We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1647
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 70: | Line 70: | ||
Th1, Th2 and Th17 cells are the main cells involved in the pathophysiology of asthma <ref name="Effect of ginger extract on expression of GATA3, T-bet and ROR-γt in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with Allergic Asthma">DOI 10.1016/j.aller.2018.12.003</ref>. In asthmatic airways, Th2 cells are activated and release several cytokines <ref name="The role of protein modifications of T-bet in cytokine production and differentiation of T helper cells">DOI 10.1155/2014/589672</ref> that regulate IgE production and inflammatory cell recruitment, such as eosinophils. Th2 cells and GATA-3 play an important role in allergic inflammation and asthma, and induce IgE production, which can be the cause of severe forms of asthma. The asthmatic patients present high levels of total IgE. On the contrary, the T-bet gene expression and Th1 pattern, along with the IFN- γ production, are usually associated with non-allergic asthmatics and healthy subjects <ref name="Asthma: T-bet--a master controller?">DOI 10.1016/s0960-9822(02)00830-8</ref>. Also, some research has shown that airway reactivity is moderated by corticosteroid use in asthma patients and that with this use, the TBX21 variant increases Th1 and decreases Th2 cytokine expression. Thus, TBX21 may be decisive in the therapy of asthma with inhaled corticosteroids <ref name="TBX21: A functional variant predicts improvement in asthma with the use of inhaled corticosteroids">DOI 10.1073/pnas.0408532102</ref>. | Th1, Th2 and Th17 cells are the main cells involved in the pathophysiology of asthma <ref name="Effect of ginger extract on expression of GATA3, T-bet and ROR-γt in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with Allergic Asthma">DOI 10.1016/j.aller.2018.12.003</ref>. In asthmatic airways, Th2 cells are activated and release several cytokines <ref name="The role of protein modifications of T-bet in cytokine production and differentiation of T helper cells">DOI 10.1155/2014/589672</ref> that regulate IgE production and inflammatory cell recruitment, such as eosinophils. Th2 cells and GATA-3 play an important role in allergic inflammation and asthma, and induce IgE production, which can be the cause of severe forms of asthma. The asthmatic patients present high levels of total IgE. On the contrary, the T-bet gene expression and Th1 pattern, along with the IFN- γ production, are usually associated with non-allergic asthmatics and healthy subjects <ref name="Asthma: T-bet--a master controller?">DOI 10.1016/s0960-9822(02)00830-8</ref>. Also, some research has shown that airway reactivity is moderated by corticosteroid use in asthma patients and that with this use, the TBX21 variant increases Th1 and decreases Th2 cytokine expression. Thus, TBX21 may be decisive in the therapy of asthma with inhaled corticosteroids <ref name="TBX21: A functional variant predicts improvement in asthma with the use of inhaled corticosteroids">DOI 10.1073/pnas.0408532102</ref>. | ||
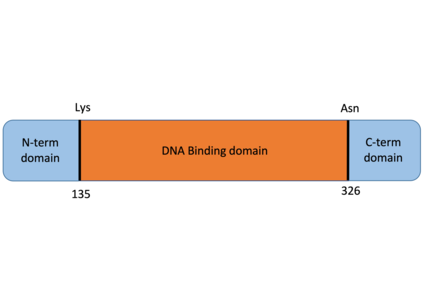
| - | In T-bet structure, ubiquitination takes place at LYS 313. It has an impact on the stability of the protein and leads to the degradation of the protein by the proteosome. Some research | + | In T-bet structure, ubiquitination takes place at LYS 313. It has an impact on the stability of the protein and leads to the degradation of the protein by the proteosome. Some research has shown the role of deubiquitinases involved in T-bet stability and function. As a deubiquitinase, USP10 belongs to the ubiquitin-specificprotease family of cysteine proteases. Cysteine 424 site on [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/USP10 USP10] is crucial for its hydrolase activity. Results have shown that USP10 could interact with T-bet and stabilize it via interaction between Lysine 313 of T-bet and Cysteine 424 of USP10. Deubiquitination inhibits its degradation by the proteosome and enhance the secretion of IFN- γ. |
Researchers believe that the USP10-dependent T-bet deubiquitination and stabilization can regulate antigen induced immune disorder especially in Th1 specific inflammation. Thus, appropriate decreasing USP10 level may contribute to the T-bet degradation and inflammation attenuation <ref name="Deubiquitination and stabilization of T-bet by USP10">DOI 10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.05.037</ref>. | Researchers believe that the USP10-dependent T-bet deubiquitination and stabilization can regulate antigen induced immune disorder especially in Th1 specific inflammation. Thus, appropriate decreasing USP10 level may contribute to the T-bet degradation and inflammation attenuation <ref name="Deubiquitination and stabilization of T-bet by USP10">DOI 10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.05.037</ref>. | ||
Revision as of 16:51, 17 January 2022
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ TBX21/T-Bet polyclonal antibody : https://www.thermofisher.com/antibody/product/TBX21-T-bet-Antibody-Polyclonal/13700-1-AP
- ↑ TBX21-GeneCards : TBX21 - T-box Transcription factor 21 :https://www.genecards.org/cgi-bin/carddisp.pl?gene=TBX21
- ↑ Mehta DS, Wurster AL, Weinmann AS, Grusby MJ. NFATc2 and T-bet contribute to T-helper-cell-subset-specific regulation of IL-21 expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Feb 8;102(6):2016-21. doi:, 10.1073/pnas.0409512102. Epub 2005 Jan 31. PMID:15684054 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0409512102
- ↑ Jang EJ, Park HR, Hong JH, Hwang ES. Lysine 313 of T-box is crucial for modulation of protein stability, DNA binding, and threonine phosphorylation of T-bet. J Immunol. 2013 Jun 1;190(11):5764-70. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1203403. Epub 2013, Apr 24. PMID:23616576 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1203403
- ↑ Wang P, Wang Y, Xie L, Xiao M, Wu J, Xu L, Bai Q, Hao Y, Huang Q, Chen X, He R, Li B, Yang S, Chen Y, Wu Y, Ye L. The Transcription Factor T-Bet Is Required for Optimal Type I Follicular Helper T Cell Maintenance During Acute Viral Infection. Front Immunol. 2019 Mar 29;10:606. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00606. eCollection, 2019. PMID:30984183 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.00606
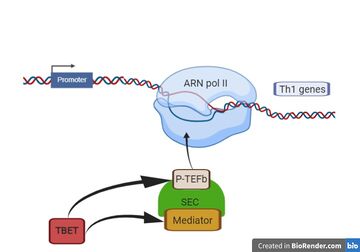
- ↑ Hertweck A, Evans CM, Eskandarpour M, Lau JC, Oleinika K, Jackson I, Kelly A, Ambrose J, Adamson P, Cousins DJ, Lavender P, Calder VL, Lord GM, Jenner RG. T-bet Activates Th1 Genes through Mediator and the Super Elongation Complex. Cell Rep. 2016 Jun 21;15(12):2756-70. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.05.054. Epub, 2016 Jun 9. PMID:27292648 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2016.05.054
- ↑ Koch MA, Tucker-Heard G, Perdue NR, Killebrew JR, Urdahl KB, Campbell DJ. The transcription factor T-bet controls regulatory T cell homeostasis and function during type 1 inflammation. Nat Immunol. 2009 Jun;10(6):595-602. doi: 10.1038/ni.1731. Epub 2009 May 3. PMID:19412181 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/ni.1731
- ↑ Szabo, S. J., Kim, S. T., Costa, G. L., Zhang, X., Fathman, C. G., & Glimcher, L. H. (2000). A novel transcription factor, T-bet, directs Th1 lineage commitment. Cell, 100(6), 655–669. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80702-3
- ↑ Lazarevic V, Chen X, Shim JH, Hwang ES, Jang E, Bolm AN, Oukka M, Kuchroo VK, Glimcher LH. T-bet represses T(H)17 differentiation by preventing Runx1-mediated activation of the gene encoding RORgammat. Nat Immunol. 2011 Jan;12(1):96-104. doi: 10.1038/ni.1969. Epub 2010 Dec 12. PMID:21151104 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/ni.1969
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Douglas.S.Robinson and Clare M Lloyd. Asthma: T-bet - A master controller ? Volume 12, Issue 9, PR322-R324, April 30, (2002) https://doi.org/10.1016/S0960-9822(02)00830-8
- ↑ Kardan M, Rafiei A, Ghaffari J, Valadan R, Morsaljahan Z, Haj-Ghorbani ST. Effect of ginger extract on expression of GATA3, T-bet and ROR-gammat in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with Allergic Asthma. Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 2019 Jul - Aug;47(4):378-385. doi:, 10.1016/j.aller.2018.12.003. Epub 2019 Feb 10. PMID:30745246 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.aller.2018.12.003
- ↑ Oh S, Hwang ES. The role of protein modifications of T-bet in cytokine production and differentiation of T helper cells. J Immunol Res. 2014;2014:589672. doi: 10.1155/2014/589672. Epub 2014 May 13. PMID:24901011 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/589672
- ↑ Tantisira KG, Hwang ES, Raby BA, Silverman ES, Lake SL, Richter BG, Peng SL, Drazen JM, Glimcher LH, Weiss ST. TBX21: a functional variant predicts improvement in asthma with the use of inhaled corticosteroids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Dec 28;101(52):18099-104. doi:, 10.1073/pnas.0408532102. Epub 2004 Dec 16. PMID:15604153 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0408532102
- ↑ Pan L, Chen Z, Wang L, Chen C, Li D, Wan H, Li B, Shi G. Deubiquitination and stabilization of T-bet by USP10. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014 Jul 4;449(3):289-94. doi:, 10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.05.037. Epub 2014 May 17. PMID:24845384 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.05.037
- ↑ Spector SL, Wangaard CH, Farr RS. Aspirin and concomitant idiosyncrasies in adult asthmatic patients. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1979 Dec;64(6 Pt 1):500-6. doi:, 10.1016/0091-6749(79)90059-9. PMID:512268 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0091-6749(79)90059-9