Sandbox Reserved 1653
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
1: IH, 2:OH]] | 1: IH, 2:OH]] | ||
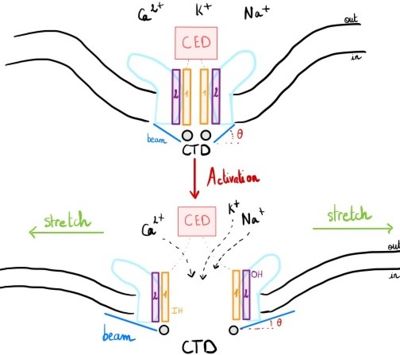
| - | Piezo1 possesses delicate force sensing and mechanotransduction mechanisms. Here, we explain how Piezo1 channels sense and transduce mechanical | + | Piezo1 possesses delicate force sensing and mechanotransduction mechanisms. Here, we explain how Piezo1 channels sense and transduce mechanical forces to gate the central ion-conducting pore. |
| - | to gate the central ion-conducting pore. | + | Piezo1 can sense membrane tension through changes in the local curvature of the membrane and the channel opens in response to this change thanks to this structure.<ref name ="Piezo Senses Tension"/> |
| - | Piezo1 can sense membrane tension through changes in the local curvature of the membrane and channel | + | Indeed, mPiezo trimer is a non-planar conformation inside lipid bilayer, it produces a local dome-shaped deformation of the membrane. In cells, this membrane curvature project towards the cytoplasm and some electrostatic interactions stabilize the trimeric assembly in its curved conformation.<ref name = "nv article"> DOI 10.7554/eLife.33660</ref> |
| - | Indeed, mPiezo trimer is non-planar conformation inside lipid bilayer, it produces a local dome-shaped deformation of the membrane. In cells, this membrane curvature project towards the cytoplasm and some | + | |
The structure of Piezo1 offers a plausible explanation for the origin of its tension [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gating_(electrophysiology)gating]. Indeed, if the semi-spherical dome becomes flatter when Piezo1 opens, then the channel membrane system will expand thanks to the flexibility of the blades. | The structure of Piezo1 offers a plausible explanation for the origin of its tension [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gating_(electrophysiology)gating]. Indeed, if the semi-spherical dome becomes flatter when Piezo1 opens, then the channel membrane system will expand thanks to the flexibility of the blades. | ||
| - | However, because flattening does not constrain the pore to open wide, expansion and pore diameter are decoupled such that Piezo1 can exhibit | + | However, because flattening does not constrain the pore to open wide, expansion and pore diameter are decoupled, such that Piezo1 can exhibit its small conductance and cation selectivity, properties that are essential to its function.<ref name ="Piezo Senses Tension"/>,<ref name="Fanny"> DOI 10.1038/s41586-019-1499-2</ref> |
| Line 46: | Line 45: | ||
==='''Blade'''=== | ==='''Blade'''=== | ||
| - | Piezo1 has a central domain which is composed of <scene name='86/868186/Cedohihctd_color2/1'>one CTD, one cap (or CED), 3 inner | + | Piezo1 has a central domain which is composed of <scene name='86/868186/Cedohihctd_color2/1'>one CTD, one cap (or CED), 3 inner helices (IH) and 3 outer helices (OH)</scene>. |
This central domain is surrounded by 3 extended arms called <scene name='86/868186/Blade/2'>blades</scene> extending out from the central pore in a rotatory manner <ref name ="Alexandra"> Zhou, Z. (2019). Structural Analysis of Piezo1 Ion Channel Reveals the Relationship between Amino Acid Sequence Mutations and Human Diseases. 139–155. DOI 10.4236/jbm.2019.712012 </ref>. | This central domain is surrounded by 3 extended arms called <scene name='86/868186/Blade/2'>blades</scene> extending out from the central pore in a rotatory manner <ref name ="Alexandra"> Zhou, Z. (2019). Structural Analysis of Piezo1 Ion Channel Reveals the Relationship between Amino Acid Sequence Mutations and Human Diseases. 139–155. DOI 10.4236/jbm.2019.712012 </ref>. | ||
"Each of these blades, deflecting at an angle of 100° perpendicular to the membrane, contains 6 tandems transmembranar helical units (THUs) constitute of 4 transmembrane domains".<ref name= "Article six"> DOI 10.1038/nature25743</ref>,<ref name="Alexandra"/> "They are not planar: instead, they lie on a spherically curved surface with the membrane bulging into the cytoplasm".<ref name= "Piezo Senses Tension "> DOI 10.1016/j.cub.2018.02.078</ref> | "Each of these blades, deflecting at an angle of 100° perpendicular to the membrane, contains 6 tandems transmembranar helical units (THUs) constitute of 4 transmembrane domains".<ref name= "Article six"> DOI 10.1038/nature25743</ref>,<ref name="Alexandra"/> "They are not planar: instead, they lie on a spherically curved surface with the membrane bulging into the cytoplasm".<ref name= "Piezo Senses Tension "> DOI 10.1016/j.cub.2018.02.078</ref> | ||
Revision as of 21:12, 10 January 2021
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Zhao Q, Wu K, Geng J, Chi S, Wang Y, Zhi P, Zhang M, Xiao B. Ion Permeation and Mechanotransduction Mechanisms of Mechanosensitive Piezo Channels. Neuron. 2016 Mar 16;89(6):1248-1263. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2016.01.046. Epub 2016, Feb 25. PMID:26924440 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2016.01.046
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Parpaite T, Coste B. Piezo channels. Curr Biol. 2017 Apr 3;27(7):R250-R252. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2017.01.048. PMID:28376327 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2017.01.048
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 Wei L, Mousawi F, Li D, Roger S, Li J, Yang X, Jiang LH. Adenosine Triphosphate Release and P2 Receptor Signaling in Piezo1 Channel-Dependent Mechanoregulation. Front Pharmacol. 2019 Nov 6;10:1304. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.01304. eCollection, 2019. PMID:31780935 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2019.01304
- ↑ Lin YC, Guo YR, Miyagi A, Levring J, MacKinnon R, Scheuring S. Force-induced conformational changes in PIEZO1. Nature. 2019 Sep;573(7773):230-234. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1499-2. Epub 2019 Aug, 21. PMID:31435018 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-1499-2
- ↑ Li J, Hou B, Tumova S, Muraki K, Bruns A, Ludlow MJ, Sedo A, Hyman AJ, McKeown L, Young RS, Yuldasheva NY, Majeed Y, Wilson LA, Rode B, Bailey MA, Kim HR, Fu Z, Carter DA, Bilton J, Imrie H, Ajuh P, Dear TN, Cubbon RM, Kearney MT, Prasad KR, Evans PC, Ainscough JF, Beech DJ. Piezo1 integration of vascular architecture with physiological force. Nature. 2014 Nov 13;515(7526):279-82. doi: 10.1038/nature13701. Epub 2014 Aug 10. PMID:25119035 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature13701
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 Liang X, Howard J. Structural Biology: Piezo Senses Tension through Curvature. Curr Biol. 2018 Apr 23;28(8):R357-R359. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2018.02.078. PMID:29689211 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2018.02.078
- ↑ Guo YR, MacKinnon R. Structure-based membrane dome mechanism for Piezo mechanosensitivity. Elife. 2017 Dec 12;6. pii: 33660. doi: 10.7554/eLife.33660. PMID:29231809 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.33660
- ↑ Lin YC, Guo YR, Miyagi A, Levring J, MacKinnon R, Scheuring S. Force-induced conformational changes in PIEZO1. Nature. 2019 Sep;573(7773):230-234. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1499-2. Epub 2019 Aug, 21. PMID:31435018 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-1499-2
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Zhou, Z. (2019). Structural Analysis of Piezo1 Ion Channel Reveals the Relationship between Amino Acid Sequence Mutations and Human Diseases. 139–155. DOI 10.4236/jbm.2019.712012
- ↑ Zhao Q, Zhou H, Chi S, Wang Y, Wang J, Geng J, Wu K, Liu W, Zhang T, Dong MQ, Wang J, Li X, Xiao B. Structure and mechanogating mechanism of the Piezo1 channel. Nature. 2018 Feb 22;554(7693):487-492. doi: 10.1038/nature25743. Epub 2018 Jan, 22. PMID:29469092 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature25743
- ↑ Guo YR, MacKinnon R. Structure-based membrane dome mechanism for Piezo mechanosensitivity. Elife. 2017 Dec 12;6. pii: 33660. doi: 10.7554/eLife.33660. PMID:29231809 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.33660
- ↑ Ge J, Li W, Zhao Q, Li N, Chen M, Zhi P, Li R, Gao N, Xiao B, Yang M. Architecture of the mammalian mechanosensitive Piezo1 channel. Nature. 2015 Nov 5;527(7576):64-9. doi: 10.1038/nature15247. Epub 2015 Sep 21. PMID:26390154 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature15247
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 Saotome K, Murthy SE, Kefauver JM, Whitwam T, Patapoutian A, Ward AB. Structure of the mechanically activated ion channel Piezo1. Nature. 2017 Dec 20. pii: nature25453. doi: 10.1038/nature25453. PMID:29261642 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature25453
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 Ge J, Li W, Zhao Q, Li N, Chen M, Zhi P, Li R, Gao N, Xiao B, Yang M. Architecture of the mammalian mechanosensitive Piezo1 channel. Nature. 2015 Nov 5;527(7576):64-9. doi: 10.1038/nature15247. Epub 2015 Sep 21. PMID:26390154 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature15247
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 15.2 15.3 Zhao Q, Zhou H, Chi S, Wang Y, Wang J, Geng J, Wu K, Liu W, Zhang T, Dong MQ, Wang J, Li X, Xiao B. Structure and mechanogating mechanism of the Piezo1 channel. Nature. 2018 Feb 22;554(7693):487-492. doi: 10.1038/nature25743. Epub 2018 Jan, 22. PMID:29469092 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature25743
- ↑ doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.4236/jbm.2019.712012
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 Albuisson J, Murthy SE, Bandell M, Coste B, Louis-Dit-Picard H, Mathur J, Feneant-Thibault M, Tertian G, de Jaureguiberry JP, Syfuss PY, Cahalan S, Garcon L, Toutain F, Simon Rohrlich P, Delaunay J, Picard V, Jeunemaitre X, Patapoutian A. Dehydrated hereditary stomatocytosis linked to gain-of-function mutations in mechanically activated PIEZO1 ion channels. Nat Commun. 2013;4:1884. doi: 10.1038/ncomms2899. PMID:23695678 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/ncomms2899
- ↑ Andolfo I, Alper SL, De Franceschi L, Auriemma C, Russo R, De Falco L, Vallefuoco F, Esposito MR, Vandorpe DH, Shmukler BE, Narayan R, Montanaro D, D'Armiento M, Vetro A, Limongelli I, Zuffardi O, Glader BE, Schrier SL, Brugnara C, Stewart GW, Delaunay J, Iolascon A. Multiple clinical forms of dehydrated hereditary stomatocytosis arise from mutations in PIEZO1. Blood. 2013 May 9;121(19):3925-35, S1-12. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-02-482489. Epub, 2013 Mar 11. PMID:23479567 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1182/blood-2013-02-482489