Sandbox Reserved 1767
From Proteopedia
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
== Signaling Cascade and Conformational Changes== | == Signaling Cascade and Conformational Changes== | ||
=== Switch I and Switch II === | === Switch I and Switch II === | ||
| - | SHOC2-PP1C-MRAS is a regulator of a cell proliferation pathway. Mutations in cell proliferation pathways are responsible for 25% of all cancers 1. If this cell proliferation pathway goes unmediated, rapid cell growth and division will occur; the leading cause of cancers is mutations in this pathway. <ref name="Lavoie">PMID: 35970881</ref> [https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-022-02189-7 Mechanistic Overview and Signaling Cascade ] shows the pathway SHOC2-PP1C-MRAS is part of. It is a receptor tyrosine kinase pathway.<ref name="Kwon">PMID: 35831509</ref> When MRAS is bound to GDP, the complex is not assembled. SHOC2, PP1C, and MRAS all exist as separate monomers. The Raf domain contains a kinase domain (KD), Ras binding domain (RBD), a C-terminal phosphoserine (CTpS), a N-terminal phosphorylated serine (NTpS), and a 14-3-3 protein dimer, restricting RAF to the cytoplasm. In the activated pathway, MRAS is bound to GTP, and the SMP complex is assembled. PP1C is now in contact with the NTpS, allowing it to become dephosphorylated. <ref name="Lavoie">PMID: 35970881</ref> This dephosphorylation causes the dimerization of two Raf proteins via their kinase domains as well as a conformational change. This conformation change causes the phosphorylation of other residues. Eventually, this leads to the unbinding of GDP from MRAS and the binding of GTP to MRAS, causing a shift from the <scene name='95/952693/Swi_open_conformation/6'>open conformation</scene> to <scene name='95/952693/Switch_i_gtp_bound/11'>closed conformation of SWI.</scene> | + | SHOC2-PP1C-MRAS is a regulator of a cell proliferation pathway. Mutations in cell proliferation pathways are responsible for 25% of all cancers 1. If this cell proliferation pathway goes unmediated, rapid cell growth and division will occur; the leading cause of cancers is mutations in this pathway. <ref name="Lavoie">PMID: 35970881</ref> [https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-022-02189-7 Mechanistic Overview and Signaling Cascade ] shows the pathway SHOC2-PP1C-MRAS is part of. It is a receptor tyrosine kinase pathway.<ref name="Kwon">PMID: 35831509</ref> When MRAS is bound to GDP, the complex is not assembled. SHOC2, PP1C, and MRAS all exist as separate monomers. The Raf domain contains a kinase domain (KD), Ras binding domain (RBD), a C-terminal phosphoserine (CTpS), a N-terminal phosphorylated serine (NTpS), and a 14-3-3 protein dimer, restricting RAF to the cytoplasm. In the activated pathway, MRAS is bound to GTP, and the SMP complex is assembled. PP1C is now in contact with the NTpS, allowing it to become dephosphorylated. <ref name="Lavoie">PMID: 35970881</ref> This dephosphorylation causes the dimerization of two Raf proteins via their kinase domains as well as a conformational change. This conformation change causes the phosphorylation of other residues. Eventually, this leads to the unbinding of GDP from MRAS and the binding of GTP to MRAS, causing a shift from the <scene name='95/952693/Swi_open_conformation/6'>open conformation</scene> to <scene name='95/952693/Switch_i_gtp_bound/11'>closed conformation of SWI.</scene> The Switch I region is made up of residues 42-48 of the MRAS domain.<ref name="Kwon">PMID: 35831509</ref> These residues are crucial for the binding of MRAS, SHOC2, and PP1C. When GDP is bound to the MRAS domain, it is in the <scene name='95/952693/Swi_open_conformation/6'>open conformation.</scene>. Since the gamma P is not bound to GDP, there are no hydrogen bond interactions with the oxygens of the phosphate group- hence the open conformation. When GTP is bound to MRAS, it is in the <scene name='95/952693/Switch_i_gtp_bound/11'>closed conformation </scene>. The closed conformation allows for the binding of SHOC2 and PP1C. The open conformation of MRAS sterically clashes with the binding site of SHOC2, which is why the complex is not assembled when GDP is bound. <ref name="Kwon">PMID: 35831509</ref>. |
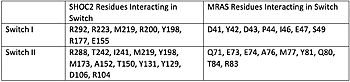
[[Image:Table.jpeg|350 px|left|thumb|Figure 1. Residues Interacting at SWI and SWII at subunits SHOC2 and PP1C.<ref name="Liau">PMID: 35768504</ref>.]] | [[Image:Table.jpeg|350 px|left|thumb|Figure 1. Residues Interacting at SWI and SWII at subunits SHOC2 and PP1C.<ref name="Liau">PMID: 35768504</ref>.]] | ||
Revision as of 18:42, 3 April 2023
| This Sandbox is Reserved from February 27 through August 31, 2023 for use in the course CH462 Biochemistry II taught by R. Jeremy Johnson at the Butler University, Indianapolis, USA. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1765 through Sandbox Reserved 1795. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Contents |
SHOC2-PP1C-MRAS
| |||||||||||
Protopedia Resources
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Hauseman ZJ, Fodor M, Dhembi A, Viscomi J, Egli D, Bleu M, Katz S, Park E, Jang DM, Porter KA, Meili F, Guo H, Kerr G, Molle S, Velez-Vega C, Beyer KS, Galli GG, Maira SM, Stams T, Clark K, Eck MJ, Tordella L, Thoma CR, King DA. Structure of the MRAS-SHOC2-PP1C phosphatase complex. Nature. 2022 Jul 13. pii: 10.1038/s41586-022-05086-1. doi:, 10.1038/s41586-022-05086-1. PMID:35830882 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-05086-1
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 Kwon JJ, Hajian B, Bian Y, Young LC, Amor AJ, Fuller JR, Fraley CV, Sykes AM, So J, Pan J, Baker L, Lee SJ, Wheeler DB, Mayhew DL, Persky NS, Yang X, Root DE, Barsotti AM, Stamford AW, Perry CK, Burgin A, McCormick F, Lemke CT, Hahn WC, Aguirre AJ. Structure-function analysis of the SHOC2-MRAS-PP1C holophosphatase complex. Nature. 2022 Jul 13. pii: 10.1038/s41586-022-04928-2. doi:, 10.1038/s41586-022-04928-2. PMID:35831509 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-04928-2
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Lavoie H, Therrien M. Structural keys unlock RAS-MAPK cellular signalling pathway. Nature. 2022 Sep;609(7926):248-249. PMID:35970881 doi:10.1038/d41586-022-02189-7
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 Liau NPD, Johnson MC, Izadi S, Gerosa L, Hammel M, Bruning JM, Wendorff TJ, Phung W, Hymowitz SG, Sudhamsu J. Structural basis for SHOC2 modulation of RAS signalling. Nature. 2022 Jun 29. pii: 10.1038/s41586-022-04838-3. doi:, 10.1038/s41586-022-04838-3. PMID:35768504 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-04838-3
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Young LC, Hartig N, Boned Del Río I, Sari S, Ringham-Terry B, Wainwright JR, Jones GG, McCormick F, Rodriguez-Viciana P. SHOC2-MRAS-PP1 complex positively regulates RAF activity and contributes to Noonan syndrome pathogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Nov 6;115(45):E10576-E10585. PMID:30348783 doi:10.1073/pnas.1720352115
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 Hurley TD, Yang J, Zhang L, Goodwin KD, Zou Q, Cortese M, Dunker AK, DePaoli-Roach AA. Structural basis for regulation of protein phosphatase 1 by inhibitor-2. J Biol Chem. 2007 Sep 28;282(39):28874-83. Epub 2007 Jul 18. PMID:17636256 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M703472200
1. Hauseman ZJ, Fodor M, Dhembi A, Viscomi J, Egli D, Bleu M, Katz S, Park E, Jang DM, Porter KA, Meili F, Guo H, Kerr G, Mollé S, Velez-Vega C, Beyer KS, Galli GG, Maira SM, Stams T, Clark K, Eck MJ, Tordella L, Thoma CR, King DA. Structure of the MRAS-SHOC2-PP1C phosphatase complex. Nature. 2022 Sep;609(7926):416-423. doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-05086-1. Epub 2022 Jul 13. PMID: 35830882; PMCID: PMC9452295.[1].
2. Hurley TD, Yang J, Zhang L, Goodwin KD, Zou Q, Cortese M, Dunker AK, DePaoli-Roach AA. Structural basis for regulation of protein phosphatase 1 by inhibitor-2. J Biol Chem. 2007 Sep 28;282(39):28874-28883. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M703472200. Epub 2007 Jul 18. PMID: 17636256.[2].
3. Kwon JJ, Hajian B, Bian Y, Young LC, Amor AJ, Fuller JR, Fraley CV, Sykes AM, So J, Pan J, Baker L, Lee SJ, Wheeler DB, Mayhew DL, Persky NS, Yang X, Root DE, Barsotti AM, Stamford AW, Perry CK, Burgin A, McCormick F, Lemke CT, Hahn WC, Aguirre AJ. Structure-function analysis of the SHOC2-MRAS-PP1C holophosphatase complex. Nature. 2022 Sep;609(7926):408-415. doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-04928-2. Epub 2022 Jul 13. PMID: 35831509; PMCID: PMC9694338.[3].
4. Liau NPD, Johnson MC, Izadi S, Gerosa L, Hammel M, Bruning JM, Wendorff TJ, Phung W, Hymowitz SG, Sudhamsu J. Structural basis for SHOC2 modulation of RAS signalling. Nature. 2022 Sep;609(7926):400-407. doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-04838-3. Epub 2022 Jun 29. PMID: 35768504; PMCID: PMC9452301.[4].
5. Lavoie H, Therrien M. Structural keys unlock RAS-MAPK cellular signalling pathway. Nature. 2022 Sep;609(7926):248-249. doi: 10.1038/d41586-022-02189-7. PMID: 35970881.[5].
6. Young LC, Hartig N, Boned Del Río I, Sari S, Ringham-Terry B, Wainwright JR, Jones GG, McCormick F, Rodriguez-Viciana P. SHOC2-MRAS-PP1 complex positively regulates RAF activity and contributes to Noonan syndrome pathogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Nov 6;115(45):E10576-E10585. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1720352115. Epub 2018 Oct 22. PMID: 30348783; PMCID: PMC6233131.[6].
Student Contributors
- Sloan August
- Rosa Trippel
- Kayla Wilhoite