Sandbox Reserved 1724
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
=== Key Substrate Binding Residues === | === Key Substrate Binding Residues === | ||
| - | VKOR uses two catalytic amino acids, tyrosine 139 and asparagine 80, to stabilize binding to all forms of <scene name='90/904329/Kohhbond/2'>vitamin K</scene> and <scene name='90/904329/Warfarinhbond/3'>vitamin K antagonists</scene>, such as Warfarin, in the binding pocket. Tyr139 and Asn80 hydrogen bond to carbonyl groups on both structures and stabilizes them within the binding pocket. | + | VKOR uses two catalytic amino acids, tyrosine 139 and asparagine 80, to stabilize binding to all forms of <scene name='90/904329/Kohhbond/2'>vitamin K</scene> and <scene name='90/904329/Warfarinhbond/3'>vitamin K antagonists</scene>, such as Warfarin, in the binding pocket. Tyr139 and Asn80 hydrogen bond to carbonyl groups on both structures and stabilizes them within the binding pocket <ref name="Liu">PMID:33154105</ref>. |
=== Hydrophobic Interactions === | === Hydrophobic Interactions === | ||
| - | Other than the two previously mentioned hydrogen bonds (Tyr139 and Asn80), <scene name='90/904329/Kohhydrophobic/2'>vitamin K</scene> and <scene name='90/904329/Warfarinhydrophobic/1'>antagonists</scene> are bound | + | Other than the two previously mentioned hydrogen bonds (Tyr139 and Asn80), <scene name='90/904329/Kohhydrophobic/2'>vitamin K</scene> and <scene name='90/904329/Warfarinhydrophobic/1'> VKOR antagonists</scene> are bound via hydrophobic interactions within the binding pocket of VKOR. Hydrophobic residues of VKOR such as Phe80, Phe87, and Tyr88, form a hydrophobic tunnel within the binding pocket <ref name="Liu">PMID:33154105</ref>. |
== Medical Relevance == | == Medical Relevance == | ||
Revision as of 19:22, 7 April 2022
| This Sandbox is Reserved from February 28 through September 1, 2022 for use in the course CH462 Biochemistry II taught by R. Jeremy Johnson at the Butler University, Indianapolis, USA. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1700 through Sandbox Reserved 1729. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
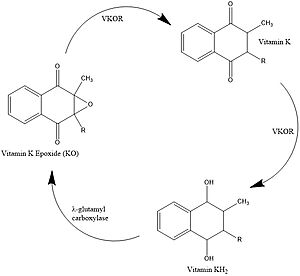
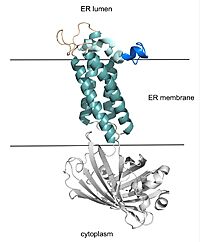
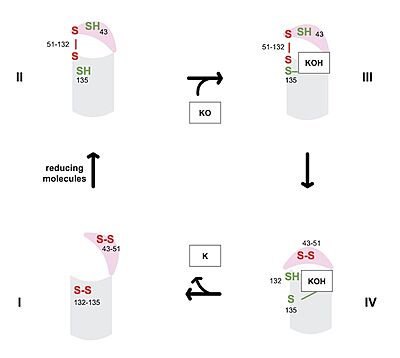
Vitamin K Epoxide Reductase
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Stafford DW. The vitamin K cycle. J Thromb Haemost. 2005 Aug;3(8):1873-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2005.01419.x. PMID:16102054 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1538-7836.2005.01419.x
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 Liu S, Li S, Shen G, Sukumar N, Krezel AM, Li W. Structural basis of antagonizing the vitamin K catalytic cycle for anticoagulation. Science. 2020 Nov 5. pii: science.abc5667. doi: 10.1126/science.abc5667. PMID:33154105 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.abc5667
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Patel S, Singh R, Preuss CV, Patel N. Warfarin PMID:29261922
- ↑ Wu S, Chen X, Jin DY, Stafford DW, Pedersen LG, Tie JK. Warfarin and vitamin K epoxide reductase: a molecular accounting for observed inhibition. Blood. 2018 Aug 9;132(6):647-657. doi: 10.1182/blood-2018-01-830901. Epub 2018, May 9. PMID:29743176 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1182/blood-2018-01-830901
- ↑ Chong YK, Mak TW. Superwarfarin (Long-Acting Anticoagulant Rodenticides) Poisoning: from Pathophysiology to Laboratory-Guided Clinical Management. Clin Biochem Rev. 2019 Nov;40(4):175-185. doi: 10.33176/AACB-19-00029. PMID:31857739 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.33176/AACB-19-00029
Student Contributors
Izabella Jordan, Emma Varness