User:Ashley Crotteau/Sandbox1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
===SET 7/9=== | ===SET 7/9=== | ||
The human lysine methyltransferase (HKMT) SET7/9 is 366 amino acids long. The overall structure looks like a dimer although it acts as a monomer. The structure is composed of the ΔSET7/9 domain. The ΔSET7/9 consists of the SET domain along with the pre- and post-SET regions. The pre- and post-SET regions are adjacent to SET domain and are cysteine rich. The pre-SET cysteine region is located near the N-terminal where the post-SET region is located near the C-terminal of the domain. These regions are said to play an important role in substrate recognition and enzymatic activity.<ref name="Schubert" /><ref name="Yeates" /> | The human lysine methyltransferase (HKMT) SET7/9 is 366 amino acids long. The overall structure looks like a dimer although it acts as a monomer. The structure is composed of the ΔSET7/9 domain. The ΔSET7/9 consists of the SET domain along with the pre- and post-SET regions. The pre- and post-SET regions are adjacent to SET domain and are cysteine rich. The pre-SET cysteine region is located near the N-terminal where the post-SET region is located near the C-terminal of the domain. These regions are said to play an important role in substrate recognition and enzymatic activity.<ref name="Schubert" /><ref name="Yeates" /> | ||
| - | The SET domain is mostly defined by turns and loops with the few antiparallel β-sheets.3 Residues 337-349 form a β-hairpin that sticks out at a right angle to the surface of the enzyme. The following three residues (350-352) accommodate a sharp bend in the peptide chain and the end of the protein adopts an α-helical conformation.1 The two most defining features of the SET domain are the C-terminal tyrosine and the knot-like fold. These two components have been recognized to be essential for S-adenosyl-L-methionine (SAM) binding and catalysis.3,4,5 The knot-like fold contains the binding sites for the cofactor SAM and the peptide substrate.2 | ||
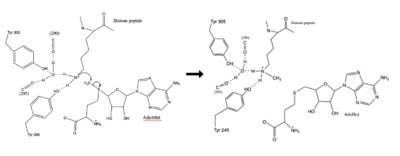
| - | The most notable feature of the HKMT is the presence of the lysine access channel.1 The cofactor and peptide substrate are actually located on opposite sides of the SET domain. This narrow channel allows these two components to interact and complete the methyltransfer. Two tyrosine residues, Tyr335 and Tyr337, are important for the formation of this channel. The β-hairpin stabilizes the conformation of these two residues and contributes to the peptide binding groove. The peptide binding groove is composed of residues 255-268. | ||
| - | The α-helix at the C-terminal packs against the β-19, through mainly Phe299, and makes hydrophobic interactions with the cofactor through Trp352. The cofactor binding site consists of four tyrosine residues (Tyr 245, 305, 335, and 337), along with five main chain carbonyl groups. | ||
| - | < | + | The SET domain is mostly defined by turns and loops with the few antiparallel β-sheets.3 Residues 337-349 form a β-hairpin that sticks out at a right angle to the surface of the enzyme. The following three residues (350-352) accommodate a sharp bend in the peptide chain and the end of the protein adopts an α-helical conformation.<ref name="Xiao" /> The two most defining features of the SET domain are the C-terminal tyrosine and the knot-like fold. These two components have been recognized to be essential for S-adenosyl-L-methionine (SAM) binding and catalysis.<ref name="Schubert" /> <ref name="Yeates" /> <ref name="Huang" /> The knot-like fold contains the binding sites for the cofactor SAM and the peptide substrate.<ref name="Licciardello" /> |
| - | < | + | |
| + | The most notable feature of the HKMT is the presence of the lysine access channel.The cofactor and peptide substrate are actually located on opposite sides of the SET domain. This narrow channel allows these two components to interact and complete the methyltransfer. Two tyrosine residues, Tyr335 and Tyr337, are important for the formation of this channel. The β-hairpin stabilizes the conformation of these two residues and contributes to the peptide binding groove. The peptide binding groove is composed of residues 255-268. <ref name="Xiao" /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The α-helix at the C-terminal packs against the β-19, through mainly Phe299, and makes hydrophobic interactions with the cofactor through Trp352. The cofactor binding site consists of four tyrosine residues (Tyr 245, 305, 335, and 337), along with five main chain carbonyl groups. <ref name="Xiao" /> | ||
| + | |||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
Revision as of 23:04, 4 April 2019
H. sapiens Lysine Methyltransferase, SET 7/9
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Xiao B, Jing C, Wilson JR, Walker PA, Vasisht N, Kelly G, Howell S, Taylor IA, Blackburn GM, Gamblin SJ. Structure and catalytic mechanism of the human histone methyltransferase SET7/9. Nature. 2003 Feb 6;421(6923):652-6. Epub 2003 Jan 22. PMID:12540855 doi:10.1038/nature01378
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Schubert HL, Blumenthal RM, Cheng X. Many paths to methyltransfer: a chronicle of convergence. Trends Biochem Sci. 2003 Jun;28(6):329-35. PMID:12826405
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Yeates TO. Structures of SET domain proteins: protein lysine methyltransferases make their mark. Cell. 2002 Oct 4;111(1):5-7. PMID:12372294
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Huang S, Shao G, Liu L. The PR domain of the Rb-binding zinc finger protein RIZ1 is a protein binding interface and is related to the SET domain functioning in chromatin-mediated gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1998 Jun 26;273(26):15933-9. PMID:9632640
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/C2014-0-02189-2
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/SET_domain#Structure