This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Sandbox Reserved 1652
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 51: | Line 51: | ||
However, the orientation of <scene name='86/868185/L515/1'>L515</scene> and <scene name='86/868185/M547/1'>M547</scene> makes this region of the vanilloid pocket narrow, which considerably limits the nature of the fragments tolerated. | However, the orientation of <scene name='86/868185/L515/1'>L515</scene> and <scene name='86/868185/M547/1'>M547</scene> makes this region of the vanilloid pocket narrow, which considerably limits the nature of the fragments tolerated. | ||
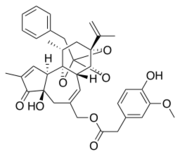
| - | The aromatic part of resiniferatoxin is located deeper in the sub-pocket near <scene name='86/868185/Y511/2'>Y511</scene> and is oriented almost parallel to the aromatic side chain of <scene name='86/868185/Y511/2'>Y511</scene>, so it establishes a strong interaction π-π. The aromatic hydroxyl and methoxy groups of the RTX form strong hydrogen bonds with E570, R557 and S512. The ester group is linked to <scene name='86/868185/Y511/2'>Y511</scene> and T550 by hydrogen bonds.<ref>K. Elokely et al., « Understanding TRPV1 activation by ligands: Insights from the binding modes of capsaicin and resiniferatoxin », Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., vol. 113, no 2, p. E137‑E145, janv. 2016, doi:10.1073/pnas.1517288113.</ref> | + | The aromatic part of resiniferatoxin is located deeper in the sub-pocket near <scene name='86/868185/Y511/2'>Y511</scene> and is oriented almost parallel to the aromatic side chain of <scene name='86/868185/Y511/2'>Y511</scene>, so it establishes a strong interaction π-π. The aromatic hydroxyl and methoxy groups of the RTX form strong hydrogen bonds with <scene name='86/868185/E570/2'>E570</scene>, <scene name='86/868185/R557/1'>R557</scene> and S512. The ester group is linked to <scene name='86/868185/Y511/2'>Y511</scene> and T550 by hydrogen bonds.<ref>K. Elokely et al., « Understanding TRPV1 activation by ligands: Insights from the binding modes of capsaicin and resiniferatoxin », Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., vol. 113, no 2, p. E137‑E145, janv. 2016, doi:10.1073/pnas.1517288113.</ref> |
=== Regulation === | === Regulation === | ||
Revision as of 11:55, 9 January 2021
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 26/11/2020, through 26/11/2021 for use in the course "Structural Biology" taught by Bruno Kieffer at the University of Strasbourg, ESBS. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1643 through Sandbox Reserved 1664. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
The Transient Receptor Potential cation channel subfamily V member 1 TRPV1
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Wikipedia contributors. (2020b, décembre 21). TRPV1. Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/TRPV1 (Consulté le: déc. 28, 2020). [En ligne].
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 Liao, M., Cao, E., Julius, D., & Cheng, Y. (2013b). Structure of the TRPV1 ion channel determined by electron cryo-microscopy. Nature, 504(7478), 107‑112. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12822(consulté le déc. 28, 2020)
- ↑ T. Rosenbaum et S. A. Simon, « TRPV1 Receptors and Signal Transduction », in TRP Ion Channel Function in Sensory Transduction and Cellular Signaling Cascades, W. B. Liedtke et S. Heller, Éd. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis, 2007
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 G. Smutzer et R. K. Devassy, « Integrating TRPV1 Receptor Function with Capsaicin Psychophysics », Advances in Pharmacological Sciences, janv. 14, 2016
- ↑ R. Kumar, A. Hazan, A. Basu, N. Zalcman, H. Matzner, et A. Priel, « Tyrosine Residue in the TRPV1 Vanilloid Binding Pocket Regulates Deactivation Kinetics », J. Biol. Chem., vol. 291, no 26, p. 13855‑13863, juin 2016, doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.726372.
- ↑ X. Yao, H.-Y. Kwan, et Y. Huang, « Regulation of TRP Channels by Phosphorylation », Neurosignals, vol. 14, no 6, p. 273‑280, 2005, doi: 10.1159/000093042
- ↑ F. Yang et J. Zheng, « Understand spiciness: mechanism of TRPV1 channel activation by capsaicin », Protein Cell, vol. 8, no 3, p. 169‑177, mars 2017, doi: 10.1007/s13238-016-0353-7.
- ↑ F. Yang et al., « Structural mechanism underlying capsaicin binding and activation of the TRPV1 ion channel », Nat. Chem. Biol., vol. 11, no 7, Art. no 7, juill. 2015, doi: 10.1038/nchembio.1835.
- ↑ K. Elokely et al., « Understanding TRPV1 activation by ligands: Insights from the binding modes of capsaicin and resiniferatoxin », Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., vol. 113, no 2, p. E137‑E145, janv. 2016, doi:10.1073/pnas.1517288113.
- ↑ K. W. Ho, N. J. Ward, et D. J. Calkins, « TRPV1: a stress response protein in the central nervous system », Am. J. Neurodegener. Dis., vol. 1, no 1, p. 1‑14, avr. 2012.
- ↑ K. W. Ho, N. J. Ward, et D. J. Calkins, « TRPV1: a stress response protein in the central nervous system », Am. J. Neurodegener. Dis., vol. 1, no 1, p. 1‑14, avr. 2012.
- ↑ G. Bhave et al., « Protein kinase C phosphorylation sensitizes but does not activate the capsaicin receptor transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1) », Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., vol. 100, no 21, p. 12480‑12485, oct. 2003, doi: 10.1073/pnas.2032100100.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 A. Danigo, L. Magy, et C. Demiot, « TRPV1 dans les neuropathies douloureuses - Des modèles animaux aux perspectives thérapeutiques », médecine/sciences, vol. 29, no 6‑7, Art. no 6‑7, juin 2013, doi: 10.1051/medsci/2013296012.