We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1647
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
T-bet can also regulate Th1 cell differentiation by directly initiating gamma interferon (IFN-γ) transcription and by suppressing Th2-specific transcription factor [https://proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/3dfx GATA-3]<ref name="A novel transcription factor, T-bet, directs Th1 lineage commitment"> Szabo, S. J., Kim, S. T., Costa, G. L., Zhang, X., Fathman, C. G., & Glimcher, L. H. (2000). A novel transcription factor, T-bet, directs Th1 lineage commitment. Cell, 100(6), 655–669. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80702-3</ref>. The T-bet induced expression of IFN-γ derives Th precursor cells to differentiate into Th1 effector cells. | T-bet can also regulate Th1 cell differentiation by directly initiating gamma interferon (IFN-γ) transcription and by suppressing Th2-specific transcription factor [https://proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/3dfx GATA-3]<ref name="A novel transcription factor, T-bet, directs Th1 lineage commitment"> Szabo, S. J., Kim, S. T., Costa, G. L., Zhang, X., Fathman, C. G., & Glimcher, L. H. (2000). A novel transcription factor, T-bet, directs Th1 lineage commitment. Cell, 100(6), 655–669. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80702-3</ref>. The T-bet induced expression of IFN-γ derives Th precursor cells to differentiate into Th1 effector cells. | ||
| - | This stimulation of IFN-γ can take place thanks to the action of a nuclear tyrosine kinase, c-Abl. C-Abl induces phosphorylation of T-bet at tyrosine residues | + | This stimulation of IFN-γ can take place thanks to the action of a nuclear tyrosine kinase, c-Abl. C-Abl induces phosphorylation of T-bet at tyrosine residues TYR 219, TYR 265, and TYR 304. C-Abl phosphorylates the tyrosine residues within the T-box domain, which is the DNA-binding domain of T-bet. This phosphorylation leads to conformational changes of the T-box domain to facilitate the DNA-binding activity of T-bet and appears to play a crucial role in the IFN-γ promoter-binding activity of T-bet. |
Recently, many studies have reported that T-bet also modulates other Th cell lineages, including [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/T_helper_17_cell Th17], [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Regulatory_T_cell Treg], and follicular Th (TFH) cells, in coordination with many transcription factors, such as the retinoic acid-related orphan receptor-𝛾t [https://proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/6b30 (ROR𝛾t)] <ref name="T-bet represses T(H)17 differentiation by preventing Runx1-mediated activation of the gene encoding RORγt">DOI 10.1038/ni.1969</ref>, runt-related transcription factor 3 [https://proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/3mpm (RUNX3)], and B-cell lymphoma-6 [https://proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/3lbz (BCL6)]. These findings suggest that T-bet is a transcription factor that is critical for fine-tuning Th cell development. | Recently, many studies have reported that T-bet also modulates other Th cell lineages, including [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/T_helper_17_cell Th17], [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Regulatory_T_cell Treg], and follicular Th (TFH) cells, in coordination with many transcription factors, such as the retinoic acid-related orphan receptor-𝛾t [https://proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/6b30 (ROR𝛾t)] <ref name="T-bet represses T(H)17 differentiation by preventing Runx1-mediated activation of the gene encoding RORγt">DOI 10.1038/ni.1969</ref>, runt-related transcription factor 3 [https://proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/3mpm (RUNX3)], and B-cell lymphoma-6 [https://proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/3lbz (BCL6)]. These findings suggest that T-bet is a transcription factor that is critical for fine-tuning Th cell development. | ||
| Line 52: | Line 52: | ||
Th1, Th2 and Th17 cells are the main cells involved in the pathophysiology of asthma <ref name="Effect of ginger extract on expression of GATA3, T-bet and ROR-γt in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with Allergic Asthma">DOI 10.1016/j.aller.2018.12.003</ref>. In asthmatic airways, Th2 cells are activated and release several cytokines <ref name="The role of protein modifications of T-bet in cytokine production and differentiation of T helper cells">DOI 10.1155/2014/589672</ref> that regulate IgE production and inflammatory cell recruitment, such as eosinophils. Th2 cells and GATA-3 play an important role in allergic inflammation and asthma, and induce IgE production. The asthmatic patients present high levels of total IgE. On the contrary, the T-bet gene expression and Th1 pattern, along with the IFN- γ production, are usually associated with non-allergic asthmatics and healthy subjects.<ref name="Asthma: T-bet--a master controller?">DOI 10.1016/s0960-9822(02)00830-8</ref> | Th1, Th2 and Th17 cells are the main cells involved in the pathophysiology of asthma <ref name="Effect of ginger extract on expression of GATA3, T-bet and ROR-γt in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with Allergic Asthma">DOI 10.1016/j.aller.2018.12.003</ref>. In asthmatic airways, Th2 cells are activated and release several cytokines <ref name="The role of protein modifications of T-bet in cytokine production and differentiation of T helper cells">DOI 10.1155/2014/589672</ref> that regulate IgE production and inflammatory cell recruitment, such as eosinophils. Th2 cells and GATA-3 play an important role in allergic inflammation and asthma, and induce IgE production. The asthmatic patients present high levels of total IgE. On the contrary, the T-bet gene expression and Th1 pattern, along with the IFN- γ production, are usually associated with non-allergic asthmatics and healthy subjects.<ref name="Asthma: T-bet--a master controller?">DOI 10.1016/s0960-9822(02)00830-8</ref> | ||
| - | In T-bet structure, ubiquitination takes place at | + | In T-bet structure, ubiquitination takes place at LYS 313. It has an impact on the stability of the protein and leads to the degradation of the protein by the proteosome. Some research found the role of deubiquitinases involved in T-bet stability and function. As a deubiquitinase, USP10 belongs to the ubiquitin-specificprotease family of cysteine proteases. Cysteine 424 site on [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/USP10 USP10] is crucial for its hydrolase activity. Results have shown that USP10 could interact with T-bet and stabilize it via interaction between Lysine 313 of T-bet and Cysteine 424 of USP10. Deubiquitination inhibits its degradation by the proteosome and enhance the secretion of IFN- γ. |
Researchers believe that the USP10-dependent T-bet deubiquitination and stabilization can regulate antigen induced immune disorder especially in Th1 specific inflammation. Thus, appropriate decreasing USP10 level may contribute to the T-bet degradation and inflammation attenuation. <ref name="Deubiquitination and stabilization of T-bet by USP10">DOI 10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.05.037</ref> | Researchers believe that the USP10-dependent T-bet deubiquitination and stabilization can regulate antigen induced immune disorder especially in Th1 specific inflammation. Thus, appropriate decreasing USP10 level may contribute to the T-bet degradation and inflammation attenuation. <ref name="Deubiquitination and stabilization of T-bet by USP10">DOI 10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.05.037</ref> | ||
Revision as of 19:20, 11 January 2022
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ TBX21-GeneCards : TBX21 - T-box Transcription factor 21 :https://www.genecards.org/cgi-bin/carddisp.pl?gene=TBX21
- ↑ Mehta DS, Wurster AL, Weinmann AS, Grusby MJ. NFATc2 and T-bet contribute to T-helper-cell-subset-specific regulation of IL-21 expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Feb 8;102(6):2016-21. doi:, 10.1073/pnas.0409512102. Epub 2005 Jan 31. PMID:15684054 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0409512102
- ↑ Jang EJ, Park HR, Hong JH, Hwang ES. Lysine 313 of T-box is crucial for modulation of protein stability, DNA binding, and threonine phosphorylation of T-bet. J Immunol. 2013 Jun 1;190(11):5764-70. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1203403. Epub 2013, Apr 24. PMID:23616576 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1203403
- ↑ Wang P, Wang Y, Xie L, Xiao M, Wu J, Xu L, Bai Q, Hao Y, Huang Q, Chen X, He R, Li B, Yang S, Chen Y, Wu Y, Ye L. The Transcription Factor T-Bet Is Required for Optimal Type I Follicular Helper T Cell Maintenance During Acute Viral Infection. Front Immunol. 2019 Mar 29;10:606. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00606. eCollection, 2019. PMID:30984183 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.00606
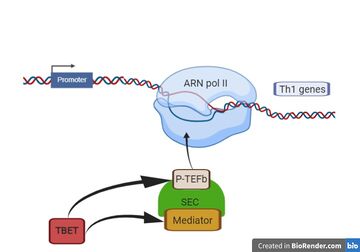
- ↑ Hertweck A, Evans CM, Eskandarpour M, Lau JC, Oleinika K, Jackson I, Kelly A, Ambrose J, Adamson P, Cousins DJ, Lavender P, Calder VL, Lord GM, Jenner RG. T-bet Activates Th1 Genes through Mediator and the Super Elongation Complex. Cell Rep. 2016 Jun 21;15(12):2756-70. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.05.054. Epub, 2016 Jun 9. PMID:27292648 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2016.05.054
- ↑ Szabo, S. J., Kim, S. T., Costa, G. L., Zhang, X., Fathman, C. G., & Glimcher, L. H. (2000). A novel transcription factor, T-bet, directs Th1 lineage commitment. Cell, 100(6), 655–669. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80702-3
- ↑ Lazarevic V, Chen X, Shim JH, Hwang ES, Jang E, Bolm AN, Oukka M, Kuchroo VK, Glimcher LH. T-bet represses T(H)17 differentiation by preventing Runx1-mediated activation of the gene encoding RORgammat. Nat Immunol. 2011 Jan;12(1):96-104. doi: 10.1038/ni.1969. Epub 2010 Dec 12. PMID:21151104 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/ni.1969
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Douglas.S.Robinson and Clare M Lloyd. Asthma: T-bet - A master controller ? Volume 12, Issue 9, PR322-R324, April 30, (2002) https://doi.org/10.1016/S0960-9822(02)00830-8
- ↑ Kardan M, Rafiei A, Ghaffari J, Valadan R, Morsaljahan Z, Haj-Ghorbani ST. Effect of ginger extract on expression of GATA3, T-bet and ROR-gammat in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with Allergic Asthma. Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 2019 Jul - Aug;47(4):378-385. doi:, 10.1016/j.aller.2018.12.003. Epub 2019 Feb 10. PMID:30745246 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.aller.2018.12.003
- ↑ Oh S, Hwang ES. The role of protein modifications of T-bet in cytokine production and differentiation of T helper cells. J Immunol Res. 2014;2014:589672. doi: 10.1155/2014/589672. Epub 2014 May 13. PMID:24901011 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/589672
- ↑ Pan L, Chen Z, Wang L, Chen C, Li D, Wan H, Li B, Shi G. Deubiquitination and stabilization of T-bet by USP10. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014 Jul 4;449(3):289-94. doi:, 10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.05.037. Epub 2014 May 17. PMID:24845384 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.05.037
12. Koch, M. A., Tucker-Heard, G., Perdue, N. R., Killebrew, J. R., Urdahl, K. B., & Campbell, D. J. (2009). The transcription factor T-bet controls regulatory T cell homeostasis and function during type 1 inflammation. Nature immunology, 10(6), 595–602. https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.1731