We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1504
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
= 2N19 = | = 2N19 = | ||
| - | < | + | <StructureSection load='2n19' scene='80/802678/Structure/3' scene='80/802678/Structure/5' size='400' frame='false' align='right'</scene> |
| - | + | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| Line 20: | Line 19: | ||
Located in the cytoplasm, the centrosome, consisting of a pair of centrioles, has the major role of being the organizing center of microtubules in animal cells. It is responsible for the formation of the microtubular mitotic spindle during the cell division on which the chromosomes move. They also allow cells to detect chemicals and even move. | Located in the cytoplasm, the centrosome, consisting of a pair of centrioles, has the major role of being the organizing center of microtubules in animal cells. It is responsible for the formation of the microtubular mitotic spindle during the cell division on which the chromosomes move. They also allow cells to detect chemicals and even move. | ||
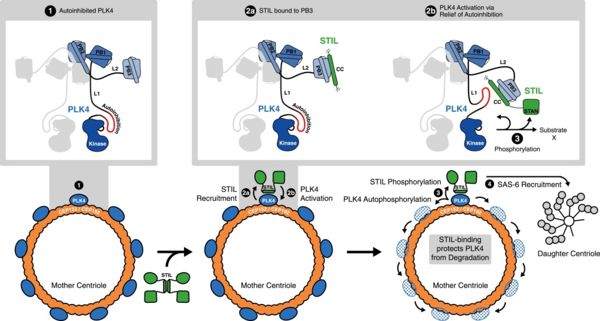
During cell division, the two centrioles duplicate forming two centrosomes. In order to occur in a suitable way, the duplication needs as many STIL as PLK4 otherwise it leads to deficient cells and thus cancer. We can explain it by the fact that PLK4 recruits STIL, and STIL is phosphorylated by PLK4. | During cell division, the two centrioles duplicate forming two centrosomes. In order to occur in a suitable way, the duplication needs as many STIL as PLK4 otherwise it leads to deficient cells and thus cancer. We can explain it by the fact that PLK4 recruits STIL, and STIL is phosphorylated by PLK4. | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| Line 37: | Line 33: | ||
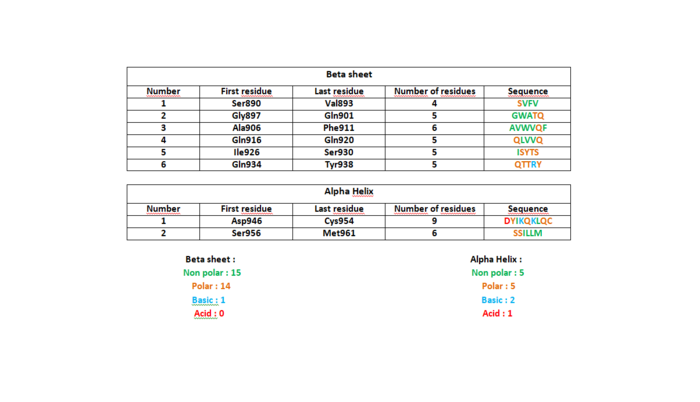
The helix is divided in 2 domains: alpha 1 and alpha 2. In this helix we can observe that each amino acid can make at least 3 hydrogen bonds with atoms which are close enough and well disposed. | The helix is divided in 2 domains: alpha 1 and alpha 2. In this helix we can observe that each amino acid can make at least 3 hydrogen bonds with atoms which are close enough and well disposed. | ||
There are almost as many polar and non-polar amino acids especially in beta strands. | There are almost as many polar and non-polar amino acids especially in beta strands. | ||
| - | [[Image:Tableau3.png | | + | [[Image:Tableau3.png | 700px | centre]] |
| Line 47: | Line 43: | ||
| - | [[Image:Meca.jpg | | + | [[Image:Meca.jpg | 600px | centre]] |
| Line 60: | Line 56: | ||
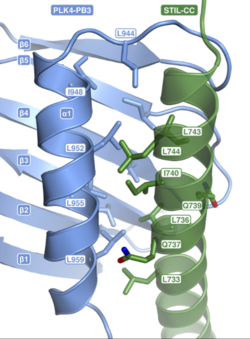
| - | [[Image:interaction.png | | + | [[Image:interaction.png | 250px | centre]] |
==Conclusion== | ==Conclusion== | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
To conclude, the most important to remind is that 2n19 is the third polo box (PB3) of the enzyme PLK4, a kinase. This enzyme is needed for the centriole duplication (and thus for mitosis…), notably when it interacts with the other protein STIL. The role of 2n19 is to keep a good contact between those 2 proteins and thus to enable the phosphorylation of STIL by PLK4, which will induce the recruitment of other factors. And this will lead to the duplication of centrioles. | To conclude, the most important to remind is that 2n19 is the third polo box (PB3) of the enzyme PLK4, a kinase. This enzyme is needed for the centriole duplication (and thus for mitosis…), notably when it interacts with the other protein STIL. The role of 2n19 is to keep a good contact between those 2 proteins and thus to enable the phosphorylation of STIL by PLK4, which will induce the recruitment of other factors. And this will lead to the duplication of centrioles. | ||
| + | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
Arquint C, Gabryjonczyk AM, Imseng S, Bohm R, Sauer E, Hiller S, Nigg EA, Maier T. STIL binding to Polo-box 3 of PLK4 regulates centriole duplication. Elife. 2015 Jul 18;4. doi: 10.7554/eLife.07888 | Arquint C, Gabryjonczyk AM, Imseng S, Bohm R, Sauer E, Hiller S, Nigg EA, Maier T. STIL binding to Polo-box 3 of PLK4 regulates centriole duplication. Elife. 2015 Jul 18;4. doi: 10.7554/eLife.07888 | ||
Current revision
2N19
| |||||||||||