User:Mathias Bortoletto Dunker/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 81: | Line 81: | ||
== Structural and Genetic Information of Keap1 == | == Structural and Genetic Information of Keap1 == | ||
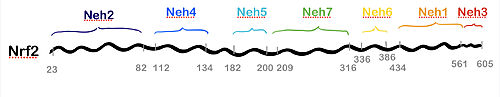
| - | Keap1 belongs to the metazoan superfamily of BTB-[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kelch_protein Kelch] proteins, a widespread group of proteins that contain multiple Kelch motifs. The Kelch domain generally occurs as a set of five to seven kelch tandem repeats that form a <scene name='89/898348/Betaprop/1'>β-propeller tertiary structure.</scene>. | + | Keap1 belongs to the metazoan superfamily of BTB-[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kelch_protein Kelch] proteins, a widespread group of proteins that contain multiple Kelch motifs. The Kelch domain generally occurs as a set of five to seven kelch tandem repeats that form a <scene name='89/898348/Betaprop/1'>β-propeller tertiary structure.</scene>. In mice, Keap1 has 624 amino acids, composing five different domains with the following caracteristics: |
| + | |||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
| - | Keap1 finalmente todos os dominios: | + | Keap1 finalmente todos os dominios (humano): |
<scene name='89/898348/Finalmentekeap1/1'>Text To Be Displayed</scene> | <scene name='89/898348/Finalmentekeap1/1'>Text To Be Displayed</scene> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Keap1 finalmente todos os dominios (mice): | ||
| + | <scene name='89/898348/Keap1mice/1'>Text To Be Displayed</scene> | ||
Nrf2 todos os dominios: | Nrf2 todos os dominios: | ||
Revision as of 05:35, 13 December 2021
Keap1-Nrf2 Complex
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Lo, S.-C., Li, X., Henzl, M.T., Beamer, L.J. and Hannink, M. (2006), Structure of the Keap1:Nrf2 interface provides mechanistic insight into Nrf2 signaling. The EMBO Journal, 25: 3605-3617. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.emboj.7601243
- ↑ Pitoniak, A., & Bohmann, D. (2015). Mechanisms and functions of Nrf2 signaling in Drosophila. Free radical biology & medicine, 88(Pt B), 302–313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2015.06.020
- ↑ Data available in https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/9817
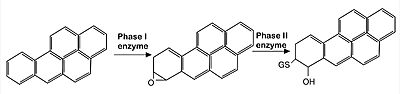
- ↑ Mathers J, Fraser JA, McMahon M, Saunders RD, Hayes JD, McLellan LI. Antioxidant and cytoprotective responses to redox stress. Biochem Soc Symp. 2004;(71):157-76. doi: 10.1042/bss0710157. PMID: 15777020.
- ↑ Jackson AL, Loeb LA. The contribution of endogenous sources of DNA damage to the multiple mutations in cancer. Mutat Res. 2001 Jun 2;477(1-2):7-21. doi: 10.1016/s0027-5107(01)00091-4. PMID: 11376682.
- ↑ Ceconi C, Boraso A, Cargnoni A, Ferrari R. Oxidative stress in cardiovascular disease: myth or fact? Arch Biochem Biophys. 2003 Dec 15;420(2):217-21. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2003.06.002. PMID: 14654060.
- ↑ Leung L, Kwong M, Hou S, Lee C, Chan JY. Deficiency of the Nrf1 and Nrf2 transcription factors results in early embryonic lethality and severe oxidative stress. J Biol Chem. 2003 Nov 28;278(48):48021-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M308439200. Epub 2003 Sep 10. PMID: 12968018.
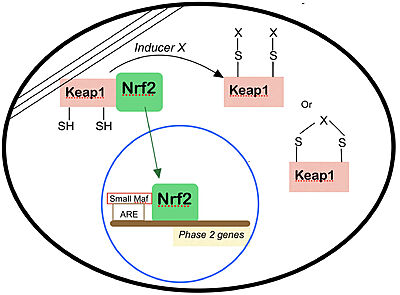
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Dinkova-Kostova AT, Holtzclaw WD, Cole RN, Itoh K, Wakabayashi N, Katoh Y, Yamamoto M, Talalay P. Direct evidence that sulfhydryl groups of Keap1 are the sensors regulating induction of phase 2 enzymes that protect against carcinogens and oxidants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Sep 3;99(18):11908-13. doi: 10.1073/pnas.172398899. Epub 2002 Aug 22. PMID: 12193649; PMCID: PMC129367.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 Motohashi H, Yamamoto M. Nrf2-Keap1 defines a physiologically important stress response mechanism. Trends Mol Med. 2004 Nov;10(11):549-57. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2004.09.003. PMID: 15519281.
- ↑ Sasaki, H. et al. (2002) Electrophile response element-mediated induction of the cystine/glutamate exchange transporter gene expression. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 44765–44771
- ↑ Chan, K. and Kan, Y.W. (1999) Nrf2 is essential for protection against acute pulmonary injury in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 96, 12731–12736
- ↑ Enomoto, A. et al. (2001) High sensitivity of Nrf2 knockout mice to Review TRENDS in Molecular Medicine Vol.10 No.11 November 2004 555 www.sciencedirect.com acetaminophen hepatotoxicity associated with decreased expression of ARE-regulated drug metabolizing enzymes and antioxidant genes. Toxicol. Sci. 59, 169–177
- ↑ Goldring, C.E. et al. (2004) Activation of hepatic Nrf2 in vivo by acetaminophen in CD-1 mice. Hepatology 39, 1267–1276
- ↑ Ramos-Gomez, M. et al. (2001) Sensitivity to carcinogenesis is increased and chemoprotective efficacy of enzyme inducers is lost in nrf2 transcription factor-deficient mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 98, 3410–3415
- ↑ Cho, H-Y. et al. (2002) Role of NRF2 in protection against hyperoxic lung injury in mice. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 26, 175–182
- ↑ Canning P, Sorrell FJ, Bullock AN. Structural basis of Keap1 interactions with Nrf2. Free Radic Biol Med. 2015;88(Pt B):101-107. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2015.05.034
- ↑ https://www.annualreviews.org/doi/full/10.1146/annurev-cancerbio-030518-055627, CC BY 4.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=94063579
- ↑ Canning P, Sorrell FJ, Bullock AN. Structural basis of Keap1 interactions with Nrf2. Free Radic Biol Med. 2015;88(Pt B):101-107. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2015.05.034