This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Journal:Molecular Cell:1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)

| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
The algorithm, '''PROSS''' (Protein Repair One-Stop Shop), is available at [http://pross.weizmann.ac.il http://pross.weizmann.ac.il ]. | The algorithm, '''PROSS''' (Protein Repair One-Stop Shop), is available at [http://pross.weizmann.ac.il http://pross.weizmann.ac.il ]. | ||
| - | <scene name='72/728277/Cv/26'>The structural basis underpinnings the stabilization in the designed variant dAChE</scene>. <font color='slateblue'><b> | + | <scene name='72/728277/Cv/26'>The structural basis underpinnings the stabilization in the designed variant dAChE</scene>. <font color='slateblue'><b> Wild type hAChE (PDB entry: [[4ey3]]) is shown in blue</b></font> and <font color='darkorange'><b>51 mutated positions, which are distributed throughout dAChE4, are indicated by orange spheres</b></font>. |
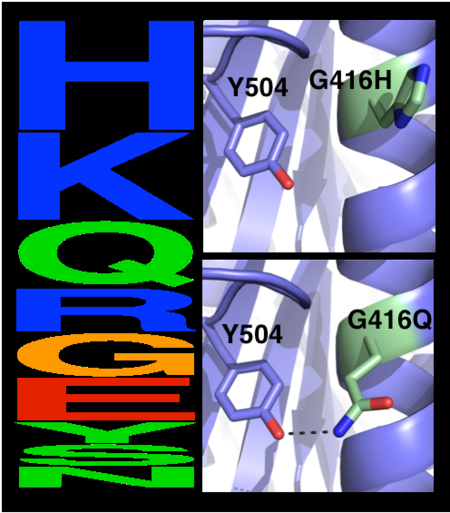
The choice of mutations at Gly416 in hAChE illustrates the role of the two filters, ''i.e.'', a '''sequence alignment scan''' and a '''computational mutation scan''', used in pruning false positives (see the static image below). Position 416 is located on a partially exposed helical surface, where the small and flexible amino acid Gly is likely to destabilize hAChE. Indeed, in the alignment of AChE homologs, Gly appears infrequently and His is the most prevalent amino acid. Modeling shows, however, that in this specific context of hAChE, His adopts a strained side-chain conformation; in contrast, Gln, the third most prevalent amino acid, is predicted to be most stabilizing owing to its high helical propensity and favorable hydrogen-bonding with Tyr504. The combined filter, therefore, favors Gln over His for downstream design calculations. | The choice of mutations at Gly416 in hAChE illustrates the role of the two filters, ''i.e.'', a '''sequence alignment scan''' and a '''computational mutation scan''', used in pruning false positives (see the static image below). Position 416 is located on a partially exposed helical surface, where the small and flexible amino acid Gly is likely to destabilize hAChE. Indeed, in the alignment of AChE homologs, Gly appears infrequently and His is the most prevalent amino acid. Modeling shows, however, that in this specific context of hAChE, His adopts a strained side-chain conformation; in contrast, Gln, the third most prevalent amino acid, is predicted to be most stabilizing owing to its high helical propensity and favorable hydrogen-bonding with Tyr504. The combined filter, therefore, favors Gln over His for downstream design calculations. | ||
Revision as of 16:04, 29 June 2021
| |||||||||||
- ↑ Goldenzweig A, Goldsmith M, Hill SE, Gertman O, Laurino P, Ashani Y, Dym O, Unger T, Albeck S, Prilusky J, Lieberman RL, Aharoni A, Silman I, Sussman JL, Tawfik DS, Fleishman SJ. Automated Structure- and Sequence-Based Design of Proteins for High Bacterial Expression and Stability. Mol Cell. 2016 Jul 21;63(2):337-346. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2016.06.012. Epub 2016, Jul 14. PMID:27425410 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2016.06.012
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
This page complements a publication in scientific journals and is one of the Proteopedia's Interactive 3D Complement pages. For aditional details please see I3DC.