We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1726
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | + | {{Template:CH462_Biochemistry_II_2022}}<!-- PLEASE ADD YOUR CONTENT BELOW HERE --> | |
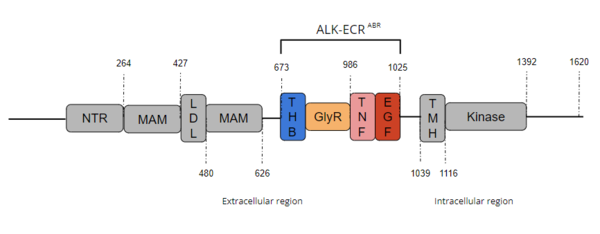
==Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase Extracellular Region== | ==Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase Extracellular Region== | ||
<StructureSection load='7N00' size='350' side='right' caption=' Structure of Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase [https://www.rcsb.org/structure/7N00 7N00]' scene='90/904331/Alk_full/1'> | <StructureSection load='7N00' size='350' side='right' caption=' Structure of Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase [https://www.rcsb.org/structure/7N00 7N00]' scene='90/904331/Alk_full/1'> | ||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
''To return to Structure of ALK with ALKAL2 bound scene click here: <scene name='90/904331/Alk_full/1'>ALK bound to ALKAL2</scene>'' | ''To return to Structure of ALK with ALKAL2 bound scene click here: <scene name='90/904331/Alk_full/1'>ALK bound to ALKAL2</scene>'' | ||
=== Dimerization of ALK === | === Dimerization of ALK === | ||
| - | After binding to one of its ligands, ALK undergoes <scene name='90/904331/Alk_full_dimerization/3'>ligand-induced dimerization</scene> <ref name="Huang">PMID:30400214</ref>. <scene name='90/904332/Thb-like_tnf-like_interface/1'>ALK receptor dimerization</scene> is mediated mostly by weak Van der Waals interactions and main chain hydrogen bonding between the TNF-like domain on one monomer and the THB-like domain on the other. <ref name ="Reshetnyak" /> The [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dimer_(chemistry) dimerization] causes trans-phosphorylation of specific [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tyrosine tyrosine] residues which in turn | + | After binding to one of its ligands, ALK undergoes <scene name='90/904331/Alk_full_dimerization/3'>ligand-induced dimerization</scene> <ref name="Huang">PMID:30400214</ref>. <scene name='90/904332/Thb-like_tnf-like_interface/1'>ALK receptor dimerization</scene> is mediated mostly by weak Van der Waals interactions and main chain hydrogen bonding between the TNF-like domain on one monomer and the THB-like domain on the other. <ref name ="Reshetnyak" /> The [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dimer_(chemistry) dimerization] causes trans-phosphorylation of specific [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tyrosine tyrosine] residues located in the extracellular region in the activation loop which in turn transmits a signal downstream<ref name="Huang" />. It has been presumed that the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phosphorylation_cascade phosphorylation cascade] activates ALK kinase activity <ref name="Huang" />. |
== Function == | == Function == | ||
ALK plays a role in [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cell_signaling cellular communication] and in the normal development and function of the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nervous_system nervous system]<ref name ="Huang" />. ALK is present in the developing nervous system of a fetus and newborn. ALK expression dwindles with age.<ref name ="Huang" /> In addition to being heavily expressed in the brain, ALK is present in the small intestine, testis, prostate, and colon <ref name="Della Corte">PMID:29455642</ref>. | ALK plays a role in [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cell_signaling cellular communication] and in the normal development and function of the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nervous_system nervous system]<ref name ="Huang" />. ALK is present in the developing nervous system of a fetus and newborn. ALK expression dwindles with age.<ref name ="Huang" /> In addition to being heavily expressed in the brain, ALK is present in the small intestine, testis, prostate, and colon <ref name="Della Corte">PMID:29455642</ref>. | ||
Revision as of 03:32, 21 April 2022
| This Sandbox is Reserved from February 28 through September 1, 2022 for use in the course CH462 Biochemistry II taught by R. Jeremy Johnson at the Butler University, Indianapolis, USA. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1700 through Sandbox Reserved 1729. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase Extracellular Region
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Iwahara T, Fujimoto J, Wen D, Cupples R, Bucay N, Arakawa T, Mori S, Ratzkin B, Yamamoto T. Molecular characterization of ALK, a receptor tyrosine kinase expressed specifically in the nervous system. Oncogene. 1997 Jan 30;14(4):439-49. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1200849. PMID:9053841 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1200849
- ↑ 2.00 2.01 2.02 2.03 2.04 2.05 2.06 2.07 2.08 2.09 2.10 2.11 Huang H. Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) Receptor Tyrosine Kinase: A Catalytic Receptor with Many Faces. Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Nov 2;19(11). pii: ijms19113448. doi: 10.3390/ijms19113448. PMID:30400214 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113448
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Della Corte CM, Viscardi G, Di Liello R, Fasano M, Martinelli E, Troiani T, Ciardiello F, Morgillo F. Role and targeting of anaplastic lymphoma kinase in cancer. Mol Cancer. 2018 Feb 19;17(1):30. doi: 10.1186/s12943-018-0776-2. PMID:29455642 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0776-2
- ↑ Palmer RH, Vernersson E, Grabbe C, Hallberg B. Anaplastic lymphoma kinase: signalling in development and disease. Biochem J. 2009 May 27;420(3):345-61. doi: 10.1042/BJ20090387. PMID:19459784 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1042/BJ20090387
- ↑ 5.00 5.01 5.02 5.03 5.04 5.05 5.06 5.07 5.08 5.09 5.10 5.11 5.12 5.13 5.14 5.15 5.16 5.17 5.18 5.19 5.20 5.21 5.22 Reshetnyak AV, Rossi P, Myasnikov AG, Sowaileh M, Mohanty J, Nourse A, Miller DJ, Lax I, Schlessinger J, Kalodimos CG. Mechanism for the activation of the anaplastic lymphoma kinase receptor. Nature. 2021 Dec;600(7887):153-157. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-04140-8. Epub 2021, Nov 24. PMID:34819673 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-04140-8
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 Borenas M, Umapathy G, Lai WY, Lind DE, Witek B, Guan J, Mendoza-Garcia P, Masudi T, Claeys A, Chuang TP, El Wakil A, Arefin B, Fransson S, Koster J, Johansson M, Gaarder J, Van den Eynden J, Hallberg B, Palmer RH. ALK ligand ALKAL2 potentiates MYCN-driven neuroblastoma in the absence of ALK mutation. EMBO J. 2021 Feb 1;40(3):e105784. doi: 10.15252/embj.2020105784. Epub 2021 Jan 7. PMID:33411331 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.15252/embj.2020105784
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 Chen S, Wang B, Fu X, Liang Y, Chai X, Ye Z, Li R, He Y, Kong G, Lian J, Li X, Chen T, Zhang X, Qiu X, Tang X, Zhou K, Lin B, Zeng J. ALKAL1 gene silencing prevents colorectal cancer progression via suppressing Sonic Hedgehog (SHH) signaling pathway. J Cancer. 2021 Jan 1;12(1):150-162. doi: 10.7150/jca.46447. eCollection 2021. PMID:33391411 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.7150/jca.46447
- ↑ Reshetnyak AV, Murray PB, Shi X, Mo ES, Mohanty J, Tome F, Bai H, Gunel M, Lax I, Schlessinger J. Augmentor alpha and beta (FAM150) are ligands of the receptor tyrosine kinases ALK and LTK: Hierarchy and specificity of ligand-receptor interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Dec 29;112(52):15862-7. doi:, 10.1073/pnas.1520099112. Epub 2015 Nov 16. PMID:26630010 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1520099112
- ↑ De Munck S, Provost M, Kurikawa M, Omori I, Mukohyama J, Felix J, Bloch Y, Abdel-Wahab O, Bazan JF, Yoshimi A, Savvides SN. Structural basis of cytokine-mediated activation of ALK family receptors. Nature. 2021 Oct 13. pii: 10.1038/s41586-021-03959-5. doi:, 10.1038/s41586-021-03959-5. PMID:34646012 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-03959-5
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 10.3 Li T, Stayrook SE, Tsutsui Y, Zhang J, Wang Y, Li H, Proffitt A, Krimmer SG, Ahmed M, Belliveau O, Walker IX, Mudumbi KC, Suzuki Y, Lax I, Alvarado D, Lemmon MA, Schlessinger J, Klein DE. Structural basis for ligand reception by anaplastic lymphoma kinase. Nature. 2021 Dec;600(7887):148-152. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-04141-7. Epub 2021, Nov 24. PMID:34819665 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-04141-7
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Carpenter EL, Haglund EA, Mace EM, Deng D, Martinez D, Wood AC, Chow AK, Weiser DA, Belcastro LT, Winter C, Bresler SC, Vigny M, Mazot P, Asgharzadeh S, Seeger RC, Zhao H, Guo R, Christensen JG, Orange JS, Pawel BR, Lemmon MA, Mosse YP. Antibody targeting of anaplastic lymphoma kinase induces cytotoxicity of human neuroblastoma. Oncogene. 2012 Nov 15;31(46):4859-67. doi: 10.1038/onc.2011.647. Epub 2012 Jan, 23. PMID:22266870 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.647