This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Methionine synthase
From Proteopedia
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
PDB ID: 1K7Y, the B12 domain of MS. | PDB ID: 1K7Y, the B12 domain of MS. | ||
| - | [ | + | [PICTURE OF B12] |
In the Cob(I)alamin binding domain, the imidazole side chain containing His 759 replaces the dimethylbenzimidazole (DMB) ligand. His 759 then bonds to Asp 757 and See 810 via hydrogen bonds to create a ligand trifecta that increases the efficiency of the methyl transfer during the catalytic cycle<ref name="Bandarian et al"/>. | In the Cob(I)alamin binding domain, the imidazole side chain containing His 759 replaces the dimethylbenzimidazole (DMB) ligand. His 759 then bonds to Asp 757 and See 810 via hydrogen bonds to create a ligand trifecta that increases the efficiency of the methyl transfer during the catalytic cycle<ref name="Bandarian et al"/>. | ||
Revision as of 14:26, 13 April 2022
This page is being worked on during the Spring 2022 semester.
Function
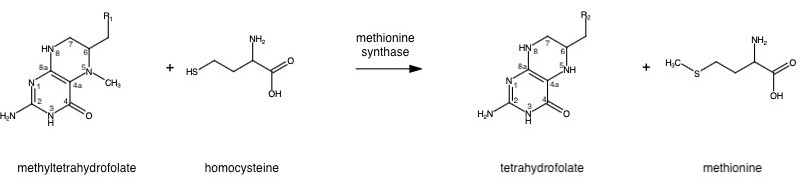
Methionine is an essential amino acid required by our bodies for healthy cell and tissue growth. It is essential because is not naturally derived, and must be obtained from our diet first in the form of homocysteine. Methionine synthase (abbrev. MS; EC: 2.1.1.13), a B12-dependent enzyme, is a critical part of the one-carbon metabolism cycle because it converts homocysteine to methionine.
The change from homocysteine to methionine is an SN2 reaction, as seen above, where the methyl group on N-5 from methyltetrahydrofolate (MTHF), is donated. MTHF is a product of Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) from the folate cycle [link Shaylie's page here]. This is a complex reaction as tetrahydrofolate (THF), the product, is a poor leaving group, thus requiring a "super nucleophile", vitamin B12 cob(I)alamin, to carry out the reaction[1].
Relevance
Methionine deficiency can result in diseases such as birth abnormalities[1].
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Kung Y, Ando N, Doukov TI, Blasiak LC, Bender G, Seravalli J, Ragsdale SW, Drennan CL. Visualizing molecular juggling within a B(12)-dependent methyltransferase complex. Nature. 2012 Mar 14. doi: 10.1038/nature10916. PMID:22419154 doi:10.1038/nature10916
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Bandarian V, Pattridge KA, Lennon BW, Huddler DP, Matthews RG, Ludwig ML. Domain alternation switches B(12)-dependent methionine synthase to the activation conformation. Nat Struct Biol. 2002 Jan;9(1):53-6. PMID:11731805 doi:10.1038/nsb738
- ↑ Barra L, Fontenelle C, Ermel G, Trautwetter A, Walker GC, Blanco C. Interrelations between glycine betaine catabolism and methionine biosynthesis in Sinorhizobium meliloti strain 102F34. J Bacteriol. 2006 Oct;188(20):7195-204. doi: 10.1128/JB.00208-06. PMID:17015658 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/JB.00208-06
- ↑ doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0906132106
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Kia Yang, Karsten Theis, Michal Harel, Anna Postnikova, Michael O'Shaughnessy