Journal:Acta Cryst F:S2053230X22007555
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)

| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
<hr/> | <hr/> | ||
<b>Molecular Tour</b><br> | <b>Molecular Tour</b><br> | ||
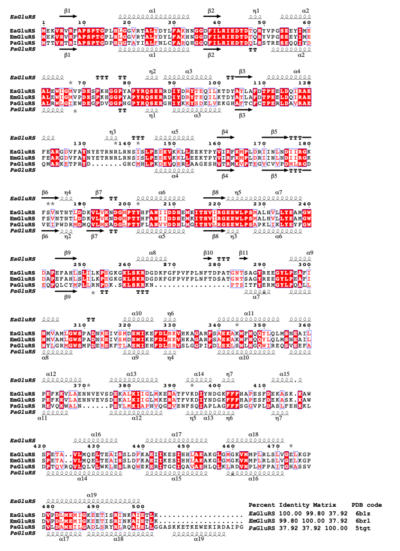
| - | ''Elizabethkingia'' bacteria are emerging pathogens globally that cause opportunistic and nosocomial infections with up to 40% mortality among the immune-compromised. ''Elizabethkingia'' species are in the pipeline of organisms for high throughput structural analysis at the Seattle Structural Genomics Center for Infectious Disease (SSGCID). These efforts include the structure-function analysis of potential therapeutic targets. Glutamyl-tRNA synthetase (GluRS) is essential to the tRNA aminoacylation and is investigated as a bacterial drug target. The SSGCID produced crystallized and determined high-resolution structures of GluRS from ''Elizabethkingia meningosepticum'' (EmGluRS) and ''Elizabethkingia anopheles'' (EaGluRS). EmGluRS was co-crystallized with glutamate, while EaGluRS is an apo-structure. | + | ''Elizabethkingia'' bacteria are emerging pathogens globally that cause opportunistic and nosocomial infections with up to 40% mortality among the immune-compromised. ''Elizabethkingia'' species are in the pipeline of organisms for high throughput structural analysis at the Seattle Structural Genomics Center for Infectious Disease (SSGCID). These efforts include the structure-function analysis of potential therapeutic targets. Glutamyl-tRNA synthetase (GluRS) is essential to the tRNA aminoacylation and is investigated as a bacterial drug target. The SSGCID produced crystallized and determined high-resolution structures of GluRS from ''Elizabethkingia meningosepticum'' (EmGluRS; [[6brl]]) and ''Elizabethkingia anopheles'' (EaGluRS; [[6b1z]]). EmGluRS was co-crystallized with glutamate, while EaGluRS is an apo-structure. |
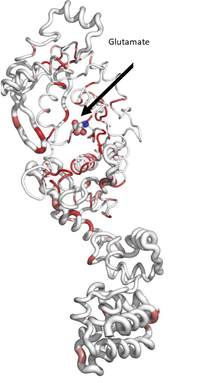
<scene name='91/917942/Cv/3'>EmGluRS monomer</scene> has a HUP-domain (orange), a Zn-binding-domain (green), and an anticodon binding domain (blue). The HUP domain and Zn-binding domain make up the N-terminal tRNA synthetases binding domain that binds the glutamate (spheres). | <scene name='91/917942/Cv/3'>EmGluRS monomer</scene> has a HUP-domain (orange), a Zn-binding-domain (green), and an anticodon binding domain (blue). The HUP domain and Zn-binding domain make up the N-terminal tRNA synthetases binding domain that binds the glutamate (spheres). | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
This page complements a publication in scientific journals and is one of the Proteopedia's Interactive 3D Complement pages. For aditional details please see I3DC.