This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
User:David Gucklhorn/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
ErbB2(also known as HER2 in human or Neu as an oncogene) is a tyrosine kinase belonging to epidermal growth factor receptor family. It is an orphan receptor, its function in the cell lies in heterodimerization with other members of its family – EGFR, ErbB3 and ErbB4 as a coreceptor. There it acts in transduction of signal by participating in transphosphorylation of kinases intracellular domain. It was found to be preferred interaction partner to other kinases from epidermal growth factor receptor family <ref>DOI 10.1093/emboj/16.7.1647</ref>. It also amplifies the signal and increases affinity for the ligands of its interaction partners <ref>DOI 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90697-D</ref>. From all its family members, it has the strongest catalytic activity. Effects of this kinase are mostly associated with promotion of proliferation, survival, and cell motility <ref>DOI 10.1038/nrm1962</ref>. | ErbB2(also known as HER2 in human or Neu as an oncogene) is a tyrosine kinase belonging to epidermal growth factor receptor family. It is an orphan receptor, its function in the cell lies in heterodimerization with other members of its family – EGFR, ErbB3 and ErbB4 as a coreceptor. There it acts in transduction of signal by participating in transphosphorylation of kinases intracellular domain. It was found to be preferred interaction partner to other kinases from epidermal growth factor receptor family <ref>DOI 10.1093/emboj/16.7.1647</ref>. It also amplifies the signal and increases affinity for the ligands of its interaction partners <ref>DOI 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90697-D</ref>. From all its family members, it has the strongest catalytic activity. Effects of this kinase are mostly associated with promotion of proliferation, survival, and cell motility <ref>DOI 10.1038/nrm1962</ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Structure == | ||
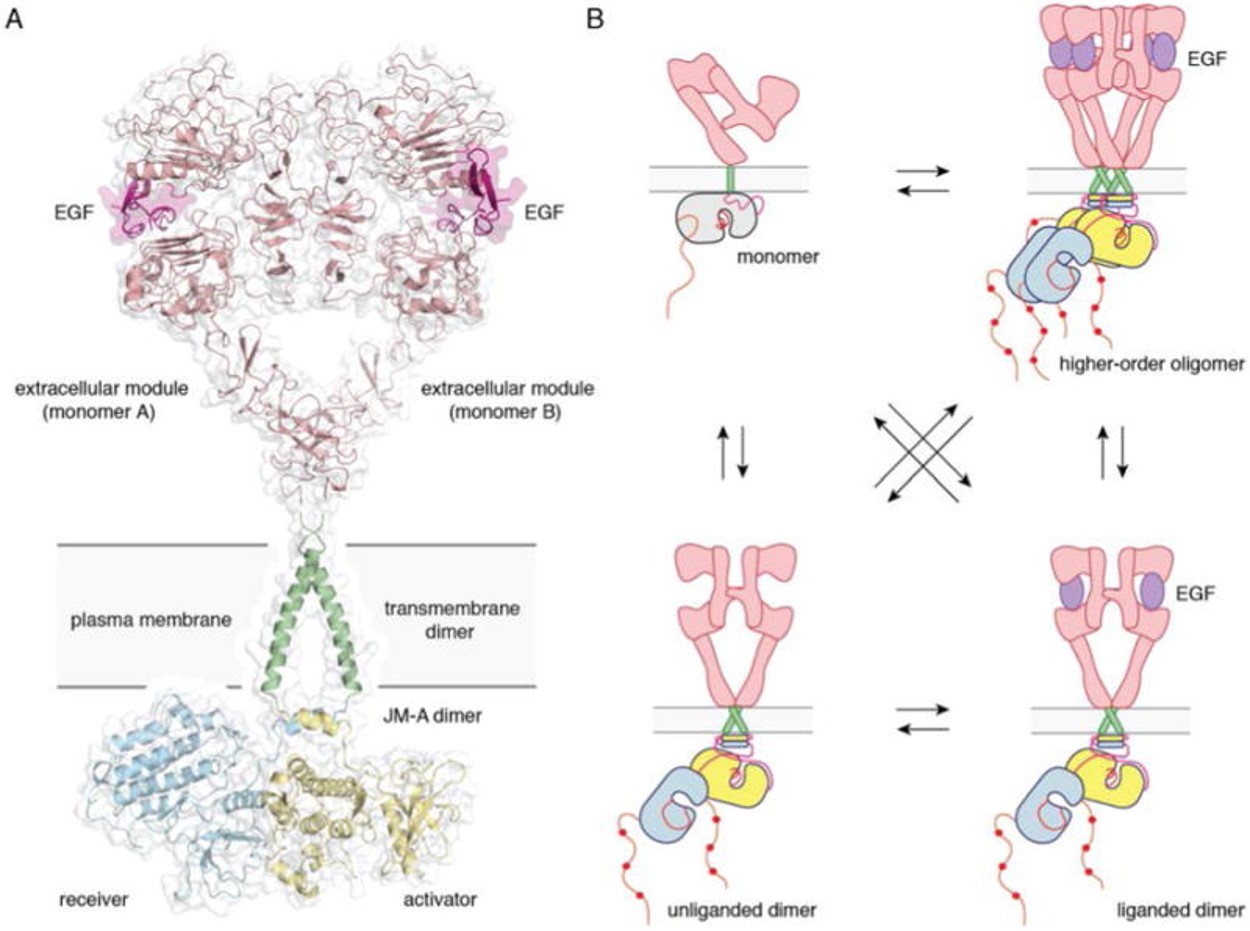
| + | ERBB receptors contain an extracellular domain (ECD), a transmembrane domain (TMD), an intracellular region that consists of a juxtamembrane domain (JMD), a kinase domain (KD) and a carboxy terminal tail domain (CTD) (Kovacs et al., 2015). The ECD is comprised of four subdomains (I-IV). In the absence of ligand, the ECD adopts an auto-inhibited tethered (closed) conformation that involves domain II and IV. Upon ligand binding between domains I and III, the dimerization arm in domain II is untethered, leading to receptor homo or heterodimerization, allosteric kinase activation, CTD phosphorylation and downstream signaling (Kovacs et al., 2015). | ||
| + | [[Image:Dg_sb_Figure1.jpg]] | ||
== Disease == | == Disease == | ||
Revision as of 19:06, 27 April 2022
ErbB2
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Graus-Porta D, Beerli RR, Daly JM, Hynes NE. ErbB-2, the preferred heterodimerization partner of all ErbB receptors, is a mediator of lateral signaling. EMBO J. 1997 Apr 1;16(7):1647-55. doi: 10.1093/emboj/16.7.1647. PMID:9130710 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/emboj/16.7.1647
- ↑ Wada T, Qian XL, Greene MI. Intermolecular association of the p185neu protein and EGF receptor modulates EGF receptor function. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1339-47. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90697-d. PMID:1973074 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(90)90697-d
- ↑ Citri A, Yarden Y. EGF-ERBB signalling: towards the systems level. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Jul;7(7):505-16. doi: 10.1038/nrm1962. PMID:16829981 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nrm1962
- ↑ Slamon DJ, Clark GM. Amplification of c-erbB-2 and aggressive human breast tumors? Science. 1988 Jun 24;240(4860):1795-8. doi: 10.1126/science.3289120. PMID:3289120 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.3289120
- ↑ Venter DJ, Tuzi NL, Kumar S, Gullick WJ. Overexpression of the c-erbB-2 oncoprotein in human breast carcinomas: immunohistological assessment correlates with gene amplification. Lancet. 1987 Jul 11;2(8550):69-72. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)92736-x. PMID:2885574 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(87)92736-x
- ↑ Fleishman SJ, Schlessinger J, Ben-Tal N. A putative molecular-activation switch in the transmembrane domain of erbB2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Dec 10;99(25):15937-40. doi:, 10.1073/pnas.252640799. Epub 2002 Dec 2. PMID:12461170 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.252640799
- ↑ Greulich H, Kaplan B, Mertins P, Chen TH, Tanaka KE, Yun CH, Zhang X, Lee SH, Cho J, Ambrogio L, Liao R, Imielinski M, Banerji S, Berger AH, Lawrence MS, Zhang J, Pho NH, Walker SR, Winckler W, Getz G, Frank D, Hahn WC, Eck MJ, Mani DR, Jaffe JD, Carr SA, Wong KK, Meyerson M. Functional analysis of receptor tyrosine kinase mutations in lung cancer identifies oncogenic extracellular domain mutations of ERBB2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Sep 4;109(36):14476-81. doi:, 10.1073/pnas.1203201109. Epub 2012 Aug 20. PMID:22908275 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1203201109
- ↑ Zabransky DJ, Yankaskas CL, Cochran RL, Wong HY, Croessmann S, Chu D, Kavuri SM, Red Brewer M, Rosen DM, Dalton WB, Cimino-Mathews A, Cravero K, Button B, Kyker-Snowman K, Cidado J, Erlanger B, Parsons HA, Manto KM, Bose R, Lauring J, Arteaga CL, Konstantopoulos K, Park BH. HER2 missense mutations have distinct effects on oncogenic signaling and migration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Nov 10;112(45):E6205-14. doi:, 10.1073/pnas.1516853112. Epub 2015 Oct 27. PMID:26508629 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1516853112
- ↑ Ross JS, Gay LM, Wang K, Ali SM, Chumsri S, Elvin JA, Bose R, Vergilio JA, Suh J, Yelensky R, Lipson D, Chmielecki J, Waintraub S, Leyland-Jones B, Miller VA, Stephens PJ. Nonamplification ERBB2 genomic alterations in 5605 cases of recurrent and metastatic breast cancer: An emerging opportunity for anti-HER2 targeted therapies. Cancer. 2016 Sep 1;122(17):2654-62. doi: 10.1002/cncr.30102. Epub 2016 Jun 10. PMID:27284958 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/cncr.30102
- ↑ Bose R, Kavuri SM, Searleman AC, Shen W, Shen D, Koboldt DC, Monsey J, Goel N, Aronson AB, Li S, Ma CX, Ding L, Mardis ER, Ellis MJ. Activating HER2 mutations in HER2 gene amplification negative breast cancer. Cancer Discov. 2013 Feb;3(2):224-37. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-12-0349. Epub 2012, Dec 7. PMID:23220880 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.CD-12-0349
- ↑ Yamamoto H, Higasa K, Sakaguchi M, Shien K, Soh J, Ichimura K, Furukawa M, Hashida S, Tsukuda K, Takigawa N, Matsuo K, Kiura K, Miyoshi S, Matsuda F, Toyooka S. Novel germline mutation in the transmembrane domain of HER2 in familial lung adenocarcinomas. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2014 Jan;106(1):djt338. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djt338. Epub 2013, Dec 7. PMID:24317180 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/jnci/djt338
- ↑ Kavuri SM, Jain N, Galimi F, Cottino F, Leto SM, Migliardi G, Searleman AC, Shen W, Monsey J, Trusolino L, Jacobs SA, Bertotti A, Bose R. HER2 activating mutations are targets for colorectal cancer treatment. Cancer Discov. 2015 Aug;5(8):832-41. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-14-1211. PMID:26243863 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.CD-14-1211
- ↑ Ou SI, Schrock AB, Bocharov EV, Klempner SJ, Haddad CK, Steinecker G, Johnson M, Gitlitz BJ, Chung J, Campregher PV, Ross JS, Stephens PJ, Miller VA, Suh JH, Ali SM, Velcheti V. HER2 Transmembrane Domain (TMD) Mutations (V659/G660) That Stabilize Homo- and Heterodimerization Are Rare Oncogenic Drivers in Lung Adenocarcinoma That Respond to Afatinib. J Thorac Oncol. 2017 Mar;12(3):446-457. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2016.11.2224. Epub, 2016 Nov 27. PMID:27903463 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jtho.2016.11.2224
- ↑ Chang MT, Bhattarai TS, Schram AM, Bielski CM, Donoghue MTA, Jonsson P, Chakravarty D, Phillips S, Kandoth C, Penson A, Gorelick A, Shamu T, Patel S, Harris C, Gao J, Sumer SO, Kundra R, Razavi P, Li BT, Reales DN, Socci ND, Jayakumaran G, Zehir A, Benayed R, Arcila ME, Chandarlapaty S, Ladanyi M, Schultz N, Baselga J, Berger MF, Rosen N, Solit DB, Hyman DM, Taylor BS. Accelerating Discovery of Functional Mutant Alleles in Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2018 Feb;8(2):174-183. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-17-0321. Epub, 2017 Dec 15. PMID:29247016 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.CD-17-0321
- ↑ Petrelli F, Tomasello G, Barni S, Lonati V, Passalacqua R, Ghidini M. Clinical and pathological characterization of HER2 mutations in human breast cancer: a systematic review of the literature. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2017 Nov;166(2):339-349. doi: 10.1007/s10549-017-4419-x., Epub 2017 Jul 31. PMID:28762010 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10549-017-4419-x
- ↑ Cousin S, Khalifa E, Crombe A, Laizet Y, Lucchesi C, Toulmonde M, Le Moulec S, Auzanneau C, Soubeyran I, Italiano A. Targeting ERBB2 mutations in solid tumors: biological and clinical implications. J Hematol Oncol. 2018 Jun 25;11(1):86. doi: 10.1186/s13045-018-0630-4. PMID:29941010 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s13045-018-0630-4