User:Neal Hayhurst/RNA Polymerase II/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
| Line 85: | Line 85: | ||
Multiple kinetic models have been proposed with largely a consensus on some form of a Brownian ratchet mechanism involving the trigger loop and bridge helix in which the RNAPII has both forward and backward motion with a preference for forward translocation<ref>DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2004.11.045</ref><ref name="Mishanina" />. | Multiple kinetic models have been proposed with largely a consensus on some form of a Brownian ratchet mechanism involving the trigger loop and bridge helix in which the RNAPII has both forward and backward motion with a preference for forward translocation<ref>DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2004.11.045</ref><ref name="Mishanina" />. | ||
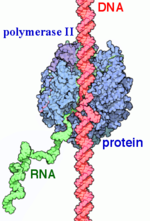
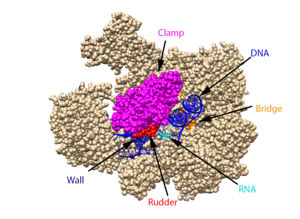
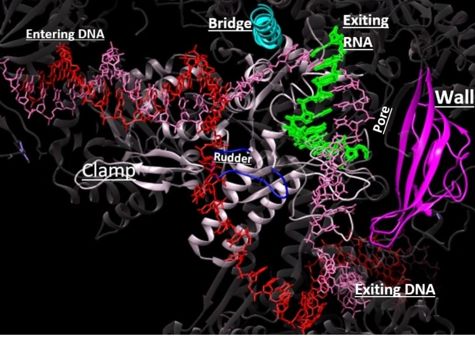
| - | RNAPII has nearly infinite processivity due to the Rpb2 <scene name='86/862212/Clamp/ | + | RNAPII has nearly infinite processivity due to the Rpb2 <scene name='86/862212/Clamp/2'>clamp</scene> subunit swinging down over DNA to trap it in the cleft<ref name="VVP" />. |
Revision as of 02:43, 1 October 2020
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Young RA. RNA polymerase II. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:689-715. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.003353. PMID:1883205 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.003353
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Myer VE, Young RA. RNA polymerase II holoenzymes and subcomplexes. J Biol Chem. 1998 Oct 23;273(43):27757-60. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.43.27757. PMID:9774381 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.273.43.27757
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Sobennikova MV, Shematorova EK, Shpakovskii GV. [C-terminal domain (CTD) of the subunit Rpb1 of nuclear RNA polymerase II and its role in the transcription cycle]. Mol Biol (Mosk). 2007 May-Jun;41(3):433-49. PMID:17685222
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 RNA polymerase II transcription initiation: A structural view D. B. Nikolov, S. K. Burley Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences Jan 1997, 94 (1) 15-22; DOI: 10.1073/pnas.94.1.15
- ↑ Hurwitz J. The discovery of RNA polymerase. J Biol Chem. 2005 Dec 30;280(52):42477-85. doi: 10.1074/jbc.X500006200. Epub 2005, Oct 17. PMID:16230341 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.X500006200
- ↑ doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nrm1796
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 Orphanides, George, Thierry Lagrange, and Danny Reinberg. The general transcription factors of RNA polymerase II. Genes & development 10.21. 1996. 2657-2683
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Xin, L.; Bushnell, D. A.; and Kornburg, R. D. RNA Polymerase II Transcription: Structure and Mechanism. Biochemica et Biophysica Acta. 2013, 1829, 2-8.
- ↑ Chang-Hui Shen; Diagnostic Molecular Biology, 2019
- ↑ He, Yuan, et al. Near-atomic resolution visualization of human transcription promoter opening. Nature 533.7603. 2016.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2 11.3 11.4 11.5 11.6 11.7 11.8 Hahn, S. Structure and Mechanism of the RNA Polymerase II Transcription Machinery. Nature Structure and Molecular Biology. 2004, 11, 394-403.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 Eick, D, Geyer, M.The RNA Polymerase II Carboxy-Terminal Domain (CTD) Code. Chemical Reviews, 2013, 113 (11), 8456-8490 DOI: 10.1021/cr400071f
- ↑ Wang W, Carey M, Gralla JD. Polymerase II Promoter Activation: Closed Complex Formation and ATP-Driven Start Site Opening. Science. 1992;255:450–453.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 14.2 14.3 14.4 14.5 14.6 14.7 14.8 14.9 Voet, D., Voet, J. G., & Pratt, C. W. (2013). Transcription and RNA Processing. In Fundamentals of biochemistry: life at the molecular level (pp. 933–942). Wiley.
- ↑ Nudler, E. RNA Polymerase Active Center: The Molecular Engine of Transcription. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2009, 78, 335-361.
- ↑ Svetlov, V., & Nudler, E. (2013). Basic mechanism of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Biochimica et biophysica acta, 1829(1), 20–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagrm.2012.08.009
- ↑ Castano E, Gross P, Wang Z, Roeder RG, Oelgeschlager T. The C-terminal domain-phosphorylated IIO form of RNA polymerase II is associated with the transcription repressor NC2 (Dr1/DRAP1) and is required for transcription activation in human nuclear extracts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Jun 20;97(13):7184-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.140202297. PMID:10852970 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.140202297
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 18.2 18.3 18.4 18.5 18.6 18.7 18.8 Wang D, Bushnell DA, Westover KD, Kaplan CD, Kornberg RD. Structural basis of transcription: role of the trigger loop in substrate specificity and catalysis. Cell. 2006 Dec 1;127(5):941-54. PMID:17129781 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2006.11.023
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 19.2 19.3 19.4 Mishanina TV, Palo MZ, Nayak D, Mooney RA, Landick R. Trigger loop of RNA polymerase is a positional, not acid-base, catalyst for both transcription and proofreading. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Jun 27;114(26):E5103-E5112. doi:, 10.1073/pnas.1702383114. Epub 2017 Jun 12. PMID:28607053 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1702383114
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 Da LT, Wang D, Huang X. Dynamics of pyrophosphate ion release and its coupled trigger loop motion from closed to open state in RNA polymerase II. J Am Chem Soc. 2012 Feb 1;134(4):2399-406. doi: 10.1021/ja210656k. Epub 2012 Jan , 24. PMID:22206270 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/ja210656k
- ↑ Bar-Nahum G, Epshtein V, Ruckenstein AE, Rafikov R, Mustaev A, Nudler E. A ratchet mechanism of transcription elongation and its control. Cell. 2005 Jan 28;120(2):183-93. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2004.11.045. PMID:15680325 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2004.11.045
Bushnell, D. A.; Westover, K. D.; Davis, R. E.; Kornberg, R. D. Structural Basis of Transcription: An RNA Polymerase II-TFIIB Cocrystal at 4.5 Angstroms. Science. 2004, 303, 983-988
Brueckner, F. and Cramer, P. Structural Basis of Transcription Inhibition by -amanitin and Implications for RNA Polymerase II Translocation. Nature Structure and Molecular Biology. 2008, 15, 811-818.
Cramer, P.; Bushnell, D. A.; Kornberg, R. D. Structural Basis of Transcription: RNA Polymerase II at 2.8 Ångstrom Resolution. Science. 2001, 292, 1863-1876
Evans, D. A.; Fitch, D. M.; Smith, T. E.; Cee, V. J. Application of Complex Aldol Reactions to the Total Synthesis of Phorboxazole B. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 10033-10046.
Gnatt, A. L.; Cramer, P; Fu, J.; Bushnell, D. A.; and Kornberg, R. D. Structural Basis of Transcription: An RNA Polymerase II Elongation Complex at 3.3 Å Resolution. Science. 2001, 292, 1876-1882 1i6h
Hahn, S. Structure and Mechanism of the RNA Polymerase II Transcription Machinery. Nature Structure and Molecular Biology. 2004, 11, 394-403.
He, Yuan, et al. Near-atomic resolution visualization of human transcription promoter opening. Nature 533.7603. 2016.
Nudler, E. RNA Polymerase Active Center: The Molecular Engine of Transcription. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2009, 78, 335-361.
Orphanides, George, Thierry Lagrange, and Danny Reinberg. The general transcription factors of RNA polymerase II. Genes & development 10.21. 1996. 2657-2683
Shah, N. et. al. Tyrosine-1 of RNA Polymerase II CTD Controls Global Termination of Gene Transcription in Mammals. Molecular Cell. 2018, 69, 48-61.
Uzman, A.; Voet, D. Student companion Fundamentals of biochemistry: life at the molecular level, 4th ed., Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. Pratt; John Wiley & amp; Sons, 2012.
Xu, J.; Lahiri, I.; Wang, W.; Wier, A.; Cianfrocco, M. A.; Chong, J.; Hare, A. A.; Dervan, P. B.; DiMaio, F.; Leschziner, A. E.; Wang, D. Structural Basis for the Initiation of Eukaryotic Transcription-coupled DNA Repair. Nature. 2017. 551, 653-657 5vvr
Xin, L.; Bushnell, D. A.; and Kornburg, R. D. RNA Polymerase II Transcription: Structure and Mechanism. Biochemica et Biophysica Acta. 2013, 1829, 2-8.
Yan, C., Dodd, T., He, Y., Tainer, J. A., Tsutakawa, S. E., & Ivanov, I. (2019). Transcription preinitiation complex structure and dynamics provide insight into genetic diseases. Nature Structural and Molecular Biology, 26(6), 397-406.
Eick, D, Geyer, M.The RNA Polymerase II Carboxy-Terminal Domain (CTD) Code. Chemical Reviews, 2013, 113 (11), 8456-8490 DOI: 10.1021/cr400071f
Chang-Hui Shen; Diagnostic Molecular Biology, 2019
Alpha-aminitin chemical structure image courtesy of https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alpha-Amanitin#/media/File:Alpha-amanitin_structure.png
Notes
From structural components:
Structural overview: [PDB: 5VVR: with highlighted sections mentioned below]
Bridge: Depicted: [PDB: 1I6H: 810-845.a]
Wall: Depicted: [PDB: 1R5U: 853-919.b; 933-972.b]
Clamp: Depicted: [PDB: 1R5U: 3-345.a; 1395-1435.a; 1158-1124.b]
Rudder: Depicted: [PDB: 5VVR: 306-321.a]
Content Donators
This page was created as a final project for the Advanced Biochemistry course at Wabash College during the Fall of 2019 and Fall of 2020. This page was reviewed by Dr. Wally Novak of Wabash College.