We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
User:Abbey Wells/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
<StructureSection load='4ymk' size='340' side='right' caption='White Space filling' scene='87/877602/White_scene/1'> | <StructureSection load='4ymk' size='340' side='right' caption='White Space filling' scene='87/877602/White_scene/1'> | ||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
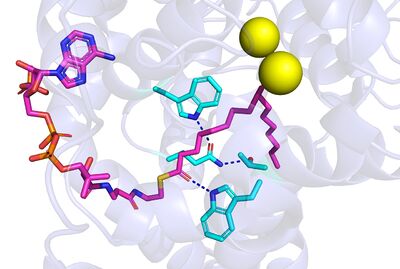
| - | This is | + | SCD stands for Stearoyl-CoA Desaturase. This enzyme is highly conserved in eukaryotes and has different isoforms. Mice have four isoforms: SCD1, SCD2, SCD3, and SCD4. Humans have two different isoforms: SCD1 and SCD5. The SCD discussed in this page is the SCD-1 found in mice. SCD was thought to have once been an anaerobic pathway found in cartilaginous fish about 450 million years ago. The enzyme’s mechanism is now aerobic and this aerobic pathway is favored. The structure of SCD1 was found using X-ray crystallography. This enzyme is embedded in the membrane of the Endoplasmic Reticulum. SCD is made up of 15 alpha helices; four helices are embedded in the membrane and 11 helices in the cytosol. The substrate binds to the helices in the cytosol. |
| - | + | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
Revision as of 15:35, 5 April 2021
Stearoyl-CoA Desaturase 1 from Mus musculus
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Ransey E, Paredes E, Dey SK, Das SR, Heroux A, Macbeth MR. Crystal structure of the Entamoeba histolytica RNA lariat debranching enzyme EhDbr1 reveals a catalytic Zn(2+) /Mn(2+) heterobinucleation. FEBS Lett. 2017 Jul;591(13):2003-2010. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.12677. Epub 2017, Jun 14. PMID:28504306 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/1873-3468.12677
Student Contributors
- Abbey Wells
- Josey McKinley
- Anthony Durand