User:Ashley Crotteau/Sandbox1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
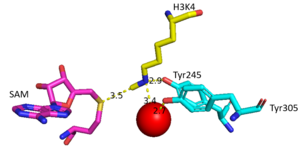
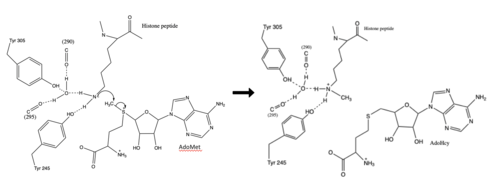
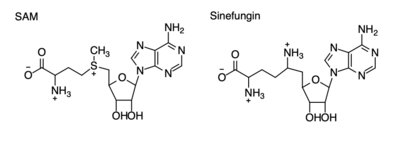
| - | Histones are a family of proteins that condense DNA into chromatin, and is an octamer composed of two of each protein core; H2A, H2B, H3, and H4. Histones are a globular protein, that often have N- or C-terminal tails. These tails can often be subjected to modifications by enzymes. Methylation of histones is one of the four common histone modifications. | + | Histones are a family of proteins that condense DNA into chromatin, and is an octamer composed of two of each protein core; H2A, H2B, H3, and H4. Histones are a globular protein, that often have N- or C-terminal tails. These tails can often be subjected to modifications by enzymes. Methylation of histones is one of the four common histone modifications. [[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Histone]] Methylation is most common on long tails of H3 and H4 due to the tail being able to enter the active site.<ref name ="DesJarlais" /> A histone can be mono-, di-, or tri- methylated. Once the histone is methylated, the DNA goes from tightly bound heterochromatin to loosely packed euchromatin. The euchromatin allows RNA pol II to bind to the DNA and start transcription. <ref name="Marino" /> Histone methylation is also a major epigenetic marker, which can be passed down from generation to generation. A epigenetic marker affects the way that genes are expressed, and can either activate or repress DNA. Histone methylation is a major epigenetic marker because it has the ability to change heterochromatin to euchromatin, and vise versa. Alterations in markers have been associated with many diseases.<ref name="Xiao" /> Lysine Methyltrasferase SET7/9 (KMT) is an enzyme that methylates the histone 3 lysine 4 (H3K4) and plays a important role in the transcription of DNA in H. sapiens.(source) It is composed of 259 residues and is a monomer containing a SET domain. There is a two-domain architecture containing a conserved anti-parallel β-barrel and an unusual knot-like structure that creates the active site. It also contains a cofactor that plays a role in the active site.The methylation of H3K4 results in transcriptional activation.<ref name="Biterge" /> The specific methylation of H3K4 does not result in a change in charge because it is a nonpolar group being added to the lysine. A change in charge could result in tighter bound heterochromatin. |
Revision as of 15:30, 12 April 2019
H. sapiens Lysine Methyltransferase, SET 7/9
| |||||||||||
References
[3] [8] [5] [6] [7] [9] [10] [11] [1] [2] [4]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 DesJarlais R, Tummino PJ. Role of Histone-Modifying Enzymes and Their Complexes in Regulation of Chromatin Biology. Biochemistry. 2016 Mar 22;55(11):1584-99. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.5b01210. Epub , 2016 Jan 26. PMID:26745824 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.5b01210
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Marino-Ramirez L, Kann MG, Shoemaker BA, Landsman D. Histone structure and nucleosome stability. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2005 Oct;2(5):719-29. PMID:16209651 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1586/14789450.2.5.719
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 3.7 3.8 3.9 Xiao B, Jing C, Wilson JR, Walker PA, Vasisht N, Kelly G, Howell S, Taylor IA, Blackburn GM, Gamblin SJ. Structure and catalytic mechanism of the human histone methyltransferase SET7/9. Nature. 2003 Feb 6;421(6923):652-6. Epub 2003 Jan 22. PMID:12540855 doi:10.1038/nature01378
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.15406/mojcsr.2016.03.00047
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 5.6 Schubert HL, Blumenthal RM, Cheng X. Many paths to methyltransfer: a chronicle of convergence. Trends Biochem Sci. 2003 Jun;28(6):329-35. PMID:12826405
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 Yeates TO. Structures of SET domain proteins: protein lysine methyltransferases make their mark. Cell. 2002 Oct 4;111(1):5-7. PMID:12372294
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Huang S, Shao G, Liu L. The PR domain of the Rb-binding zinc finger protein RIZ1 is a protein binding interface and is related to the SET domain functioning in chromatin-mediated gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1998 Jun 26;273(26):15933-9. PMID:9632640
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/C2014-0-02189-2
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 9.4 9.5 Del Rizzo PA, Couture JF, Dirk LM, Strunk BS, Roiko MS, Brunzelle JS, Houtz RL, Trievel RC. SET7/9 catalytic mutants reveal the role of active site water molecules in lysine multiple methylation. J Biol Chem. 2010 Oct 8;285(41):31849-58. Epub 2010 Aug 1. PMID:20675860 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.114587
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 10.3 10.4 Sun G, Reddy MA, Yuan H, Lanting L, Kato M, Natarajan R. Epigenetic histone methylation modulates fibrotic gene expression. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2010 Dec;21(12):2069-80. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2010060633. Epub 2010, Oct 7. PMID:20930066 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2010060633
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Tian X, Zhang S, Liu HM, Zhang YB, Blair CA, Mercola D, Sassone-Corsi P, Zi X. Histone lysine-specific methyltransferases and demethylases in carcinogenesis: new targets for cancer therapy and prevention. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2013 Jun;13(5):558-79. doi:, 10.2174/1568009611313050007. PMID:23713993 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.2174/1568009611313050007
Student Contributors
Ashley Crotteau
Parker Hiday
Lauren Allman