We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1652
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
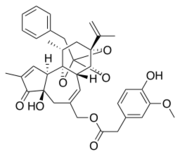
Bound [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Capsaicin capsaicin] is oriented in a « tail-up, head down » configuration. In this configuration the vanillyl and amide groups of capsaicin form specific interactions with TRPV1,capsaicin is anchored into the receptor.<ref>F. Yang et al., « Structural mechanism underlying capsaicin binding and activation of the TRPV1 ion channel », Nat. Chem. Biol., vol. 11, no 7, Art. no 7, juill. 2015, doi: 10.1038/nchembio.1835.</ref> | Bound [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Capsaicin capsaicin] is oriented in a « tail-up, head down » configuration. In this configuration the vanillyl and amide groups of capsaicin form specific interactions with TRPV1,capsaicin is anchored into the receptor.<ref>F. Yang et al., « Structural mechanism underlying capsaicin binding and activation of the TRPV1 ion channel », Nat. Chem. Biol., vol. 11, no 7, Art. no 7, juill. 2015, doi: 10.1038/nchembio.1835.</ref> | ||
| - | The capsaicin cycle binds via hydrogen bounds to amino acids on the S3 helix (Y511, S513), on the S4-S5 linker (E571) and on the S6 helix (T671). The amid group of capsaicin binds the S4 helix (T551).<ref | + | The capsaicin cycle binds via hydrogen bounds to amino acids on the S3 helix (Y511, S513), on the S4-S5 linker (E571) and on the S6 helix (T671). The amid group of capsaicin binds the S4 helix (T551).<ref name="Integrating TRPV1 Receptor Function with Capsaicin Psychophysics"> |
Capsaicin maintains TRPV1 in an open state by «pull and contact» interactions. A conformational change wave spread over the whole pore.<ref>F. Yang et al., « The conformational wave in capsaicin activation of transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 ion channel », Nat. Commun., vol. 9, no 1, Art. no 1, juill. 2018, doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-05339-6.</ref>. This leads to the massive enter of Ca2+ and Na+ in the cytoplasm of the nerve fiber and to the depolarization of the nerve fiber. When depolarization reach a theshold value it triggers the generation of an [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Action_potential action potential] causing a painful sensation.<ref name="TRPV1"/> | Capsaicin maintains TRPV1 in an open state by «pull and contact» interactions. A conformational change wave spread over the whole pore.<ref>F. Yang et al., « The conformational wave in capsaicin activation of transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 ion channel », Nat. Commun., vol. 9, no 1, Art. no 1, juill. 2018, doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-05339-6.</ref>. This leads to the massive enter of Ca2+ and Na+ in the cytoplasm of the nerve fiber and to the depolarization of the nerve fiber. When depolarization reach a theshold value it triggers the generation of an [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Action_potential action potential] causing a painful sensation.<ref name="TRPV1"/> | ||
| Line 56: | Line 56: | ||
====Sensitization==== | ====Sensitization==== | ||
| - | '''Phosphorylation''' of the TRPV1 receptor leads to its sensitization.Phosphorylations occurs on multiple phosphorylation sites at both N-terminal and C-terminal sites of TRPV1 by [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kinase kinases]. Phosphorylations are either caused by '''PKC''' (IP3 signalling), by '''PKA''' (AMPc signalling) or by '''CamKII'''.<ref>K. W. Ho, N. J. Ward, et D. J. Calkins, « TRPV1: a stress response protein in the central nervous system », Am. J. Neurodegener. Dis., vol. 1, no 1, p. 1‑14, avr. 2012.</ref><ref | + | '''Phosphorylation''' of the TRPV1 receptor leads to its sensitization.Phosphorylations occurs on multiple phosphorylation sites at both N-terminal and C-terminal sites of TRPV1 by [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kinase kinases]. Phosphorylations are either caused by '''PKC''' (IP3 signalling), by '''PKA''' (AMPc signalling) or by '''CamKII'''.<ref>K. W. Ho, N. J. Ward, et D. J. Calkins, « TRPV1: a stress response protein in the central nervous system », Am. J. Neurodegener. Dis., vol. 1, no 1, p. 1‑14, avr. 2012.</ref><ref name="Integrating TRPV1 Receptor Function with Capsaicin Psychophysics"> |
PKC phosphorlyates TRPV1 at S800,S502, PKA phosphorylates TRPV1 at S116. The phosphorylation of TRPV1 lead to an increase in the expression of TRPV1 at the membrane surface.<ref>K. W. Ho, N. J. Ward, et D. J. Calkins, « TRPV1: a stress response protein in the central nervous system », Am. J. Neurodegener. Dis., vol. 1, no 1, p. 1‑14, avr. 2012.</ref>. Moreover, phosphorylated TRPV1 would have a reduced channel opening threshold.<ref>G. Bhave et al., « Protein kinase C phosphorylation sensitizes but does not activate the capsaicin receptor transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1) », Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., vol. 100, no 21, p. 12480‑12485, oct. 2003, doi: 10.1073/pnas.2032100100.</ref>. As a result phosphorylated TRPV1 are more responsive to agonist because they are '''overexpressed''' and because the same quantity of agonist leads to a better openings of ion channels. | PKC phosphorlyates TRPV1 at S800,S502, PKA phosphorylates TRPV1 at S116. The phosphorylation of TRPV1 lead to an increase in the expression of TRPV1 at the membrane surface.<ref>K. W. Ho, N. J. Ward, et D. J. Calkins, « TRPV1: a stress response protein in the central nervous system », Am. J. Neurodegener. Dis., vol. 1, no 1, p. 1‑14, avr. 2012.</ref>. Moreover, phosphorylated TRPV1 would have a reduced channel opening threshold.<ref>G. Bhave et al., « Protein kinase C phosphorylation sensitizes but does not activate the capsaicin receptor transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1) », Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., vol. 100, no 21, p. 12480‑12485, oct. 2003, doi: 10.1073/pnas.2032100100.</ref>. As a result phosphorylated TRPV1 are more responsive to agonist because they are '''overexpressed''' and because the same quantity of agonist leads to a better openings of ion channels. | ||
Revision as of 21:54, 7 January 2021
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 26/11/2020, through 26/11/2021 for use in the course "Structural Biology" taught by Bruno Kieffer at the University of Strasbourg, ESBS. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1643 through Sandbox Reserved 1664. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
The Transient Receptor Potential cation channel subfamily V member 1 TRPV1
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Wikipedia contributors. (2020b, décembre 21). TRPV1. Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/TRPV1 (Consulté le: déc. 28, 2020). [En ligne].
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 Liao, M., Cao, E., Julius, D., & Cheng, Y. (2013b). Structure of the TRPV1 ion channel determined by electron cryo-microscopy. Nature, 504(7478), 107‑112. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12822(consulté le déc. 28, 2020)
- ↑ T. Rosenbaum et S. A. Simon, « TRPV1 Receptors and Signal Transduction », in TRP Ion Channel Function in Sensory Transduction and Cellular Signaling Cascades, W. B. Liedtke et S. Heller, Éd. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis, 2007
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 G. Smutzer et R. K. Devassy, « Integrating TRPV1 Receptor Function with Capsaicin Psychophysics », Advances in Pharmacological Sciences, janv. 14, 2016
- ↑ R. Kumar, A. Hazan, A. Basu, N. Zalcman, H. Matzner, et A. Priel, « Tyrosine Residue in the TRPV1 Vanilloid Binding Pocket Regulates Deactivation Kinetics », J. Biol. Chem., vol. 291, no 26, p. 13855‑13863, juin 2016, doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.726372.
- ↑ X. Yao, H.-Y. Kwan, et Y. Huang, « Regulation of TRP Channels by Phosphorylation », Neurosignals, vol. 14, no 6, p. 273‑280, 2005, doi: 10.1159/000093042
- ↑ F. Yang et J. Zheng, « Understand spiciness: mechanism of TRPV1 channel activation by capsaicin », Protein Cell, vol. 8, no 3, p. 169‑177, mars 2017, doi: 10.1007/s13238-016-0353-7.
- ↑ F. Yang et al., « Structural mechanism underlying capsaicin binding and activation of the TRPV1 ion channel », Nat. Chem. Biol., vol. 11, no 7, Art. no 7, juill. 2015, doi: 10.1038/nchembio.1835.
- ↑ K. Elokely et al., « Understanding TRPV1 activation by ligands: Insights from the binding modes of capsaicin and resiniferatoxin », Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., vol. 113, no 2, p. E137‑E145, janv. 2016, doi:10.1073/pnas.1517288113.
- ↑ K. W. Ho, N. J. Ward, et D. J. Calkins, « TRPV1: a stress response protein in the central nervous system », Am. J. Neurodegener. Dis., vol. 1, no 1, p. 1‑14, avr. 2012.
- ↑ G. Bhave et al., « Protein kinase C phosphorylation sensitizes but does not activate the capsaicin receptor transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1) », Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., vol. 100, no 21, p. 12480‑12485, oct. 2003, doi: 10.1073/pnas.2032100100.
- ↑ A. Danigo, L. Magy, et C. Demiot, « TRPV1 dans les neuropathies douloureuses - Des modèles animaux aux perspectives thérapeutiques », médecine/sciences, vol. 29, no 6‑7, Art. no 6‑7, juin 2013, doi: 10.1051/medsci/2013296012.
- ↑ A. Danigo, L. Magy, et C. Demiot, « TRPV1 dans les neuropathies douloureuses - Des modèles animaux aux perspectives thérapeutiques », médecine/sciences, vol. 29, no 6‑7, Art. no 6‑7, juin 2013, doi: 10.1051/medsci/2013296012.