We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1724
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
===Superwarfarins=== | ===Superwarfarins=== | ||
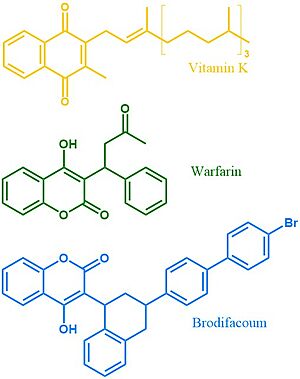
| - | [[Image:VKOR_Substrates.jpg|300 px| | + | [[Image:VKOR_Substrates.jpg|300 px|left|thumb|'''Figure 4. Vitamin K, Warfarin, and Brodifacoum''' Above is a comparison of the 2D structures of VKOR's natural substrate, the blood thinner warfarin, and the superwarfarin brodifacoum.]] |
More potent warfarin derivatives, called [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Superwarfarin superwarfarins], are used as rodenticides. Superwarfarins have bulkier side chains that allow them to stay bound to VKOR for long periods of time, causing prolonged and uncontrolled bleeding<ref name="Chong">PMID:31857739</ref>. The enhanced binding is due to interactions between the bulky side chains and the hydrophobic residues of VKOR's binding pocket. The duration of one superwarfarin, [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Brodifacoum brodifacoum], has been reported as 15-30 days <ref name="Chong">PMID:31857739</ref> vs. the clinical warfarin duration of 2-5 days<ref name="Patel">PMID:29261922</ref>. | More potent warfarin derivatives, called [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Superwarfarin superwarfarins], are used as rodenticides. Superwarfarins have bulkier side chains that allow them to stay bound to VKOR for long periods of time, causing prolonged and uncontrolled bleeding<ref name="Chong">PMID:31857739</ref>. The enhanced binding is due to interactions between the bulky side chains and the hydrophobic residues of VKOR's binding pocket. The duration of one superwarfarin, [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Brodifacoum brodifacoum], has been reported as 15-30 days <ref name="Chong">PMID:31857739</ref> vs. the clinical warfarin duration of 2-5 days<ref name="Patel">PMID:29261922</ref>. | ||
Revision as of 17:36, 14 April 2022
–
| This Sandbox is Reserved from February 28 through September 1, 2022 for use in the course CH462 Biochemistry II taught by R. Jeremy Johnson at the Butler University, Indianapolis, USA. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1700 through Sandbox Reserved 1729. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
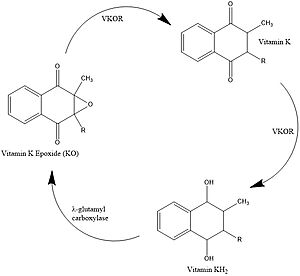
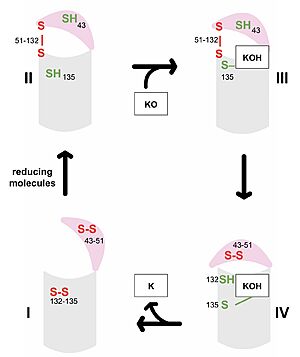
Vitamin K Epoxide Reductase
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Stafford DW. The vitamin K cycle. J Thromb Haemost. 2005 Aug;3(8):1873-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2005.01419.x. PMID:16102054 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1538-7836.2005.01419.x
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Blanchard RA, Furie BC, Jorgensen M, Kruger SF, Furie B. Acquired vitamin K-dependent carboxylation deficiency in liver disease. N Engl J Med. 1981 Jul 30;305(5):242-8. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198107303050502. PMID:6165889 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1056/NEJM198107303050502
- ↑ Swanson JC, Suttie JW. Vitamin K dependent in vitro production of prothrombin. Biochemistry. 1982 Nov 9;21(23):6011-8. doi: 10.1021/bi00266a044. PMID:6758841 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/bi00266a044
- ↑ 4.00 4.01 4.02 4.03 4.04 4.05 4.06 4.07 4.08 4.09 4.10 4.11 Liu S, Li S, Shen G, Sukumar N, Krezel AM, Li W. Structural basis of antagonizing the vitamin K catalytic cycle for anticoagulation. Science. 2020 Nov 5. pii: science.abc5667. doi: 10.1126/science.abc5667. PMID:33154105 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.abc5667
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Patel S, Singh R, Preuss CV, Patel N. Warfarin PMID:29261922
- ↑ Wu S, Chen X, Jin DY, Stafford DW, Pedersen LG, Tie JK. Warfarin and vitamin K epoxide reductase: a molecular accounting for observed inhibition. Blood. 2018 Aug 9;132(6):647-657. doi: 10.1182/blood-2018-01-830901. Epub 2018, May 9. PMID:29743176 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1182/blood-2018-01-830901
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Chong YK, Mak TW. Superwarfarin (Long-Acting Anticoagulant Rodenticides) Poisoning: from Pathophysiology to Laboratory-Guided Clinical Management. Clin Biochem Rev. 2019 Nov;40(4):175-185. doi: 10.33176/AACB-19-00029. PMID:31857739 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.33176/AACB-19-00029
Student Contributors
Izabella Jordan, Emma Varness