Piezo1 proteins constitute a family of excitatory ion channels directly gated by mechanical forces. Piezo1 is functionally conserved and very important because all living organisms are subjected to mechanical forces from their environment for instance proprioception, osmoregulation, vascular tone, blood flow regulation, muscle homeostasis, flow sensing in kidney, bladder and lungs.[1],[2]
Structure
Blade
Piezo1 has a central domain which is composed of .
This central domain is surrounded by 3 extended arms called extending out from the central pore in a rotatory manner [3].
"Each of these blades, deflecting at an angle of 100° perpendicular to the membrane, contains 6 tandems transmembranar helical units (THUs) constitute of 4 transmembrane domains".[4],[3] "They are not planar: instead, they lie on a spherically curved surface with the membrane bulging into the cytoplasm".[5]
These flexible blades are inside the membrane and force the membrane to curve. That is why, they are considered as mechanotransduction modules, force sensors and transducers to gate the central pore. "These 3 blades propeller architecture is mechanically interesting because 3 blades are the minimum for omnidirectional sensitivity".[5],[6]
CED or cap
The (carboxyterminal extracellular domain) also called cap is a large extracellular domain in loop shape that forms a trimer. This CED is located in the central module surrounded by the and contains 240 residus.[7],[1]
This CED mediates efficient ion conduction and cation selectivity because it may allow cations to enter or exit the transmembrane pore. For this, the cap structure may provide a mechanism for enriching cation at the extracellular vestibule by utilizing a large patch of ).
CED constitutes the extracellular pathway to regulate ion permeation as selecticity properties of Piezo1 channels.[1]
Ion conducting pore
The of Piezo1 is lined with the , inner helix and cytosolic . The extracellular cations can approach the pore entry “vertically through the internal cavity along the threefold axis of the cap domain”, they can also approach laterally through spaces (gaps) between the flexible linkers which connect the cap with inner and outer helices.[8] The is situated below the , and is lined by the three inner transmembrane helices. The possible access for lipids or other hydrophobic molecules through the pore could be “two lateral openings between the inner helices separated by a ‘seal’ formed by ”. These openings are approximately 11 Å wide and 16 Å tall.[8]
CTD and Beam
CTD and are intracellular. The beam interacts with the CTD, and both are required for mechanical activation of the channel.[7]
The is a trimeric structure and is a part of the pore module of Piezo1 channel. The CTD interacts with the long , and forms a hydrophobic interface. This forms a tripartite interaction with the .[4]
It forms an intracellular vestibule along the z-axis, and it is essential for ion permeation properties.[7] The CTD triangular plane has a beam-facing side of the triangular, and it is separated into two surfaces with negative and positive electrostatic potentials.[4]
The beam is a 90 Å-long intracellular structure in the central region of the ion channel. It is a , propeller-shaped architecture characteristic of Piezo1. It is a piece of the “beam-CTD-anchor-OH-IH” relaying interface that forms the central pore module. It is because the beam connects the THU, to the CTD and the outer helix (OH) that it enables the transmission of the mechanical force, and thus the opening of Piezo1’s pore.[4] It delivers the mechanical signals from the blades, or the plasma membrane, to the central pore module region.[3]
Indeed, the beams are connected to the transmembrane helical units (THUs), which forms a triangular plane above its proximal end. This makes the largest intracellular loop of Piezo1, and it starts at the distal end of the beam, interacts with the CTD, and then folds back to the distal end of the beam before connecting to a transmembrane region. Moreover, the beam crosses through the beam-facing side of the triangular CTD, forming interactions with both CTDα 1 and CTDα 2.
This position and connections of the beam render it an ideal structure for mechanical transmission from the distal THUs to the central ion-conducting pore. The lever-like mechanotransduction apparatus constituted by the beam is possible because of its uneven movement. It displays large motion at the distal beam while subtle movement at the proximal end. It enables Piezo1 channels to effectively convert a large conformational change of the distal blades to a relatively slight opening of the central pore, allowing cation-selective permeation.[4]
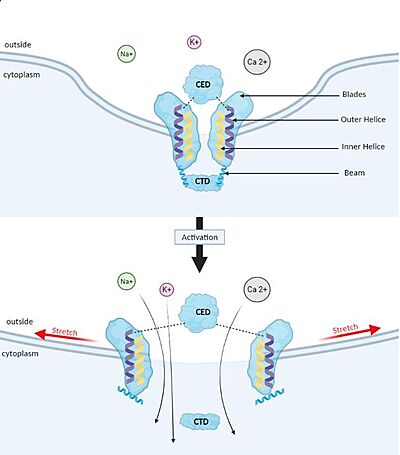
Membrane deformation and Gating mechanism of Piezo1 before and after activation by an external mechanical force. Gating mechanism
Piezo1 possesses delicate force sensing and mechanotransduction mechanisms. Here, we explain how Piezo1 channels sense and transduce mechanical forces to gate the central ion-conducting pore.
Piezo1 can sense membrane tension through changes in the local curvature of the membrane and the channel opens in response to this change thanks to this structure.[5]
Indeed, mPiezo trimer is a non-planar conformation inside lipid bilayer, it produces a local dome-shaped deformation of the membrane. In cells, this membrane curvature project towards the cytoplasm and some electrostatic interactions stabilize the trimeric assembly in its curved conformation.[6]
The structure of Piezo1 offers a plausible explanation for the origin of its tension gating. Indeed, if the semi-spherical dome becomes flatter when Piezo1 opens, then the channel membrane system will expand thanks to the flexibility of the blades.
However, because flattening does not constrain the pore to open wide, expansion and pore diameter are decoupled, such that Piezo1 can exhibit its small conductance and cation selectivity, properties that are essential to its function.[5],[9]
Function
The different forces perceived by Piezo1
Piezo1 is a mechanosensitive channel which means, it can sense external mechanical forces such as fluid flow-induced shear stress, osmotic stress, and pressure-induced membrane stretch. Moreover, “studies have demonstrated wide expression of the Piezo1 channel that enables many different types of cells to sense a diversity of “outside-in” mechanical forces, including indentation, membrane stretch, shear stress, osmotic stress, ultrasound, and compression”.[10] Since Piezo1 channel could also be activated by traction forces, there are two different mechanisms that have been proposed to explain the mechanical activation of Piezo1 channel. These mechanisms are called “force-from-lipids” and “force-from-filaments”.[10]
For the “force-from-lipids” mechanism, membrane tension is induced by mechanical forces. This membrane tension leads to a reorganization of lipids within and surrounding the channel proteins. This reorganization of lipids results into membrane lipid-channel protein interactions that induce the channel to open. We can note that a recent study (Lin et al., 2019)[9] gave support to this mechanism.
The “force-from-filaments” mechanism proposes that conformational changes occur thanks to interactions between the channel and extracellular matrix or intracellular cytoskeletal proteins resulting in the channel opening.[10]
The wide variety of Piezo1’s functions
Cells are able to perceive the filling of the stomach or the bladder, blood flow and lungs inflation.
Piezo1 is a sensor of mechanical forces in endothelial, urothelial and renal epithelial cells. For instance, Piezo1 is involved in shear stress sensing in blood vessel endothelial cells and is implicated in the development and physiological functions of the circulatory system, including the proper formation of blood, vessels, regulation of vascular tone and remodelling of small resistance arteries upon hypertension. It is also involved in the homeostasis of the volume of red blood cells.[2]
Piezo1 mediates cationic non-selective currents. Indeed, monovalent (Na+, K+) and divalent (Ca2+, Mg2+) can flow through Piezo1.
However, Piezo1 is implicated in excitatory channels because cations can enter into the cells which leads to the membrane depolarisation or calcium-dependent signalling pathway (if Ca2+ enters).[10]
When calcium-dependent signalling pathway is activated, NO can be released by endothelial cells and leads to vasodilation but also, some channels can be activated in red blood cells.[10]
Piezo1 has a wide variety of functions, but we will focus on the vascularisation.
Vascularisation: detection of shearing forces
Piezo1 plays a critical role in the formation of blood vessels. Indeed, fluid flow induces a frictional force, and this shear stress activates the Piezo1 channels located in endothelial cells’ membranes. It results in an alignment process, leading to healthy vascular development. The entry of Ca2+ is the key to the process. The shear stress-enhanced Ca2+ entry through Piezo1 channels is coupled with calpain activation. From this association steams proteolytic cleavage of cytoskeletal actin and focal adhesion proteins, which induces endothelial cell organisation and alignment.
A deficit in Piezo1’s expression can lead to a cobblestone-like appearance of endothelial cells’ organisation, instead of its standard linear appearance.
The subcellular localisation of Piezo1 is also determining. In static conditions, its repartition is even on the membrane, but when a mechanical stimulus arises, Piezo1 accumulates at the cell’s apical. This process characterises endothelial cells’ alignment toward frictional force.
However, Piezo1 is also able to drive endothelial cells migration without shear stress, through endothelial oxide synthase, a protein with major roles in vascular biology.[11]
Diseases
Since Piezo1 is implicated in the functioning of many cells and organs, modifications on its structure lead to diseases.
For instance, Hereditary Xerocytosis (HX) is a rare disease, also called Dehydrated hereditary stomatocytosis (DHS). This genetic disease leads to impaired red blood cell (RBC) membrane properties that affect intracellular cation concentrations.[12] The RBCs are abnormally shaped and they result in haemolytic anaemia. Those modifications are due to mutations on the FAM38A gene on chromosome 16 which encodes for Piezo 1. Piezo1 is expressed in the plasma membranes of RBCs, and its role is to control RBCs’ osmolarity. It also plays a prevalent role in the erythroid differentiation. Mutations in Piezo1 distort mechanosensitive channel regulation, leading to increased cation transport in erythroid cells. Those mutations affect different parts of the channel. For instance, six gain-of-function mutations, gathered in the central core region of the Piezo channel structure, are directly linked to the decrease of inactivation rate of the channel. Mutations in the N-terminal part of the protein also have a role in channel gating. Therefore, not every channel is affected in the same way and by the same mutation. Indeed it depends on the environment, the permeability of RBC and the combination of mutations [13].
Those mutations could provoke increases in permeability of cations in RBC by different mechanisms. It could induce mechanically activated currents that inactivate more slowly than wild-type currents. They could also affect the inactivation process by either destabilising the inactivated state or stabilising the channel in the open state. As a result, the open to inactivated state equilibrium shifts towards open. Na+ and Ca2+ ion influx consequently increase, and the intracellular K+ concentration decreases in a steady state. The evolution of Piezo1’s function steams from a change in its 3D structure.
Lymphatic dysplasia [14] is also a disease linked to loss of function mutations on Piezo1. The lymphatic system is independent from the vascular one, and its role is to transport antigens responsible for the immune response. If the interstitial fluid is not drained correctly back to the blood, it leads to local inflammation. The mutations on Piezo1 inactivate the channel gate and in this case the concentration of calcium is not increased. The protein isn’t sensitive to the pressure anymore.
Potential therapeutic target
Piezo1 is a protein discovered recently. Therefore, its potential in medicine is in constant evolution.
Piezo1 can be used as diagnostic biomarkers because it detects different mechanical forces and triggers a specific response adapted to the changes in the environment. For instance, it is sensitive to shear stress which has a major role in cardiovascular physiology[15].
This mechanosensitive receptor is a candidate for therapeutic innovation more specifically in the case of cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases.
These new therapies could be based on Piezo1 pharmacological modulators. Recently, several modulators have been found.
- Antagonists like peptide GsMTx4 [16] prevent the induction of demyelination, playing therefore a neuroprotective role. This peptide is an inhibitor of Piezo1.
- Agonists like Yoda1 [17] (a synthetic small molecule) enhance channels opening leading to demyelination and damaging the central nervous system. This molecule can activate the Piezo1 channel without mechanical stimulation. However, it can be useful to suppress the migration of transformed cells like fibroblasts. Jedi2 is another chemical activator of Piezo1, but it doesn’t act on the same site as Yoda1.
- Tubeimoside 1 (TBMS1) is an inhibitor of Yoda1 allowing a decrease of the activity of Piezo 1 channels in endothelial cells. The mechanism is still unclear but according to studies [18], TBMS1 might be a competitive inhibitor, meaning that it fixes itself on the same binding site as Yoda1 and is specific to Piezo1 channels.
Discovering those modulators allows a better understanding of the mechanisms of Piezo1 channels and highlights its usefulness in the pharmacological field.
Relevance
Even if a lot is already known about Piezo1's structure, the precise mechanism of the pore is still unknown. Moreover, Piezo1 is present in a large number of tissues, but the differences in its roles are unclear. Further research is required to allow a better understanding of diseases linked to Piezo1 (like DHS), and thus a better treatment of those diseases.
PBD

