From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
proteopedia linkproteopedia link
|
|
| Line 33: |
Line 33: |
| | == General Transcription Factors == | | == General Transcription Factors == |
| | | | |
| - | In both eukaryotes and prokaryotes, the basic mechanism for initiating transcription is the same: protein factors selectively bind to promoter regions on DNA. Prokaryotes use sigma factors while eukaryotes use a complex of 6 general transcription factors(GTFs). The combination of all the transcription factors bound to the DNA promoter region, in complex with RNAP II, is known as the pre-initiation complex. The formation of the PIC occurs in an ordered pathway, beginning with the TATA box which is a promoter region on DNA at position -27. | + | In both eukaryotes and prokaryotes, the basic mechanism for initiating transcription is the same: protein factors selectively bind to promoter regions on DNA. Prokaryotes use sigma factors while eukaryotes use a complex of 6 general transcription factors(GTFs). The combination of all the transcription factors bound to the DNA promoter region, in complex with RNAP II, is known as the preinitiation complex. This complex is necessary for an accurate initiation. The formation of the PIC occurs in an ordered pathway, beginning with the TATA box which is a promoter region on DNA at position -27. |
| | | | |
| | Process of PIC formation: | | Process of PIC formation: |
| | | | |
| - | 1. <scene name='82/824648/Tfiid-tbp/3'>TFIID</scene> contains a subunit named the TATA-binding protein (TBP), which recognizes and binds to the TATA box on the DNA promoter. | + | Source: https://www.pnas.org/content/94/1/151. <scene name='82/824648/Tfiid-tbp/3'>TFIID</scene> is highly conserved among eukaryotes. It recognizes and binds the TATA box. This is facillitated by a subunit named the TATA-binding protein (TBP). This subunit also causes slight deformations in the helix which may be important for further binding of the PIC units. |
| | | | |
| - | 2. <scene name='82/824648/Tfiib/3'>TFIIB</scene> and <scene name='82/824648/Tfiia/3'>TFIIA</scene> and interact with TBP and are recruted to the promoter. | + | 2. <scene name='82/824648/Tfiib/3'>TFIIB</scene> and <scene name='82/824648/Tfiia/3'>TFIIA</scene> and interact with TBP and are recruited to the promoter. |
| | | | |
| | 3. <scene name='82/824648/Tfiif/5'>TFIIF</scene> binds directly to RNAP II and escorts it to the promoter while TFIIB helps the complex bind correctly. | | 3. <scene name='82/824648/Tfiif/5'>TFIIF</scene> binds directly to RNAP II and escorts it to the promoter while TFIIB helps the complex bind correctly. |
Revision as of 02:33, 22 September 2020
|
Introduction
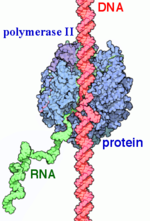 RNAP II transcription process.
RNA polymerase II (RNAP II) is an enzyme that transcribes protein-encoding genes, and it therefore is responsible for the synthesis of mRNA. There are three RNA polymerase enzymes found in eukaryotic nuclei but RNAP II is the most studied. RNAP II is a 550 kDa multi-protein complex that includes 12 subunits. Several transcription factors are used to bind promoters upstream of the start site and are necessary for joining RNAP II and DNA. Bound RNAP II transcribes DNA into a strand of messenger RNA. Messenger RNA (mRNA) is a single stranded RNA molecule that is complementary to the template strand of DNA. The mRNA stand transports genetic information from DNA to the ribosome, where it is used to specify the amino acid sequence for the production of proteins.
Structural Components
This section will briefly discuss the chief structural components involved in the mechanism.
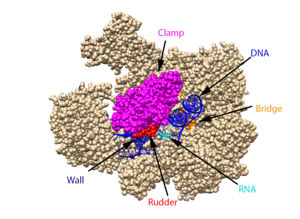 The clamp (magenta), wall (navy blue), rudder (red), bridge (orange), RNA (light blue), and DNA (blue) are depicted. See below for PDB's and residue numbers. To begin, the swings to trap the DNA in the cleft. Further along, the sends the DNA template through the cleft in approximately a 90° turn. Both the clamp and wall are parts of the Rpb2 subunit. Further along in the process, the separates the newly synthesized RNA strand from the DNA template. The DNA reforms into a double helix as it leaves RNA pol II.
Other components of RNA pol II include the following:
The jaw is the opening through which DNA enters. The funnel is what the NTP’s travel through to be incorporated into the growing RNA strand, and the pore is the end of the funnel. The is an Rpb1 segment that translocates the DNA-RNA complex at the end of each cycle of catalysis. is located within the active site and functions as the catalyst.
Transcription
Transcription can largely be divided into three sections: initiation, elongation, and termination. In the process of initiation, RNAP II recruits several general transcription factors (GTFs) to bind to the promoter region of the DNA, and this eventually forms the preinitiation complex (PIC). The DNA enters RNAP II through the clamp, and then it is unwound, creating a transcription bubble. With the DNA unwound, the active site of RNAP II catalyzes the synthesis of the first few RNA bonds. Once the carboxy-terminal domain (CTD) becomes phosphorylated, the clamp undergoes a conformation change to effectively trap the DNA, and a few of the GTFs dissociate, which changes complex to the Elongator complex.
After initiation, the process of elongation begins with the entry of NTPs. These NTPs largely enter through the funnel, and this tends to be a slow process because the funnel is only 12 Å in diameter, meaning that only one NTP can go through at a time. Once they have passed through the funnel, the NTPs enter which contains an Mg ion that is bound by three aspartate residues at positions D739, D741, and D743. If the NTP is complementary to the DNA strand, it is loaded onto the insertion site next to the RNA and held in place by the bridge. While in this insertion site, the metal ion and aspartate residues catalyze the reaction that forms a phosphodiester bond between the 3’ end of the RNA and the 5’ end of the NTP. This step then leads into a translocation step. To make room for the next NTP, there is a Brownian ratchet mechanism in which the nearby trigger loop undergoes a conformation change that causes the bridge to move to the next transition site. During the bridge’s transition, the DNA-RNA hybrid is partially help in place by the -amanitin. Once the bridge is in the new initiation site, the trigger loop returns to its original conformation, allowing the process to begin again.
In the termination stage, the CTD becomes dephosphorylated, which acts as a signal to dissociate the elongation complex. Once this signal is received, the new mRNA is released from RNP II through the rudder. Before being released, its 3’ end is polyadenylated. The DNA is brought back together at the other end of the transcription bubble, returning it to its original double-stranded form. Finally, RNAP II and the remaining GTFs dissociate from the DNA.
α-Amanitin
α-Amanitin is a bicyclic octapeptide that adheres tightly with RNAP II, which blocks the elongation steps. α-amanitin binds in the funnel and interacts with the bridge helix and adjacent Rpb1, but it does not inhibit the RNA pol II’s interaction with NTP. Instead, α-amanitin likely challenges the bridge’s conformational change that is necessary for the purposed RNAP translocation step. α-Amanitin, found in the poisonous mushroom death cap, leads to death after several days. This time frame aligns with the rate at which mRNA’s and proteins turnover.
 The chemical structure of α-amanitin.
General Transcription Factors
In both eukaryotes and prokaryotes, the basic mechanism for initiating transcription is the same: protein factors selectively bind to promoter regions on DNA. Prokaryotes use sigma factors while eukaryotes use a complex of 6 general transcription factors(GTFs). The combination of all the transcription factors bound to the DNA promoter region, in complex with RNAP II, is known as the preinitiation complex. This complex is necessary for an accurate initiation. The formation of the PIC occurs in an ordered pathway, beginning with the TATA box which is a promoter region on DNA at position -27.
Process of PIC formation:
Source: https://www.pnas.org/content/94/1/151. is highly conserved among eukaryotes. It recognizes and binds the TATA box. This is facillitated by a subunit named the TATA-binding protein (TBP). This subunit also causes slight deformations in the helix which may be important for further binding of the PIC units.
2. and and interact with TBP and are recruited to the promoter.
3. binds directly to RNAP II and escorts it to the promoter while TFIIB helps the complex bind correctly.
4. and are sequentually recruited which completes the .
Once the is formed, initiates RNA synthesis and produces a short transcript. When RNAP II becomes phosphorylated, it releases some of the GTFs from the complex and moves away from the promoter. TFIID stays bound to the promoter and can reinitiate transcription. The transcription factors are replaced by a new six-protein complex call the Elongator. TFIIF and TFIIH both remain associated with RNAP II during elongation.
|
References
Bushnell, D. A.; Westover, K. D.; Davis, R. E.; Kornberg, R. D. Structural Basis of Transcription: An RNA Polymerase II-TFIIB Cocrystal at 4.5 Angstroms. Science. 2004, 303, 983-988
Brueckner, F. and Cramer, P. Structural Basis of Transcription Inhibition by -amanitin and Implications for RNA Polymerase II Translocation. Nature Structure and Molecular Biology. 2008, 15, 811-818.
Cramer, P.; Bushnell, D. A.; Kornberg, R. D. Structural Basis of Transcription: RNA Polymerase II at 2.8 Ångstrom Resolution. Science. 2001, 292, 1863-1876
Evans, D. A.; Fitch, D. M.; Smith, T. E.; Cee, V. J. Application of Complex Aldol Reactions to the Total Synthesis of Phorboxazole B. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 10033-10046.
Gnatt, A. L.; Cramer, P; Fu, J.; Bushnell, D. A.; and Kornberg, R. D. Structural Basis of Transcription: An RNA Polymerase II Elongation Complex at 3.3 Å Resolution. Science. 2001, 292, 1876-1882 1i6h
Hahn, S. Structure and Mechanism of the RNA Polymerase II Transcription Machinery. Nature Structure and Molecular Biology. 2004, 11, 394-403.
He, Yuan, et al. Near-atomic resolution visualization of human transcription promoter opening. Nature 533.7603. 2016.
Nudler, E. RNA Polymerase Active Center: The Molecular Engine of Transcription. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2009, 78, 335-361.
Orphanides, George, Thierry Lagrange, and Danny Reinberg. The general transcription factors of RNA polymerase II. Genes & development 10.21. 1996. 2657-2683
Shah, N. et. al. Tyrosine-1 of RNA Polymerase II CTD Controls Global Termination of Gene Transcription in Mammals. Molecular Cell. 2018, 69, 48-61.
Uzman, A.; Voet, D. Student companion Fundamentals of biochemistry: life at the molecular level, 4th ed., Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. Pratt; John Wiley & amp; Sons, 2012.
Xu, J.; Lahiri, I.; Wang, W.; Wier, A.; Cianfrocco, M. A.; Chong, J.; Hare, A. A.; Dervan, P. B.; DiMaio, F.; Leschziner, A. E.; Wang, D. Structural Basis for the Initiation of Eukaryotic Transcription-coupled DNA Repair. Nature. 2017. 551, 653-657 5vvr
Xin, L.; Bushnell, D. A.; and Kornburg, R. D. RNA Polymerase II Transcription: Structure and Mechanism. Biochemica et Biophysica Acta. 2013, 1829, 2-8.
Yan, C., Dodd, T., He, Y., Tainer, J. A., Tsutakawa, S. E., & Ivanov, I. (2019). Transcription preinitiation complex structure and dynamics provide insight into genetic diseases. Nature Structural and Molecular Biology, 26(6), 397-406.
Alpha-aminitin chemical structure image courtesy of https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alpha-Amanitin#/media/File:Alpha-amanitin_structure.png
Notes
From structural components:
Structural overview: [PDB: 5VVR: with highlighted sections mentioned below]
Bridge: Depicted: [PDB: 1I6H: 810-845.a]
Wall: Depicted: [PDB: 1R5U: 853-919.b; 933-972.b]
Clamp: Depicted: [PDB: 1R5U: 3-345.a; 1395-1435.a; 1158-1124.b]
Rudder: Depicted: [PDB: 5VVR: 306-321.a]
Content Donators
This page was created as a final project for the Advanced Biochemistry course at Wabash College during the Fall of 2019. This page was reviewed by Dr. Wally Novak of Wabash College.



