SARS-CoV-2 virus proteins
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
* NSP5: [[SARS-CoV-2 enzyme 3CL-PRO|SARS 3CL-PRO]]: Main proteinase | * NSP5: [[SARS-CoV-2 enzyme 3CL-PRO|SARS 3CL-PRO]]: Main proteinase | ||
* [[SARS-CoV-2_protein_NSP6|NSP6]]: '''''AlphaFold2 Theoretical Model''''' - Plays a role in the initial induction of autophagosomes from host reticulum endoplasmic. | * [[SARS-CoV-2_protein_NSP6|NSP6]]: '''''AlphaFold2 Theoretical Model''''' - Plays a role in the initial induction of autophagosomes from host reticulum endoplasmic. | ||
| - | * [[SARS-CoV-2_protein_NSP7|NSP7]]: | + | * [[SARS-CoV-2_protein_NSP7|NSP7]]: NSP7 together with NSP8 aid the virus to make new copies of the RNA genome. |
* [[SARS-CoV-2_protein_NSP8|NSP8]]: ''Non-structural protein 8''. | * [[SARS-CoV-2_protein_NSP8|NSP8]]: ''Non-structural protein 8''. | ||
* [[SARS-CoV-2_protein_NSP9|NSP9]]: ''Non-structural protein 9''. | * [[SARS-CoV-2_protein_NSP9|NSP9]]: ''Non-structural protein 9''. | ||
Revision as of 12:54, 8 February 2022
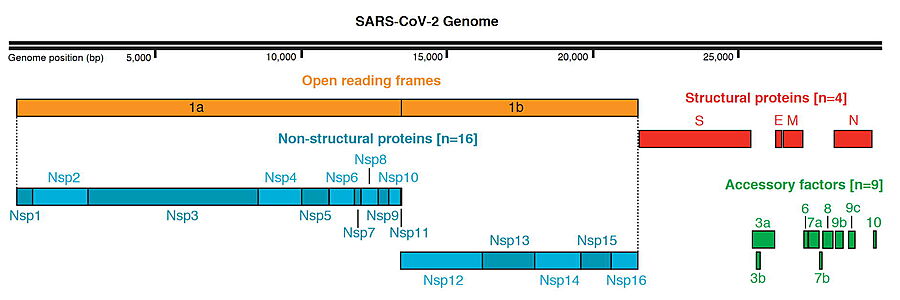
SARS-CoV-2 Protein Organization, from Gordon et al. & Krogan (2020)[1] )
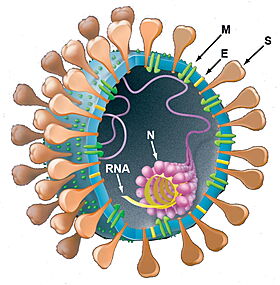
Organization of SARS-CoV-2 virus (from Holmes & Enjuanes (2003)[2])
| The quality of SARS-CoV-2 experimentally determined structures varies widely (Grabowski et al., 2021). Validated and corrected structures can be obtained from COVID19.BioReproducibility.Org. |
The genome of the SARS-CoV-2 virus codes for 28 proteins:
Out of those, 19 have already been characterized structurally. For the rest there are accurate AlphaFold2 predicted structures.
Details of the 3D structure & function of the key proteins & RNA inside the virus can be seen in the NY Times[3].
"The first viral protein created inside the infected cell, ORF1ab, is actually a chain of 16 proteins joined together. Two of these proteins act like scissors, snipping the links between the different proteins and freeing them to do their jobs."[3]
- Main protease: it is a cysteine protease that is essential for the viral life cycle.
- NSP1: Inhibits host translation by interacting with the 40S ribosomal subunit.
- NSP2: May play a role in the modulation of host cell survival signaling pathway by interacting with host PHB and PHB2.
- NSP3: Papain-like proteinase
- NSP4: Participates in the assembly of virally-induced cytoplasmic double-membrane vesicles necessary for viral replication.[1][2]
- NSP5: SARS 3CL-PRO: Main proteinase
- NSP6: AlphaFold2 Theoretical Model - Plays a role in the initial induction of autophagosomes from host reticulum endoplasmic.
- NSP7: NSP7 together with NSP8 aid the virus to make new copies of the RNA genome.
- NSP8: Non-structural protein 8.
- NSP9: Non-structural protein 9.
- NSP10: Non-structural protein 10.
- RNA-directed RNA polymerase (RdRp)
- Helicase (Hel): Multi-functional protein with a zinc-binding domain in N-terminus
- Guanine-N7 methyltransferase (ExoN)
- Uridylate-specific endoribonuclease (NendoU)
- 2'-O-methyltransferase (2'-O-MT): Methyltransferase that mediates mRNA cap 2'-O-ribose methylation to the 5'-cap structure of viral mRNAs.
- Surface glycoprotein (S) and SARS-CoV-2 protein S priming by furin
- ORF3a: Forms homotetrameric potassium sensitive ion channels (viroporin) and may modulate virus release.
- Protein E: Plays a central role in virus morphogenesis and assembly.
- Protein M: AlphaFold2 Theoretical Model - Component of the viral envelope.
- Protein N: AlphaFold2 Theoretical Model - Packages the positive strand viral genome RNA into a helical ribonucleocapsid (RNP).
- ORF6: Could be a determinant of virus virulence.
- ORF7a: Non-structural protein which is dispensable for virus replication in cell culture.
- ORF8: Open Reading Frame 8.
- ORF10:AlphaFold2 Theoretical Model - It is currently unclear whether this region translates into a functional protein.
References
- ↑ Gordon DE, Jang GM, Bouhaddou M, Xu J, Obernier K, O'Meara MJ, Guo JZ, Swaney DL, Tummino TA, Huttenhain R, Kaake RM, Richards AL, Tutuncuoglu B, Foussard H, Batra J, Haas K, Modak M, Kim M, Haas P, Polacco BJ, Braberg H, Fabius JM, Eckhardt M, Soucheray M, Bennett MJ, Cakir M, McGregor MJ, Li Q, Naing ZZC, Zhou Y, Peng S, Kirby IT, Melnyk JE, Chorba JS, Lou K, Dai SA, Shen W, Shi Y, Zhang Z, Barrio-Hernandez I, Memon D, Hernandez-Armenta C, Mathy CJP, Perica T, Pilla KB, Ganesan SJ, Saltzberg DJ, Ramachandran R, Liu X, Rosenthal SB, Calviello L, Venkataramanan S, Lin Y, Wankowicz SA, Bohn M, Trenker R, Young JM, Cavero D, Hiatt J, Roth T, Rathore U, Subramanian A, Noack J, Hubert M, Roesch F, Vallet T, Meyer B, White KM, Miorin L, Agard D, Emerman M, Ruggero D, Garcia-Sastre A, Jura N, von Zastrow M, Taunton J, Schwartz O, Vignuzzi M, d'Enfert C, Mukherjee S, Jacobson M, Malik HS, Fujimori DG, Ideker T, Craik CS, Floor S, Fraser JS, Gross J, Sali A, Kortemme T, Beltrao P, Shokat K, Shoichet BK, Krogan NJ. A SARS-CoV-2-Human Protein-Protein Interaction Map Reveals Drug Targets and Potential Drug-Repurposing. bioRxiv. 2020 Mar 22. doi: 10.1101/2020.03.22.002386. PMID:32511329 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/2020.03.22.002386
- ↑ Holmes KV, Enjuanes L. Virology. The SARS coronavirus: a postgenomic era. Science. 2003 May 30;300(5624):1377-8. doi: 10.1126/science.1086418. PMID:12775826 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.1086418
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 NY Times (3-Apr-2020) Bad News Wrapped in Protein: Inside the Coronavirus Genome
