Methionine synthase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Methionine synthase== | ==Methionine synthase== | ||
| - | <StructureSection load='1k7y' size='310' side='right' caption=' | + | <StructureSection load='1k7y' size='310' side='right' caption='B12 dependent fragment of E. coli methionine synthase with Cobalt (in pink)' scene=''> |
This page is being worked on during the Spring 2022 semester. | This page is being worked on during the Spring 2022 semester. | ||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
PDB ID: 1K7Y - cobalamin, 1K98 - AdoMet complex | PDB ID: 1K7Y - cobalamin, 1K98 - AdoMet complex | ||
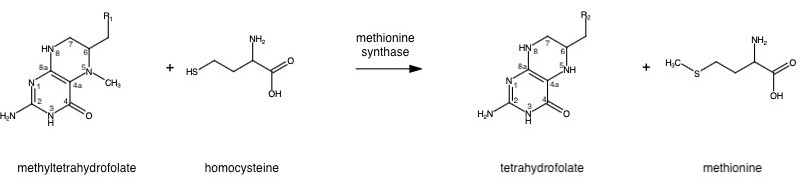
| - | Methionine is an essential amino acid required by our bodies for healthy cell and tissue growth. It is essential as it is not naturally derived, and | + | Methionine is an essential amino acid required by our bodies for healthy cell and tissue growth. It is essential as it is not naturally derived, and is obtained from our diet first in the form of homocysteine. Methionine synthase (MetH) is a B12-dependent enzyme that methylates homocysteine to regenerate methionine as needed. |
| - | + | == Structural highlights == | |
| - | The | + | The <scene name='90/907471/Superposition_1/2'>full structure of MetH</scene> has yet to be determined but we understand it contains 4 domains of B12 cobalamin (in pink), methyltetrahydrofolate (blue), homocysteine (yellow), and SAH (as part of the SAM cycle; in red). Each domain with an important function required for catalytic and reactivation cycles<ref>DOI: 10.1038/nsb738</ref>. |
| - | + | [[Image:Overall.jpeg]] | |
| - | + | The change from homocysteine to methionine is an SN2 reaction where the methyl group from methyltetrahydrofolate (MTHF), located on N-5, is donated. MTHF is a product of MTHFR. | |
| - | + | This is a complex reaction as the product, tetrahydrofolate, is a poor leaving group, thus requiring a "super nucleophile"<ref>DOI: 10.1038/nature10916</ref> with a protein-bound vitamin B12 cobalamin as the methyl carrier. | |
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
| - | == Vitamin | + | == Vitamin B12 == |
| + | MetH is B12 d | ||
== Oxidation States of Cobalamin == | == Oxidation States of Cobalamin == | ||
Revision as of 18:46, 5 April 2022
Contents |
Methionine synthase
| |||||||||||
Vitamin B12
MetH is B12 d
Oxidation States of Cobalamin
Co(I) - active, unstable, high energy
Co(II) - common oxidation state
Relevance
Methionine deficiency can result in diseases such as birth abnormalities[3].
References
- ↑ Bandarian V, Pattridge KA, Lennon BW, Huddler DP, Matthews RG, Ludwig ML. Domain alternation switches B(12)-dependent methionine synthase to the activation conformation. Nat Struct Biol. 2002 Jan;9(1):53-6. PMID:11731805 doi:10.1038/nsb738
- ↑ Kung Y, Ando N, Doukov TI, Blasiak LC, Bender G, Seravalli J, Ragsdale SW, Drennan CL. Visualizing molecular juggling within a B(12)-dependent methyltransferase complex. Nature. 2012 Mar 14. doi: 10.1038/nature10916. PMID:22419154 doi:10.1038/nature10916
- ↑ Kung Y, Ando N, Doukov TI, Blasiak LC, Bender G, Seravalli J, Ragsdale SW, Drennan CL. Visualizing molecular juggling within a B(12)-dependent methyltransferase complex. Nature. 2012 Mar 14. doi: 10.1038/nature10916. PMID:22419154 doi:10.1038/nature10916
- ↑ Barra L, Fontenelle C, Ermel G, Trautwetter A, Walker GC, Blanco C. Interrelations between glycine betaine catabolism and methionine biosynthesis in Sinorhizobium meliloti strain 102F34. J Bacteriol. 2006 Oct;188(20):7195-204. doi: 10.1128/JB.00208-06. PMID:17015658 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/JB.00208-06
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Kia Yang, Karsten Theis, Michal Harel, Anna Postnikova, Michael O'Shaughnessy