We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1692
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
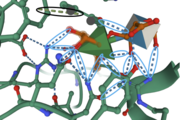
The image to the right shows important amino acids in the active site. Hydrogen bonding and pi-stacking interactions are indicated by the blue and black circles, respectively. | The image to the right shows important amino acids in the active site. Hydrogen bonding and pi-stacking interactions are indicated by the blue and black circles, respectively. | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
| - | Secondary Structure: In this enzyme, there are around <scene name='89/892735/Beta_sheets/3'>30 anti-parallel beta sheets</scene> and three small <scene name='89/892735/Helices/1'>alpha helices</scene>. Compared to parallel beta sheets, anti-parallel beta sheets provide stronger hydrogen bonding between side chains of amino acids. The alpha helices provide structure for the formation of the active site, allowing the substrate (Rha) to bind in the active site. | + | Secondary Structure: In this enzyme, there are around <scene name='89/892735/Beta_sheets/3'>30 anti-parallel beta sheets</scene> and three small <scene name='89/892735/Helices/1'>alpha helices</scene>. Compared to parallel beta sheets, anti-parallel beta sheets provide stronger hydrogen bonding between side chains of amino acids. The alpha helices provide structure for the formation of the active site, allowing the substrate (Rha) to bind in the active site. |
| - | Tertiary Structure: The structure of FoRham1 consists of a <scene name='89/892735/Beta_propeller/4'>seven-bladed Beta-propellor domain</scene>, providing a favorable conformation for the substrate binding into the active site, located on the anterior side of the enzyme. | + | |
| - | Provided <scene name='89/892735/Spacefill/1'>here</scene> is the protein structure in space fill. This structure representation | + | Tertiary Structure: The structure of FoRham1 consists of a <scene name='89/892735/Beta_propeller/4'>seven-bladed Beta-propellor domain</scene>, providing a favorable conformation for the substrate binding into the active site, located on a central cleft towards the anterior side of the enzyme. This beta-propeller is stabilized through hydrophobic interactions of the beta sheets, as well as hydrogen bonding that occurs between the N and C terminus of the beta sheets. B-propeller 1 is indicated by the red anti-parallel beta sheets, B-propeller 7 is indicated by the yellow anti-parallel beta sheets. |
| + | |||
| + | Quaternary Structure: This protein does not have quaternary structure. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Provided <scene name='89/892735/Spacefill/1'>here</scene> is the protein structure in space fill. This structure representation shows how much space certain molecules take up, indicating the depths of the active site and showing how deeply bound the ligand is to the enzyme. This representation also shows what size molecule fit into the active site, giving scientists an idea of other similar-sized ligands that may also fit into this binding pocket. Tan represents the enzyme, green represents the ligands, and pink represents the solvent. | ||
== Other important features == | == Other important features == | ||
Revision as of 18:26, 8 December 2021
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 10/01/2021 through 01/01//2022 for use in Biochemistry taught by Bonnie Hall at Grand View University, Des Moines, USA. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1690 through Sandbox Reserved 1699. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Structure and Function of FoRham1
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Kondo T, Kichijo M, Maruta A, Nakaya M, Takenaka S, Arakawa T, Fushinobu S, Sakamoto T. Structural and functional analysis of gum arabic l-rhamnose-alpha-1,4-d-glucuronate lyase establishes a novel polysaccharide lyase family. J Biol Chem. 2021 Jul 22:101001. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.101001. PMID:34303708 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2021.101001