Serine/threonine protein kinase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
==Structure of Anticancer Ruthenium Half-Sandwich Complex Bound to Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3ß <ref>DOI 10.1007/s00775-010-0699-x</ref>== | ==Structure of Anticancer Ruthenium Half-Sandwich Complex Bound to Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3ß <ref>DOI 10.1007/s00775-010-0699-x</ref>== | ||
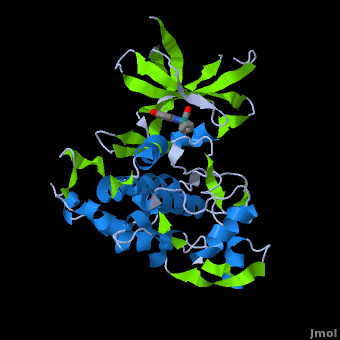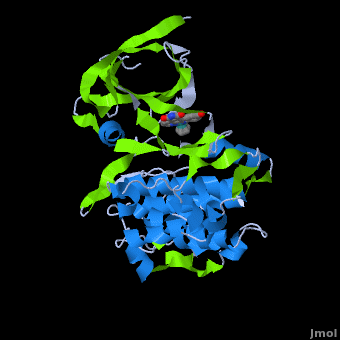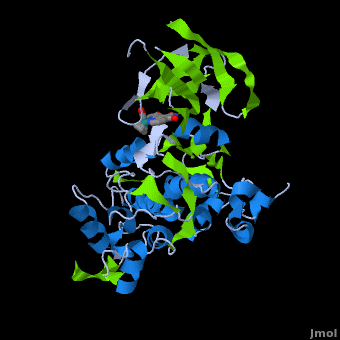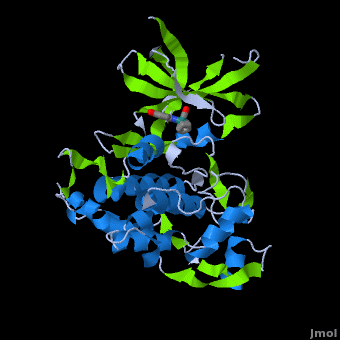
A crystal structure of an <scene name='Journal:JBIC:2/Half_sandwich_complex_no_bonds/1'>organometallic half-sandwich ruthenium complex </scene>bound to the protein kinase glycogen synthase kinase 3ß (GSK-3ß) has been determined and reveals that the inhibitor binds to the <scene name='Journal:JBIC:2/Atp_binding_site2/2'>ATP binding site</scene> via an induced fit mechanism utlizing several <scene name='Journal:JBIC:2/Half_sandwich_complex/3'>hydrogen bonds</scene> and <scene name='Journal:JBIC:2/Half_sandwich_hydrophobic_stic/1'>hydrophobic interactions</scene>. Importantly, the metal is not involved in any direct interaction with the protein kinase but fulfills a purely structural role. The unique, bulky molecular structure of the half-sandwich complex with the CO-ligand oriented perpendicular to the pyridocarbazole heterocycle allows the complex to stretch the whole distance <scene name='Journal:JBIC:2/Half_sandwich_hydrophobic/5'>sandwiched between the faces of the N- and C-terminal lobes</scene> and to interact tightly with <scene name='Journal:JBIC:2/Glycine_rich_loop2/4'>the flexible glycine-rich loop</scene>. Although this complex is a conventional ATP-competitive binder, the unique shape of the complex allows novel interactions with the glycine-rich loop which are crucial for binding potency and selectivity. It can be hypothesized that coordination spheres which present other ligands towards the glycine-rich loop might display completely different protein kinase selectivities. | A crystal structure of an <scene name='Journal:JBIC:2/Half_sandwich_complex_no_bonds/1'>organometallic half-sandwich ruthenium complex </scene>bound to the protein kinase glycogen synthase kinase 3ß (GSK-3ß) has been determined and reveals that the inhibitor binds to the <scene name='Journal:JBIC:2/Atp_binding_site2/2'>ATP binding site</scene> via an induced fit mechanism utlizing several <scene name='Journal:JBIC:2/Half_sandwich_complex/3'>hydrogen bonds</scene> and <scene name='Journal:JBIC:2/Half_sandwich_hydrophobic_stic/1'>hydrophobic interactions</scene>. Importantly, the metal is not involved in any direct interaction with the protein kinase but fulfills a purely structural role. The unique, bulky molecular structure of the half-sandwich complex with the CO-ligand oriented perpendicular to the pyridocarbazole heterocycle allows the complex to stretch the whole distance <scene name='Journal:JBIC:2/Half_sandwich_hydrophobic/5'>sandwiched between the faces of the N- and C-terminal lobes</scene> and to interact tightly with <scene name='Journal:JBIC:2/Glycine_rich_loop2/4'>the flexible glycine-rich loop</scene>. Although this complex is a conventional ATP-competitive binder, the unique shape of the complex allows novel interactions with the glycine-rich loop which are crucial for binding potency and selectivity. It can be hypothesized that coordination spheres which present other ligands towards the glycine-rich loop might display completely different protein kinase selectivities. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==3D structures of serine/threonine protein kinase== | ||
| + | [[Serine/threonine protein kinase 3D structures]] | ||
| + | |||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
| Line 224: | Line 228: | ||
**[[5l2q]] – hChk40 kinase homology domain<br /> | **[[5l2q]] – hChk40 kinase homology domain<br /> | ||
| - | *'''Rac-α hChk'''; domains: pleckstrin homology 1-123; kinase 144-480 | + | *'''Rac-α hChk (AKT1)'''; domains: pleckstrin homology 1-123; kinase 144-480 |
**[[1unp]], [[1unr]] – hRac-α hChk pleckstrin homology domain <br /> | **[[1unp]], [[1unr]] – hRac-α hChk pleckstrin homology domain <br /> | ||
**[[2uzr]], [[2uzs]] – hRac-α hChk pleckstrin homology domain (mutant) <br /> | **[[2uzr]], [[2uzs]] – hRac-α hChk pleckstrin homology domain (mutant) <br /> | ||
**[[1h10]], [[1unq]], [[2uvm]] – hRac-α hChk pleckstrin homology domain + inositol tetrakisphosphate<br /> | **[[1h10]], [[1unq]], [[2uvm]] – hRac-α hChk pleckstrin homology domain + inositol tetrakisphosphate<br /> | ||
| - | **[[ | + | **[[3o96]], [[4ejn]], [[6s9w]], [[6s9x]], [[6hhj]], [[6hhi]], [[6hhh]], [[6hhg]], [[6hhf]] - hRac-α hChk pleckstrin homology+kinase domains + inhibitor<br /> |
| - | **[[ | + | **[[5kcv]] - hRac-α hChk (mutant) + inhibitor<br /> |
| - | **[[ | + | **[[4gv1]], [[4ekl]] - hRac-α hChk kinase domain + inhibitor<br /> |
| - | **[[ | + | **[[3qkm]], [[6ccy]] - hRac-α hChk kinase domain (mutant) + inhibitor<br /> |
| + | **[[6npz]], [[6buu]] - hRac-α hChk kinase domain + bisubstrate peptide<br /> | ||
**[[4ekk]] - hRac-α hChk kinase domain (mutant) + glycogen synthase kinase-3 peptide + AMPPNP<br /> | **[[4ekk]] - hRac-α hChk kinase domain (mutant) + glycogen synthase kinase-3 peptide + AMPPNP<br /> | ||
**[[6npz]] - hRac-α hChk kinase domain + peptide + inhibitor<br /> | **[[6npz]] - hRac-α hChk kinase domain + peptide + inhibitor<br /> | ||
| Line 255: | Line 260: | ||
**[[1wxm]] – hA-Raf RAS-binding domain - NMR<br /> | **[[1wxm]] – hA-Raf RAS-binding domain - NMR<br /> | ||
| - | *'''B-Raf'''; domains - Ras-binding 153-237; kinase 445-723 | + | *'''B-Raf'''; domains - BRS 38-116; Ras-binding 153-237; kinase 445-723 |
**[[1uwh]], [[3c4c]] – hB-Raf kinase domain + anticancer drug<br /> | **[[1uwh]], [[3c4c]] – hB-Raf kinase domain + anticancer drug<br /> | ||
**[[1uwj]] – hB-Raf kinase domain (mutant) + anticancer drug<br /> | **[[1uwj]] – hB-Raf kinase domain (mutant) + anticancer drug<br /> | ||
**[[2fb8]], [[3d4q]], [[3ii5]], [[3psd]], [[3skc]], [[3tv6]], [[4g9c]], [[4ksp]], [[4ksq]], [[3psb]], [[3ppj]], [[3ppk]], [[3prf]], [[3pri]], [[3tv4]], [[4dbn]], [[4e4x]], [[4mbj]], [[4ehe]], [[3q4c]], [[3q96]], [[3e26]], [[4h58]], [[4e26]], [[4fc0]], [[4pp7]], [[6cad]] – hB-Raf kinase domain + pyrazole inhibitor<br /> | **[[2fb8]], [[3d4q]], [[3ii5]], [[3psd]], [[3skc]], [[3tv6]], [[4g9c]], [[4ksp]], [[4ksq]], [[3psb]], [[3ppj]], [[3ppk]], [[3prf]], [[3pri]], [[3tv4]], [[4dbn]], [[4e4x]], [[4mbj]], [[4ehe]], [[3q4c]], [[3q96]], [[3e26]], [[4h58]], [[4e26]], [[4fc0]], [[4pp7]], [[6cad]] – hB-Raf kinase domain + pyrazole inhibitor<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4jvg]], [[4ehg]], [[4fk3]], [[3idp]], [[4g9r]], [[4wo5]], [[4mnf]], [[4r5y]], [[4rzv]], [[4rzw]], [[4xv1]], [[4xv2]], [[4xv3]], [[4xv9]], [[4yht]], [[5c9c]], [[5hi2]], [[5ita]], [[5jrq]], [[5jsm]], [[5jt2]] – hB-Raf kinase domain (mutant) + pyrazole inhibitor<br /> | + | **[[4jvg]], [[4ehg]], [[4fk3]], [[3idp]], [[4g9r]], [[4wo5]], [[4mnf]], [[4r5y]], [[4rzv]], [[4rzw]], [[4xv1]], [[4xv2]], [[4xv3]], [[4xv9]], [[4yht]], [[5c9c]], [[5hi2]], [[5ita]], [[5jrq]], [[5jsm]], [[5jt2]], [[6nsq]] – hB-Raf kinase domain (mutant) + pyrazole inhibitor<br /> |
| - | **[[5csw]], [[5csx]], [[5ct7]], [[5fd2]], [[5hid]], [[5hie]], [[5val]], [[5vam]], [[6b8u]] - hB-Raf kinase domain + inhibitor<br /> | + | **[[5csw]], [[5csx]], [[5ct7]], [[5fd2]], [[5hid]], [[5hie]], [[5val]], [[5vam]], [[6b8u]], [[6n0q]], [[6n0p]] - hB-Raf kinase domain + inhibitor<br /> |
**[[4mne]] – hB-Raf kinase domain + MAPKK1<br /> | **[[4mne]] – hB-Raf kinase domain + MAPKK1<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6u2h]] – hB-Raf kinase domain + 14-3-3 ζ/δ<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6pp9]] – hB-Raf kinase domain + MEK1 + ANP<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6u2g]] – hB-Raf kinase domain + MEK1 + AMPPCP<br /> | ||
| + | **[[5vr3]] – hB-Raf BRS domain <br /> | ||
**[[2l05]], [[5j17]], [[5j2r]] – hB-Raf RAS-binding domain - NMR<br /> | **[[2l05]], [[5j17]], [[5j2r]] – hB-Raf RAS-binding domain - NMR<br /> | ||
**[[3ny5]] – hB-Raf RAS-binding domain <br /> | **[[3ny5]] – hB-Raf RAS-binding domain <br /> | ||
**[[5j18]] – hB-Raf RAS-binding domain + inhibitor - NMR<br /> | **[[5j18]] – hB-Raf RAS-binding domain + inhibitor - NMR<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6uan]], [[6q0k]] – hB-Raf + 14-3-3 ζ – Cryo EM<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6nyb]] – hB-Raf + 14-3-3 ζ + MEK1 – Cryo EM<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6q0t]], [[6q0j]] – hB-Raf (mutant) + 14-3-3 ζ + MEK1 – Cryo EM<br /> | ||
*'''c-Raf''' | *'''c-Raf''' | ||
Revision as of 09:16, 4 December 2019
| |||||||||||
3D structures of serine/threonine protein kinase
Updated on 04-December-2019
References
- ↑ Bartek J, Lukas J. Chk1 and Chk2 kinases in checkpoint control and cancer. Cancer Cell. 2003 May;3(5):421-9. PMID:12781359
- ↑ Ducat D, Zheng Y. Aurora kinases in spindle assembly and chromosome segregation. Exp Cell Res. 2004 Nov 15;301(1):60-7. PMID:15501446 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2004.08.016
- ↑ Takai N, Hamanaka R, Yoshimatsu J, Miyakawa I. Polo-like kinases (Plks) and cancer. Oncogene. 2005 Jan 10;24(2):287-91. PMID:15640844 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208272
- ↑ Dummler B, Ohshiro K, Kumar R, Field J. Pak protein kinases and their role in cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2009 Jun;28(1-2):51-63. doi: 10.1007/s10555-008-9168-1. PMID:19165420 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10555-008-9168-1
- ↑ Forde JE, Dale TC. Glycogen synthase kinase 3: a key regulator of cellular fate. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2007 Aug;64(15):1930-44. PMID:17530463 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00018-007-7045-7
- ↑ Brose MS, Volpe P, Feldman M, Kumar M, Rishi I, Gerrero R, Einhorn E, Herlyn M, Minna J, Nicholson A, Roth JA, Albelda SM, Davies H, Cox C, Brignell G, Stephens P, Futreal PA, Wooster R, Stratton MR, Weber BL. BRAF and RAS mutations in human lung cancer and melanoma. Cancer Res. 2002 Dec 1;62(23):6997-7000. PMID:12460918
- ↑ Antony R, Emery CM, Sawyer AM, Garraway LA. C-RAF mutations confer resistance to RAF inhibitors. Cancer Res. 2013 Aug 1;73(15):4840-51. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-4089. Epub, 2013 Jun 4. PMID:23737487 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-4089
- ↑ Laplante M, Sabatini DM. mTOR signaling in growth control and disease. Cell. 2012 Apr 13;149(2):274-93. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.03.017. PMID:22500797 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2012.03.017
- ↑ Ravindran R, Loebbermann J, Nakaya HI, Khan N, Ma H, Gama L, Machiah DK, Lawson B, Hakimpour P, Wang YC, Li S, Sharma P, Kaufman RJ, Martinez J, Pulendran B. The amino acid sensor GCN2 controls gut inflammation by inhibiting inflammasome activation. Nature. 2016 Mar 24;531(7595):523-7. doi: 10.1038/nature17186. Epub 2016 Mar 16. PMID:26982722 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature17186
- ↑ Atilla-Gokcumen GE, Di Costanzo L, Meggers E. Structure of anticancer ruthenium half-sandwich complex bound to glycogen synthase kinase 3beta. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2010 Sep 7. PMID:20821241 doi:10.1007/s00775-010-0699-x