We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1656
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
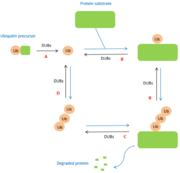
Deubiquitinases are key enzymes belonging to the vast group of '''proteases'''.They take part in the removal of ubiquitin molecules on proteins which have been ubiquitinated, allowing the degradation of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ubiquitin ubiquitin]-tagged proteins. As a result, these enzymes play an important role being implicated in the regulation of '''protein degradation'''. Indeed, the pathway for a protein to be degraded involves, an enzymatic cascade that will add a poly-ubiquitin fragment to the protein. This mechanism is called [https://fr.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ubiquitination ubiquitination(fr)] [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ubiquitin#Ubiquitylation (en)]. Following this step, mono or poly-ubiquitin is by deubiquitinases from the protein. | Deubiquitinases are key enzymes belonging to the vast group of '''proteases'''.They take part in the removal of ubiquitin molecules on proteins which have been ubiquitinated, allowing the degradation of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ubiquitin ubiquitin]-tagged proteins. As a result, these enzymes play an important role being implicated in the regulation of '''protein degradation'''. Indeed, the pathway for a protein to be degraded involves, an enzymatic cascade that will add a poly-ubiquitin fragment to the protein. This mechanism is called [https://fr.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ubiquitination ubiquitination(fr)] [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ubiquitin#Ubiquitylation (en)]. Following this step, mono or poly-ubiquitin is by deubiquitinases from the protein. | ||
| - | ==== | + | ==== Classes ==== |
| - | Deubiquitinases belong to the protease family. This family | + | Deubiquitinases belong to the large protease family. This family gathers into '''five classes''',all of them definded according to the nature of the amino acid composition of their active site carrying out the catalysis. It can be either : serine proteases, [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cysteine_protease cysteine proteases], acid proteases, metalloproteases, or threonine proteases. DUBs belong to only two of these families: '''metalloproteases''' and '''cysteine proteases'''. |
| - | Among the cysteine proteins, four subfamilies can be described according to their catalytic domains: ubiquitin-specific proteases ( | + | Among the cysteine proteins, four subfamilies can be described according to their catalytic domains: ubiquitin-specific proteases (USPs),the Ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolases (UCHs),Ovarian tumore-related proteases (OTUs) and Machado-Joseph disease proteases (MJD). The deubiquitinases belonging to the family of metalloproteases all have a JAMM catalytic domain (JAB1/MPN/Mov34 metalloenzyme). |
Within these two families, DUBs are classified into subfamilies according to the differences in their amino acid sequences surrounding the catalytically active amino acid residues. <ref>PMID:15571815</ref> | Within these two families, DUBs are classified into subfamilies according to the differences in their amino acid sequences surrounding the catalytically active amino acid residues. <ref>PMID:15571815</ref> | ||
Revision as of 13:11, 17 January 2022
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 26/11/2020, through 26/11/2021 for use in the course "Structural Biology" taught by Bruno Kieffer at the University of Strasbourg, ESBS. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1643 through Sandbox Reserved 1664. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Deubiquitinases
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Mukhopadhyay D, Riezman H. Proteasome-independent functions of ubiquitin in endocytosis and signaling. Science. 2007 Jan 12;315(5809):201-5. doi: 10.1126/science.1127085. PMID:17218518 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.1127085
- ↑ Schnell JD, Hicke L. Non-traditional functions of ubiquitin and ubiquitin-binding proteins. J Biol Chem. 2003 Sep 19;278(38):35857-60. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R300018200. Epub 2003, Jul 14. PMID:12860974 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.R300018200
- ↑ Amerik AY, Hochstrasser M. Mechanism and function of deubiquitinating enzymes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004 Nov 29;1695(1-3):189-207. doi:, 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2004.10.003. PMID:15571815 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2004.10.003
- ↑ Urbe S, Liu H, Hayes SD, Heride C, Rigden DJ, Clague MJ. Systematic survey of deubiquitinase localization identifies USP21 as a regulator of centrosome- and microtubule-associated functions. Mol Biol Cell. 2012 Mar;23(6):1095-103. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E11-08-0668. Epub 2012, Feb 1. PMID:22298430 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E11-08-0668
- ↑ Huang OW, Ma X, Yin J, Flinders J, Maurer T, Kayagaki N, Phung Q, Bosanac I, Arnott D, Dixit VM, Hymowitz SG, Starovasnik MA, Cochran AG. Phosphorylation-dependent activity of the deubiquitinase DUBA. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2012 Jan 15;19(2):171-5. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2206. PMID:22245969 doi:10.1038/nsmb.2206
- ↑ Huang OW, Ma X, Yin J, Flinders J, Maurer T, Kayagaki N, Phung Q, Bosanac I, Arnott D, Dixit VM, Hymowitz SG, Starovasnik MA, Cochran AG. Phosphorylation-dependent activity of the deubiquitinase DUBA. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2012 Jan 15;19(2):171-5. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2206. PMID:22245969 doi:10.1038/nsmb.2206
- ↑ https://authors.library.caltech.edu/261/1/AMBpb04.pdf
- ↑ Das C, Hoang QQ, Kreinbring CA, Luchansky SJ, Meray RK, Ray SS, Lansbury PT, Ringe D, Petsko GA. Structural basis for conformational plasticity of the Parkinson's disease-associated ubiquitin hydrolase UCH-L1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Mar 21;103(12):4675-80. Epub 2006 Mar 13. PMID:16537382
- ↑ Huang OW, Ma X, Yin J, Flinders J, Maurer T, Kayagaki N, Phung Q, Bosanac I, Arnott D, Dixit VM, Hymowitz SG, Starovasnik MA, Cochran AG. Phosphorylation-dependent activity of the deubiquitinase DUBA. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2012 Jan 15;19(2):171-5. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2206. PMID:22245969 doi:10.1038/nsmb.2206
- ↑ Amerik AY, Hochstrasser M. Mechanism and function of deubiquitinating enzymes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004 Nov 29;1695(1-3):189-207. doi:, 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2004.10.003. PMID:15571815 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2004.10.003
- ↑ Singhal S, Taylor MC, Baker RT. Deubiquitylating enzymes and disease. BMC Biochem. 2008 Oct 21;9 Suppl 1:S3. doi: 10.1186/1471-2091-9-S1-S3. PMID:19007433 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1471-2091-9-S1-S3
- ↑ Sun J, Shi X, Mamun MAA, Gao Y. The role of deubiquitinating enzymes in gastric cancer. Oncol Lett. 2020 Jan;19(1):30-44. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.11062. Epub 2019 Nov 7. PMID:31897112 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.3892/ol.2019.11062
- ↑ Saldana M, VanderVorst K, Berg AL, Lee H, Carraway KL. Otubain 1: a non-canonical deubiquitinase with an emerging role in cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2019 Jan 1;26(1):R1-R14. doi: 10.1530/ERC-18-0264. PMID:30400005 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1530/ERC-18-0264