User:Neal Hayhurst/RNA Polymerase II/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
=== Pre-Initiation Complex === | === Pre-Initiation Complex === | ||
| - | In both eukaryotes and prokaryotes, the basic mechanism for initiating transcription is the same: protein factors selectively bind to promoter regions on DNA <ref name="L">Orphanides, George, Thierry Lagrange, and Danny Reinberg. The general transcription factors of RNA polymerase II. Genes & development 10.21. 1996. 2657-2683</ref> | + | In both eukaryotes and prokaryotes, the basic mechanism for initiating transcription is the same: protein factors selectively bind to promoter regions on DNA <ref name="L">Orphanides, George, Thierry Lagrange, and Danny Reinberg. The general transcription factors of RNA polymerase II. Genes & development 10.21. 1996. 2657-2683</ref><ref name="N">Xin, L.; Bushnell, D. A.; and Kornburg, R. D. RNA Polymerase II Transcription: Structure and Mechanism. Biochemica et Biophysica Acta. 2013, 1829, 2-8. |
| + | </ref>. Prokaryotes use sigma factors while eukaryotes use a complex of 6 general transcription factors (GTFs). These GTFs are all named similarly and begin with TF, for transcription factor, followed by the Roman numeral II since they are involved in transcription by RNAP II. The combination of all the transcription factors bound to the DNA promoter region, in complex with RNAP II, is called the pre-initiation complex (PIC)<ref name="L">Orphanides, George, Thierry Lagrange, and Danny Reinberg. The general transcription factors of RNA polymerase II. Genes & development 10.21. 1996. 2657-2683</ref><ref name="N">Xin, L.; Bushnell, D. A.; and Kornburg, R. D. RNA Polymerase II Transcription: Structure and Mechanism. Biochemica et Biophysica Acta. 2013, 1829, 2-8. | ||
| + | </ref>. The formation of the PIC occurs in an ordered pathway, beginning with the upstream -35 promoter region, the -10 promoter region, and the transcription start site (TSS)<ref name="P">Chang-Hui Shen; Diagnostic Molecular Biology, 2019</ref> . | ||
Process of PIC formation<ref name="L">Orphanides, George, Thierry Lagrange, and Danny Reinberg. The general transcription factors of RNA polymerase II. Genes & development 10.21. 1996. 2657-2683</ref><ref name="K">He, Yuan, et al. Near-atomic resolution visualization of human transcription promoter opening. Nature 533.7603. 2016.</ref>: | Process of PIC formation<ref name="L">Orphanides, George, Thierry Lagrange, and Danny Reinberg. The general transcription factors of RNA polymerase II. Genes & development 10.21. 1996. 2657-2683</ref><ref name="K">He, Yuan, et al. Near-atomic resolution visualization of human transcription promoter opening. Nature 533.7603. 2016.</ref>: | ||
Revision as of 01:31, 1 October 2020
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Young RA. RNA polymerase II. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:689-715. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.003353. PMID:1883205 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.003353
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Myer VE, Young RA. RNA polymerase II holoenzymes and subcomplexes. J Biol Chem. 1998 Oct 23;273(43):27757-60. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.43.27757. PMID:9774381 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.273.43.27757
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Sobennikova MV, Shematorova EK, Shpakovskii GV. [C-terminal domain (CTD) of the subunit Rpb1 of nuclear RNA polymerase II and its role in the transcription cycle]. Mol Biol (Mosk). 2007 May-Jun;41(3):433-49. PMID:17685222
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 RNA polymerase II transcription initiation: A structural view D. B. Nikolov, S. K. Burley Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences Jan 1997, 94 (1) 15-22; DOI: 10.1073/pnas.94.1.15
- ↑ Hurwitz J. The discovery of RNA polymerase. J Biol Chem. 2005 Dec 30;280(52):42477-85. doi: 10.1074/jbc.X500006200. Epub 2005, Oct 17. PMID:16230341 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.X500006200
- ↑ doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nrm1796
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 Orphanides, George, Thierry Lagrange, and Danny Reinberg. The general transcription factors of RNA polymerase II. Genes & development 10.21. 1996. 2657-2683
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Xin, L.; Bushnell, D. A.; and Kornburg, R. D. RNA Polymerase II Transcription: Structure and Mechanism. Biochemica et Biophysica Acta. 2013, 1829, 2-8.
- ↑ Chang-Hui Shen; Diagnostic Molecular Biology, 2019
- ↑ He, Yuan, et al. Near-atomic resolution visualization of human transcription promoter opening. Nature 533.7603. 2016.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2 11.3 11.4 11.5 11.6 11.7 11.8 Hahn, S. Structure and Mechanism of the RNA Polymerase II Transcription Machinery. Nature Structure and Molecular Biology. 2004, 11, 394-403.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 Eick, D, Geyer, M.The RNA Polymerase II Carboxy-Terminal Domain (CTD) Code. Chemical Reviews, 2013, 113 (11), 8456-8490 DOI: 10.1021/cr400071f
- ↑ Wang W, Carey M, Gralla JD. Polymerase II Promoter Activation: Closed Complex Formation and ATP-Driven Start Site Opening. Science. 1992;255:450–453.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 14.2 14.3 14.4 14.5 14.6 14.7 14.8 14.9 Voet, D., Voet, J. G., & Pratt, C. W. (2013). Transcription and RNA Processing. In Fundamentals of biochemistry: life at the molecular level (pp. 933–942). Wiley.
- ↑ Nudler, E. RNA Polymerase Active Center: The Molecular Engine of Transcription. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2009, 78, 335-361.
- ↑ Svetlov, V., & Nudler, E. (2013). Basic mechanism of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Biochimica et biophysica acta, 1829(1), 20–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagrm.2012.08.009
- ↑ Bar-Nahum G, Epshtein V, Ruckenstein AE, Rafikov R, Mustaev A, Nudler E. A ratchet mechanism of transcription elongation and its control. Cell. 2005 Jan 28;120(2):183-93. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2004.11.045. PMID:15680325 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2004.11.045
Bushnell, D. A.; Westover, K. D.; Davis, R. E.; Kornberg, R. D. Structural Basis of Transcription: An RNA Polymerase II-TFIIB Cocrystal at 4.5 Angstroms. Science. 2004, 303, 983-988
Brueckner, F. and Cramer, P. Structural Basis of Transcription Inhibition by -amanitin and Implications for RNA Polymerase II Translocation. Nature Structure and Molecular Biology. 2008, 15, 811-818.
Cramer, P.; Bushnell, D. A.; Kornberg, R. D. Structural Basis of Transcription: RNA Polymerase II at 2.8 Ångstrom Resolution. Science. 2001, 292, 1863-1876
Evans, D. A.; Fitch, D. M.; Smith, T. E.; Cee, V. J. Application of Complex Aldol Reactions to the Total Synthesis of Phorboxazole B. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 10033-10046.
Gnatt, A. L.; Cramer, P; Fu, J.; Bushnell, D. A.; and Kornberg, R. D. Structural Basis of Transcription: An RNA Polymerase II Elongation Complex at 3.3 Å Resolution. Science. 2001, 292, 1876-1882 1i6h
Hahn, S. Structure and Mechanism of the RNA Polymerase II Transcription Machinery. Nature Structure and Molecular Biology. 2004, 11, 394-403.
He, Yuan, et al. Near-atomic resolution visualization of human transcription promoter opening. Nature 533.7603. 2016.
Nudler, E. RNA Polymerase Active Center: The Molecular Engine of Transcription. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2009, 78, 335-361.
Orphanides, George, Thierry Lagrange, and Danny Reinberg. The general transcription factors of RNA polymerase II. Genes & development 10.21. 1996. 2657-2683
Shah, N. et. al. Tyrosine-1 of RNA Polymerase II CTD Controls Global Termination of Gene Transcription in Mammals. Molecular Cell. 2018, 69, 48-61.
Uzman, A.; Voet, D. Student companion Fundamentals of biochemistry: life at the molecular level, 4th ed., Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. Pratt; John Wiley & amp; Sons, 2012.
Xu, J.; Lahiri, I.; Wang, W.; Wier, A.; Cianfrocco, M. A.; Chong, J.; Hare, A. A.; Dervan, P. B.; DiMaio, F.; Leschziner, A. E.; Wang, D. Structural Basis for the Initiation of Eukaryotic Transcription-coupled DNA Repair. Nature. 2017. 551, 653-657 5vvr
Xin, L.; Bushnell, D. A.; and Kornburg, R. D. RNA Polymerase II Transcription: Structure and Mechanism. Biochemica et Biophysica Acta. 2013, 1829, 2-8.
Yan, C., Dodd, T., He, Y., Tainer, J. A., Tsutakawa, S. E., & Ivanov, I. (2019). Transcription preinitiation complex structure and dynamics provide insight into genetic diseases. Nature Structural and Molecular Biology, 26(6), 397-406.
Eick, D, Geyer, M.The RNA Polymerase II Carboxy-Terminal Domain (CTD) Code. Chemical Reviews, 2013, 113 (11), 8456-8490 DOI: 10.1021/cr400071f
Chang-Hui Shen; Diagnostic Molecular Biology, 2019
Alpha-aminitin chemical structure image courtesy of https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alpha-Amanitin#/media/File:Alpha-amanitin_structure.png
Notes
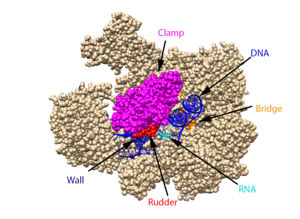
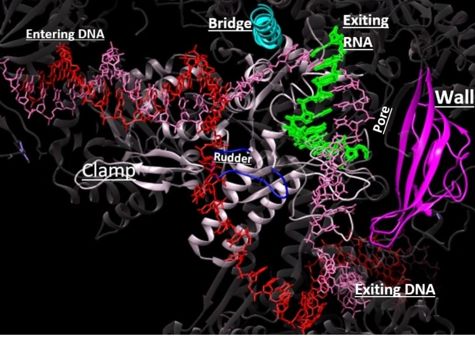
From structural components:
Structural overview: [PDB: 5VVR: with highlighted sections mentioned below]
Bridge: Depicted: [PDB: 1I6H: 810-845.a]
Wall: Depicted: [PDB: 1R5U: 853-919.b; 933-972.b]
Clamp: Depicted: [PDB: 1R5U: 3-345.a; 1395-1435.a; 1158-1124.b]
Rudder: Depicted: [PDB: 5VVR: 306-321.a]
Content Donators
This page was created as a final project for the Advanced Biochemistry course at Wabash College during the Fall of 2019 and Fall of 2020. This page was reviewed by Dr. Wally Novak of Wabash College.