We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1653
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | <references/><StructureSection load='5z10' size='350' side='right' caption='Structure of the mechanosensitive Piezo1 channel 1 from | + | <references/><StructureSection load='5z10' size='350' side='right' caption='Structure of the mechanosensitive Piezo1 channel 1 from [http://www.rcsb.org/structure/5Z10 PBD]' scene=''> |
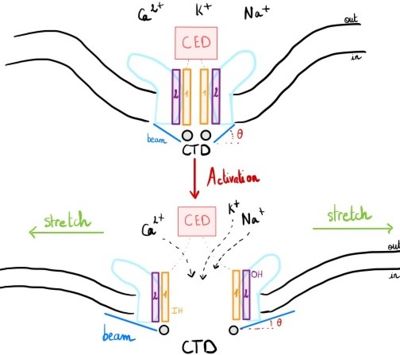
Piezo1 proteins constitute a family of excitatory [[ion channels]] directly gated by mechanical forces. Piezo1 is functionally conserved and very important because all living organisms are subjected to mechanical forces from their environment for instance [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Proprioception proprioception], [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Osmoregulation osmoregulation], vascular tone, blood flow regulation, muscle [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Homeostasis homeostasis], flow sensing in kidney, bladder and lungs.<ref name="Ion Permeation"> DOI 10.1016/j.neuron.2016.01.046 </ref>,<ref name = "Cell Press"> DOI 10.1016/j.cub.2017.01.048 </ref> | Piezo1 proteins constitute a family of excitatory [[ion channels]] directly gated by mechanical forces. Piezo1 is functionally conserved and very important because all living organisms are subjected to mechanical forces from their environment for instance [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Proprioception proprioception], [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Osmoregulation osmoregulation], vascular tone, blood flow regulation, muscle [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Homeostasis homeostasis], flow sensing in kidney, bladder and lungs.<ref name="Ion Permeation"> DOI 10.1016/j.neuron.2016.01.046 </ref>,<ref name = "Cell Press"> DOI 10.1016/j.cub.2017.01.048 </ref> | ||
Revision as of 19:02, 12 January 2021
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Zhao Q, Wu K, Geng J, Chi S, Wang Y, Zhi P, Zhang M, Xiao B. Ion Permeation and Mechanotransduction Mechanisms of Mechanosensitive Piezo Channels. Neuron. 2016 Mar 16;89(6):1248-1263. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2016.01.046. Epub 2016, Feb 25. PMID:26924440 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2016.01.046
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Parpaite T, Coste B. Piezo channels. Curr Biol. 2017 Apr 3;27(7):R250-R252. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2017.01.048. PMID:28376327 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2017.01.048
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 Wei L, Mousawi F, Li D, Roger S, Li J, Yang X, Jiang LH. Adenosine Triphosphate Release and P2 Receptor Signaling in Piezo1 Channel-Dependent Mechanoregulation. Front Pharmacol. 2019 Nov 6;10:1304. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.01304. eCollection, 2019. PMID:31780935 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2019.01304
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Lin YC, Guo YR, Miyagi A, Levring J, MacKinnon R, Scheuring S. Force-induced conformational changes in PIEZO1. Nature. 2019 Sep;573(7773):230-234. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1499-2. Epub 2019 Aug, 21. PMID:31435018 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-1499-2
- ↑ Li J, Hou B, Tumova S, Muraki K, Bruns A, Ludlow MJ, Sedo A, Hyman AJ, McKeown L, Young RS, Yuldasheva NY, Majeed Y, Wilson LA, Rode B, Bailey MA, Kim HR, Fu Z, Carter DA, Bilton J, Imrie H, Ajuh P, Dear TN, Cubbon RM, Kearney MT, Prasad KR, Evans PC, Ainscough JF, Beech DJ. Piezo1 integration of vascular architecture with physiological force. Nature. 2014 Nov 13;515(7526):279-82. doi: 10.1038/nature13701. Epub 2014 Aug 10. PMID:25119035 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature13701
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 Liang X, Howard J. Structural Biology: Piezo Senses Tension through Curvature. Curr Biol. 2018 Apr 23;28(8):R357-R359. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2018.02.078. PMID:29689211 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2018.02.078
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Guo YR, MacKinnon R. Structure-based membrane dome mechanism for Piezo mechanosensitivity. Elife. 2017 Dec 12;6. pii: 33660. doi: 10.7554/eLife.33660. PMID:29231809 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.33660
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 Zhou, Z. (2019). Structural Analysis of Piezo1 Ion Channel Reveals the Relationship between Amino Acid Sequence Mutations and Human Diseases. 139–155. DOI 10.4236/jbm.2019.712012
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 9.4 Zhao Q, Zhou H, Chi S, Wang Y, Wang J, Geng J, Wu K, Liu W, Zhang T, Dong MQ, Wang J, Li X, Xiao B. Structure and mechanogating mechanism of the Piezo1 channel. Nature. 2018 Feb 22;554(7693):487-492. doi: 10.1038/nature25743. Epub 2018 Jan, 22. PMID:29469092 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature25743
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 Ge J, Li W, Zhao Q, Li N, Chen M, Zhi P, Li R, Gao N, Xiao B, Yang M. Architecture of the mammalian mechanosensitive Piezo1 channel. Nature. 2015 Nov 5;527(7576):64-9. doi: 10.1038/nature15247. Epub 2015 Sep 21. PMID:26390154 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature15247
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Saotome K, Murthy SE, Kefauver JM, Whitwam T, Patapoutian A, Ward AB. Structure of the mechanically activated ion channel Piezo1. Nature. 2017 Dec 20. pii: nature25453. doi: 10.1038/nature25453. PMID:29261642 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature25453
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 Albuisson J, Murthy SE, Bandell M, Coste B, Louis-Dit-Picard H, Mathur J, Feneant-Thibault M, Tertian G, de Jaureguiberry JP, Syfuss PY, Cahalan S, Garcon L, Toutain F, Simon Rohrlich P, Delaunay J, Picard V, Jeunemaitre X, Patapoutian A. Dehydrated hereditary stomatocytosis linked to gain-of-function mutations in mechanically activated PIEZO1 ion channels. Nat Commun. 2013;4:1884. doi: 10.1038/ncomms2899. PMID:23695678 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/ncomms2899
- ↑ Andolfo I, Alper SL, De Franceschi L, Auriemma C, Russo R, De Falco L, Vallefuoco F, Esposito MR, Vandorpe DH, Shmukler BE, Narayan R, Montanaro D, D'Armiento M, Vetro A, Limongelli I, Zuffardi O, Glader BE, Schrier SL, Brugnara C, Stewart GW, Delaunay J, Iolascon A. Multiple clinical forms of dehydrated hereditary stomatocytosis arise from mutations in PIEZO1. Blood. 2013 May 9;121(19):3925-35, S1-12. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-02-482489. Epub, 2013 Mar 11. PMID:23479567 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1182/blood-2013-02-482489