1040-4. PMID:16355230 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature04224
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Ferreira KN, Iverson TM, Maghlaoui K, Barber J, Iwata S. Architecture of the photosynthetic oxygen-evolving center. Science. 2004 Mar 19;303(5665):1831-8. Epub 2004 Feb 5. PMID:14764885 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.1093087
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Emily Forschler, Michal Harel, Ilan Samish, Alexander Berchansky, Eric Martz, Jaime Prilusky, Eran Hodis, Joel L. Sussman, David Canner, Karl Oberholser