Sandbox Reserved 1506
From Proteopedia
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
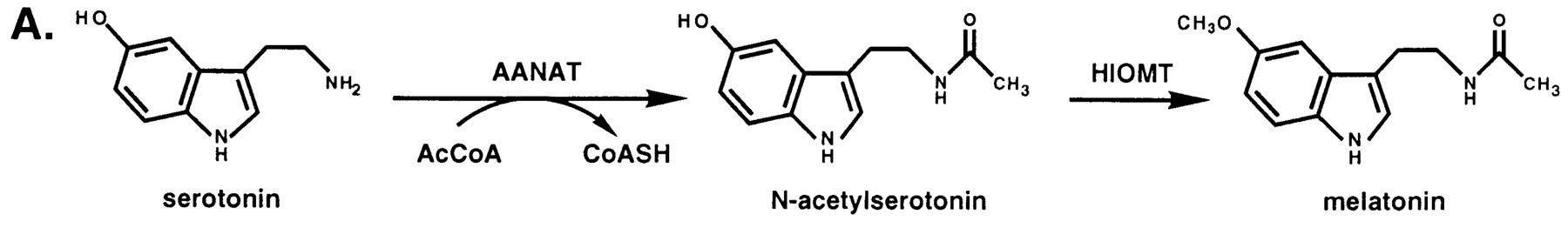
| - | Serotonin N-acetyltransferase is also named aralkylamine-N-acetyltransferase (ANAAT). This enzyme catalyzes the acetylation of the amine group on serotonin, an intermediate in melatonin synthesis. It | + | Serotonin N-acetyltransferase is also named aralkylamine-N-acetyltransferase (ANAAT). This enzyme catalyzes the acetylation of the amine group on serotonin, an intermediate in melatonin synthesis. It is the penultimate enzyme in the melatonin pathway, as it is shown on fig1.[1]. |
[[Image:melationin synthesis.jpg]] | [[Image:melationin synthesis.jpg]] | ||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
== Relevance == | == Relevance == | ||
| - | Circulating melatonin plays a role in the circadian rythm. Day/night differences in circulating melatonin levels provide a hormonal analog signal of environmental lighting, which is used in a variety of ways to optimize circadian and circannual rhythms in physiology[2]. | + | Circulating melatonin plays a role in the circadian rythm. Day/night differences in circulating melatonin levels provide a hormonal analog signal of environmental lighting, which is used in a variety of ways to optimize circadian and circannual rhythms in physiology[2]. |
| - | + | The amount of circulating melatonin is correlated with ANAAT activity, as enzyme activity varies in parallel with melationin amount. For example, in some species the night/day differences in melatonin, AANAT activity, and protein are 10- to 100-fold [3]. | |
| - | + | ||
== Structure == | == Structure == | ||
| - | AANAT consists of an 8 stranded β sheet with five α helices, with a conserved motif in the center of the sheet forming a binding site for acetyl-CoA, the acetyl source. | + | AANAT consists of an 8 stranded β sheet with five α helices, with a conserved motif in the center of the sheet forming a binding site for acetyl-CoA, the acetyl source.[1] |
== Regulation == | == Regulation == | ||
| - | + | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
Revision as of 13:00, 2 January 2019
|
|
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 06/12/2018, through 30/06/2019 for use in the course "Structural Biology" taught by Bruno Kieffer at the University of Strasbourg, ESBS. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1480 through Sandbox Reserved 1543. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
This is a default text for your page b6. Click above on edit this page to modify. Be careful with the < and > signs.
You may include any references to papers as in: the use of JSmol in Proteopedia [1] or to the article describing Jmol [2] to the rescue.
Contents |
Function
Serotonin N-acetyltransferase is also named aralkylamine-N-acetyltransferase (ANAAT). This enzyme catalyzes the acetylation of the amine group on serotonin, an intermediate in melatonin synthesis. It is the penultimate enzyme in the melatonin pathway, as it is shown on fig1.[1].
Relevance
Circulating melatonin plays a role in the circadian rythm. Day/night differences in circulating melatonin levels provide a hormonal analog signal of environmental lighting, which is used in a variety of ways to optimize circadian and circannual rhythms in physiology[2]. The amount of circulating melatonin is correlated with ANAAT activity, as enzyme activity varies in parallel with melationin amount. For example, in some species the night/day differences in melatonin, AANAT activity, and protein are 10- to 100-fold [3].
Structure
AANAT consists of an 8 stranded β sheet with five α helices, with a conserved motif in the center of the sheet forming a binding site for acetyl-CoA, the acetyl source.[1]
Regulation
</StructureSection>
References
[1] Hickman, A. B; Klein, D. C; Dyda, F. Melatonin Biosynthesis: The Structure of Serotonin N-Acetyltransferase at 2.5A Resolution Suggests a Catalytic Mechanism. Mol. Cell. 1999, 3-1, 23-32.
[2] Arendt, J. (1995) Melatonin and the Mammalian Pineal Gland (Chapman & Hall, London), pp. 201–285.
[3] Klein, D.C., and Weller, J.L. (1972). Rapid light induced decrease in pineal serotonin N-acetyltransferase activity. Science 177, 532–533.
[4]Gastel, J.A., Roseboom, P.H., Rinaldi, P.A., Weller, J.L., and Klein,D.C. (1998). Melatonin production: proteasomal proteolysis in serotonin N-acetyltransferase regulation. Science 279, 1358–1360.
[5] Melatonin synthesis: 14-3-3-dependent activation and inhibition of arylalkylamine N -acetyltransferase mediated by phosphoserine-205 - Surajit Ganguly, Joan L. Weller, Anthony Ho, Philippe Chemineau, Benoit Malpaux, and David C. Klein - PNAS, January 25, 2005.
[6] The Structural Basis of Ordered Substrate Binding by Serotonin N-Acetyltransferase: Enzyme Complex at 1.8 A ˚ Resolution with a Bisubstrate Analog - Alison Burgess Hickman,M. A. A. Namboodiri, David C. Klein, and Fred Dyda - Cell, Vol. 97, 361–369, April 30, 1999.
- ↑ Hanson, R. M., Prilusky, J., Renjian, Z., Nakane, T. and Sussman, J. L. (2013), JSmol and the Next-Generation Web-Based Representation of 3D Molecular Structure as Applied to Proteopedia. Isr. J. Chem., 53:207-216. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijch.201300024
- ↑ Herraez A. Biomolecules in the computer: Jmol to the rescue. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2006 Jul;34(4):255-61. doi: 10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644. PMID:21638687 doi:10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644