User:Daniel Mulawa/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
< User:Daniel Mulawa(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
='''Gamma Secretase'''= | ='''Gamma Secretase'''= | ||
| - | + | <StructureSection load='5FN2' size='350' frame='true' side='right' caption='Human Gamma Secretase Basic Structure.' scene=’’> | |
| - | <StructureSection load=' | + | |
=Gamma Secretase= | =Gamma Secretase= | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
Anterior pharynx-defective 1 (APH-1) serves as a scaffold for anchoring and supporting the flexible conformational changes of PS1 | Anterior pharynx-defective 1 (APH-1) serves as a scaffold for anchoring and supporting the flexible conformational changes of PS1 | ||
Activation of the active site is dependent on the binding of Presenilin enhancer 2 (PEN-2). PEN-2 is also important in maturation of the enzyme. | Activation of the active site is dependent on the binding of Presenilin enhancer 2 (PEN-2). PEN-2 is also important in maturation of the enzyme. | ||
| - | |||
| - | [[Image:Ribbon structure of whole.png|350 px|right|thumb|Figure 1]] | ||
| - | [http://http://proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/5a63 5A63 Article] | ||
| - | ===practice=== | ||
| - | |||
| - | <scene name='83/837256/Practice_scene_1/2'>practice 2</scene> | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| Line 33: | Line 25: | ||
===Active Site=== | ===Active Site=== | ||
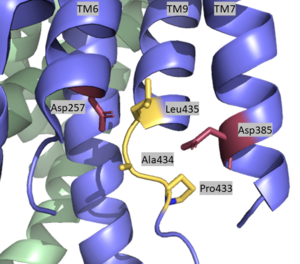
| - | The active site is located between TM6 and TM7 of the PS1 subunit, which is mainly hydrophilic and disordered. Each of these transmembrane helices has an aspartate residue, | + | [[Image:Asp with Pal labeled.png|300 px|right|thumb|Active Site of Gamma Secretase]] |
| + | The <scene name='83/832945/Active_site/1'>active site</scene> is located between TM6 and TM7 of the PS1 subunit, which is mainly hydrophilic and disordered. Each of these transmembrane helices has an aspartate residue, <scene name='83/832945/Asp_257_and_asp_385/1'>Asp 257 and Asp 385</scene>, which are located approximately 10.6 A˚ apart when inactive.<ref name="Bai">PMID:26280335</ref> The PAL sequence of <scene name='83/832945/Pal_sequence/1'>Pro433, Ala434, and Leu435</scene> is in close proximity with the catalytic aspartates and is important to substrate recognition. Gamma secretase becomes active upon substrate binding, when TM2 and TM6 each rotate about 15 degrees to more closely associate and the two Asp residues hydrogen bond to each other during catalysis. Asp257 and Asp385 are located 6–7 Å away from the scissile peptide bond of the substrate. | ||
| + | |||
==Relevance== | ==Relevance== | ||
| Line 43: | Line 37: | ||
Important to look at differences between substrates | Important to look at differences between substrates | ||
| - | |||
| + | </StructureSection> | ||
| - | </StructureSection> | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
| - | 1.Bai X, Yan C, Guanghui Yang, et al. 2015. An atomic structure of human γ-secretase. Nature. 525:212-217. | ||
| - | 2.Carroll CM, and Li YM. 2016. Physiological and pathological roles of the γ-secretase complex. Brain research bulletin. 126:199-206. | ||
| - | 3.Yang G, Zhou R, Shi Y. 2017. Cryo-EM structures of human γ-secretase. Current Opinion in Structural Biology. 46:55–64. | ||
| - | 4.Yang G, Zhou R, Zhou Q, et al. 2019. Structural basis of Notch recognition by human γ-secretase. Nature. 565: 192-197. | ||
| - | 5.Zhou R, Yang G, Guo X, et al. 2019. Recognition of the amyloid precursor protein by human γ-secretase. Science. 363:1-8. | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
==Student Contributors== | ==Student Contributors== | ||
Layla Wisser | Layla Wisser | ||
| + | |||
Daniel Mulawa | Daniel Mulawa | ||
Current revision
Gamma Secretase
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Bai XC, Yan C, Yang G, Lu P, Ma D, Sun L, Zhou R, Scheres SH, Shi Y. An atomic structure of human gamma-secretase. Nature. 2015 Aug 17. doi: 10.1038/nature14892. PMID:26280335 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature14892
Student Contributors
Layla Wisser
Daniel Mulawa