This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
User:Abbey Wells/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
| - | SCD stands for Stearoyl-CoA Desaturase. This enzyme is highly conserved in eukaryotes and has different isoforms. Mice have four isoforms: SCD1, SCD2, SCD3, and SCD4. Humans have two different isoforms: SCD1 and SCD5. The SCD discussed in this page is the SCD-1 found in mice. SCD was thought to have once been an anaerobic pathway found in cartilaginous fish about 450 million years ago. The enzyme’s mechanism is now aerobic and this aerobic pathway is favored. The structure of SCD1 was found using X-ray crystallography | + | SCD stands for Stearoyl-CoA Desaturase. This enzyme is highly conserved in eukaryotes and has different isoforms. Mice have four isoforms: SCD1, SCD2, SCD3, and SCD4. Humans have two different isoforms: SCD1 and SCD5. The SCD discussed in this page is the SCD-1 found in mice. SCD was thought to have once been an anaerobic pathway found in cartilaginous fish about 450 million years ago. The enzyme’s mechanism is now aerobic and this aerobic pathway is favored. The structure of SCD1 was found using X-ray crystallography. |
| - | [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stearoyl-CoA_desaturase-1 Stearoyl-CoA Desaturase 1 (SCD1)] is an iron-containing [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fatty_acid_desaturase Δ-9-desaturase] that is a key regulator of fatty-acid metabolism where it catalyzes the rate-limiting step in the conversion of [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stearoyl-CoA Stearoyl-CoA] to [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Oleic_acid oleic acid], an essential substrate in the biosynthesis of phospholipids, triacyclglycerols, and cholesterol. SCD1 is embedded within the membrane of the [http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/cells/endoplasmicreticulum/endoplasmicreticulum.html endoplasmic reticulum] and consists of 4 transmembrane alpha helices and 11 cytosolic helices. | + | [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stearoyl-CoA_desaturase-1 Stearoyl-CoA Desaturase 1 (SCD1)] is an iron-containing [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fatty_acid_desaturase Δ-9-desaturase] that is a key regulator of fatty-acid metabolism where it catalyzes the rate-limiting step in the conversion of [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stearoyl-CoA Stearoyl-CoA] to [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Oleic_acid oleic acid], an essential substrate in the biosynthesis of phospholipids, triacyclglycerols, and cholesterol. |
| + | == Structure == | ||
| + | === Overall Structure === | ||
| + | SCD1 is embedded within the membrane of the [http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/cells/endoplasmicreticulum/endoplasmicreticulum.html endoplasmic reticulum] and consists of 4 transmembrane alpha helices and 11 cytosolic helices. | ||
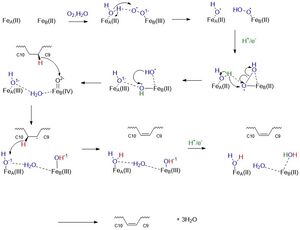
Its substrate, Stearoyl-CoA, binds to the cytosolic region which contains a "kink" that properly orients Stearoyl-CoA to undergo a [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dehydrogenation#:~:text=Dehydrogenation%20is%20the%20a%20chemical,reaction%20and%20a%20serious%20problem.&text=Enzymes%20that%20catalyze%20dehydrogenation%20are%20called%20dehydrogenases. dehydrogenation] reaction between the <scene name='87/877606/Ligand-highlighted/3'>9th and 10th carbons</scene> of Stearoyl-CoA. This reaction is catalyzed by <scene name='87/877606/Di-iron-ions/2'>two iron ions</scene> that reside within the catalytic center of SCD1 which are oriented by 8 essential histidine residues. | Its substrate, Stearoyl-CoA, binds to the cytosolic region which contains a "kink" that properly orients Stearoyl-CoA to undergo a [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dehydrogenation#:~:text=Dehydrogenation%20is%20the%20a%20chemical,reaction%20and%20a%20serious%20problem.&text=Enzymes%20that%20catalyze%20dehydrogenation%20are%20called%20dehydrogenases. dehydrogenation] reaction between the <scene name='87/877606/Ligand-highlighted/3'>9th and 10th carbons</scene> of Stearoyl-CoA. This reaction is catalyzed by <scene name='87/877606/Di-iron-ions/2'>two iron ions</scene> that reside within the catalytic center of SCD1 which are oriented by 8 essential histidine residues. | ||
Mechanistically, this reaction involves a molecular oxygen, water molecule, and the transport of electrons down an [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electron_transport_chain electron transport chain] consisting of cytochrome b5 reductase, cytochrome b5, and NADH to the irons ions within SCD1 which then through a series of redox reactions introduces a double bond between the 9th and 10th carbons of Stearoyl-CoA forming oleic acid. | Mechanistically, this reaction involves a molecular oxygen, water molecule, and the transport of electrons down an [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electron_transport_chain electron transport chain] consisting of cytochrome b5 reductase, cytochrome b5, and NADH to the irons ions within SCD1 which then through a series of redox reactions introduces a double bond between the 9th and 10th carbons of Stearoyl-CoA forming oleic acid. | ||
| - | |||
| - | == Structure == | ||
=== Binding of Substrate === | === Binding of Substrate === | ||
Revision as of 17:14, 8 April 2021
Stearoyl-CoA Desaturase 1 from Mus musculus
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Bai Y, McCoy JG, Levin EJ, Sobrado P, Rajashankar KR, Fox BG, Zhou M. X-ray structure of a mammalian stearoyl-CoA desaturase. Nature. 2015 Jun 22. doi: 10.1038/nature14549. PMID:26098370 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature14549
- ↑ Shen J, Wu G, Tsai AL, Zhou M. Structure and Mechanism of a Unique Diiron Center in Mammalian Stearoyl-CoA Desaturase. J Mol Biol. 2020 May 27. pii: S0022-2836(20)30367-3. doi:, 10.1016/j.jmb.2020.05.017. PMID:32470559 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2020.05.017
Student Contributors
- Abbey Wells
- Josey McKinley
- Anthony Durand