Sandbox Reserved 1791
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
== Specific Residues and Interactions== | == Specific Residues and Interactions== | ||
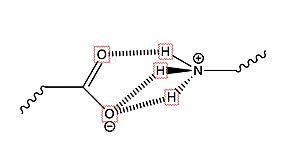
[[Image:Salt bridge LYS.jpg|300 px|right|thumb|(Fig.2) Salt bridge interaction between LYS and Glu or Asp]] | [[Image:Salt bridge LYS.jpg|300 px|right|thumb|(Fig.2) Salt bridge interaction between LYS and Glu or Asp]] | ||
| - | There are two <scene name='95/952719/Specific_residues/3'>lysine residues</scene> in the binding pocket of TSHR that are the main contributors to the binding of the antibodies. The concave structure of the binding pocket allows a <scene name='95/952719/Lock_and_key/ | + | There are two <scene name='95/952719/Specific_residues/3'>lysine residues</scene> in the binding pocket of TSHR that are the main contributors to the binding of the antibodies. The concave structure of the binding pocket allows a <scene name='95/952719/Lock_and_key/5'>tight interaction</scene>with the antibodies. These antibodies make tight interactions with a lot of intermolecular forces at play. <scene name='95/952719/K---e_interaction/1'>LYS 58</scene> interacts with Glu 118 on the antibodies to make a [https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-018-31935-z salt bridge interaction]. <scene name='95/952719/K---d_interaction/1'>LYS 209</scene> interacts with Asp 11 on the antibodies to make a salt bridge interaction. Specifically, the two residues make an ionic interaction. The interaction is not close enough to make a hydrogen bond. Instead, the interaction between the Lys residues with the Asp or Glu residues is a salt bridge interaction. This is the main bond that holds these two molecules together. When in the inactive form, LYS 209 does not interact with any residue but LYS 58 has interaction with Glu 118 and this interaction pulls the molecule into the bent position. |
Revision as of 21:06, 6 April 2023
| This Sandbox is Reserved from February 27 through August 31, 2023 for use in the course CH462 Biochemistry II taught by R. Jeremy Johnson at the Butler University, Indianapolis, USA. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1765 through Sandbox Reserved 1795. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Thyroid Stimulating Hormone Receptor (TSHR)
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Faust B, Billesbolle CB, Suomivuori CM, Singh I, Zhang K, Hoppe N, Pinto AFM, Diedrich JK, Muftuoglu Y, Szkudlinski MW, Saghatelian A, Dror RO, Cheng Y, Manglik A. Autoantibody mimicry of hormone action at the thyrotropin receptor. Nature. 2022 Aug 8. pii: 10.1038/s41586-022-05159-1. doi:, 10.1038/s41586-022-05159-1. PMID:35940205 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-05159-1
- ↑ Duan J, Xu P, Luan X, Ji Y, He X, Song N, Yuan Q, Jin Y, Cheng X, Jiang H, Zheng J, Zhang S, Jiang Y, Xu HE. Hormone- and antibody-mediated activation of the thyrotropin receptor. Nature. 2022 Aug 8. pii: 10.1038/s41586-022-05173-3. doi:, 10.1038/s41586-022-05173-3. PMID:35940204 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-05173-3
Student Contributions
- Alex Kem
- Grace Lane
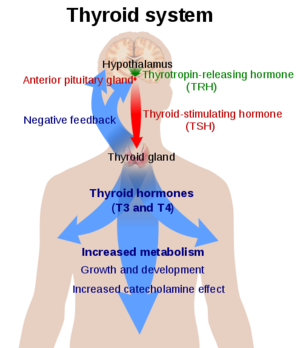
![(Fig. 3) TSH’s role in the diagnosis of Hyperthyroidism and Hypothyroidism: [1]](/wiki/images/thumb/9/95/TSH_role.jpeg/400px-TSH_role.jpeg)
